
Treatment of ammonia with excess ethyl chloride will yield?
A.Triethylamine
B.Diethylamine
C.Ethylamine
D.Tetraethyl ammonium chlorides
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: Ammonia is an inorganic compound. When ammonia reacts with ethyl chloride nucleophilic substitution reaction happens. In this reaction, ammonia acts as a nucleophile and ethyl chloride as an electrophile. Ammonia shows nucleophilicity by its lone pair of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
Treatment of ammonia with excess ethyl chloride will yield aliphatic amines. The nucleophilicity of ammonia depends upon the lone pair donating ability. With increasing the electron-donating group, the electron density on nitrogen increases as well as the nucleophilicity.
Now in presence of excess ethyl chloride, the following reaction will happen.
\[
N{H_3} + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {C_2}{H_5}N{H_2} + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {({C_2}H_5^{})_2}NH + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {({C_2}H_5^{})_3}N \\
{({C_2}{H_5})_3}N + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {({C_2}H_5^{})_4}{N^ + }{C^ - } \\
\]
In this reaction due to the addition of ethyl groups, the nucleophilicity of nitrogen increases with increases in the rate of the next step. Due to this, we get Tetraethyl ammonium chlorides at the end.
So, the correct option is D.
Additional information:
The parent compound in this given compound can be understood by the suffix added at the end of the name of the compound. As we can see, the name of the given compound ends with the suffix -amine.
Hence, the parent compound is A mine in this question. The structure of amine can be given as:
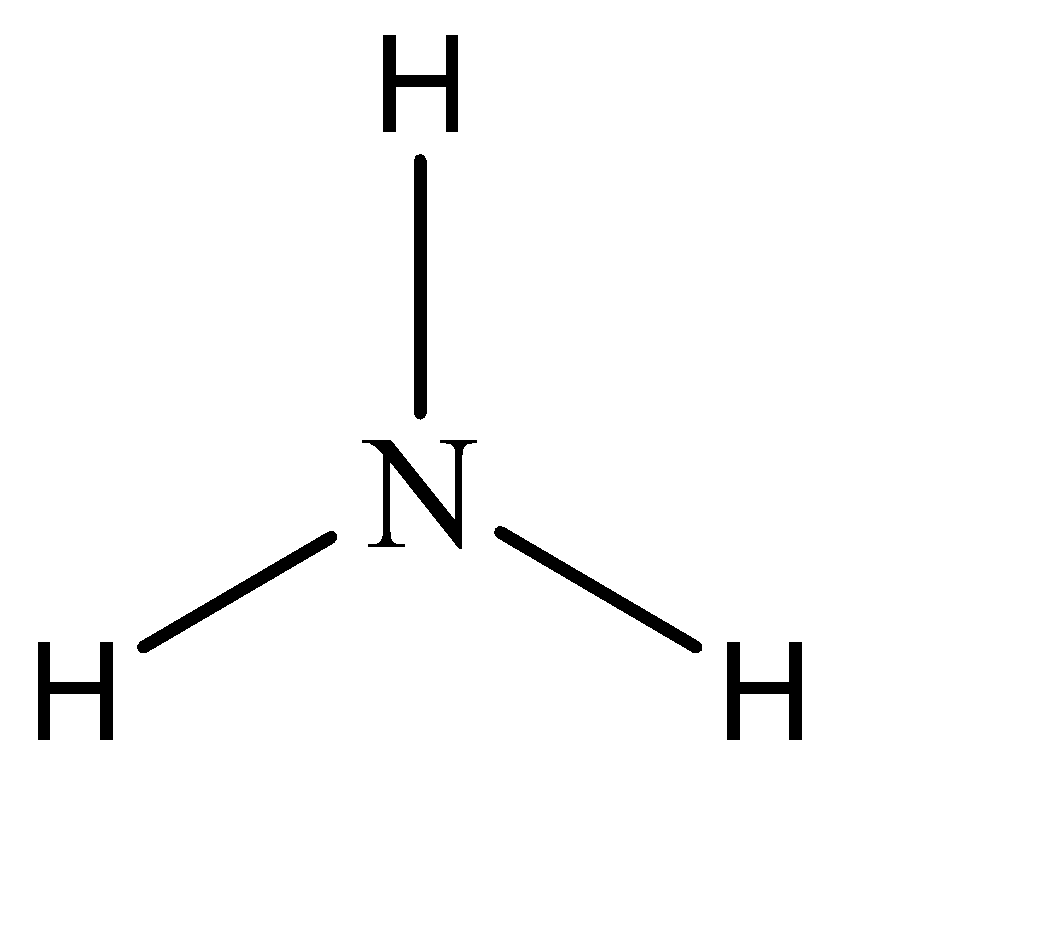
Now, while naming derivative compounds of amine, the rules that are followed include placing the corresponding replacing functional groups in alphabetical order followed by the suffix ‘amine’.
The name of the given compound is n – methylethanamine. This means that two of the hydrogen atoms are substituted from amine. The functional groups that have substituted these hydrogen atoms are ethyl and methyl. Hence the structure of n – methylethanamine can be given as:
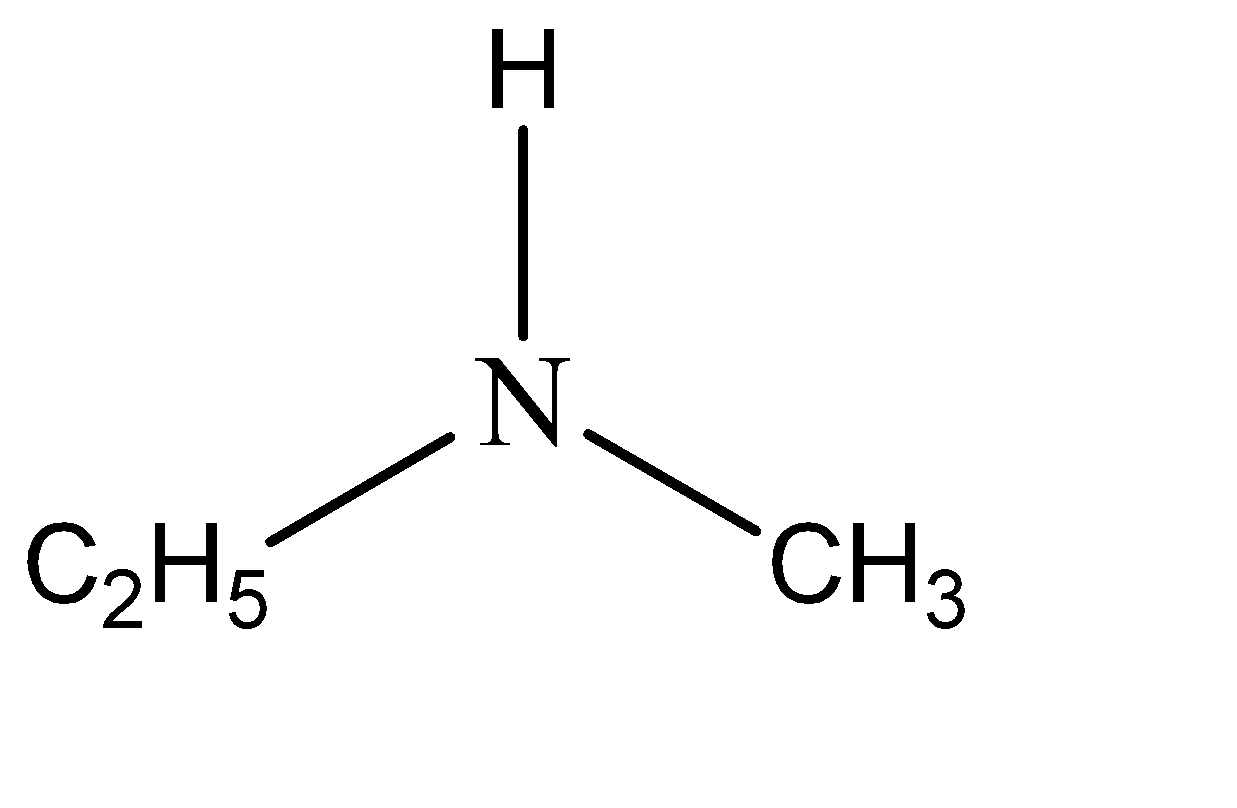
Note: In the aqueous phase, if R is a methyl group then the order of basicity is secondary amine> primary amine > tertiary amine but if R is any group other than methyl group, then the order is secondary > tertiary > primary. The derivatives of amine are formed by substituting the hydrogen atoms that are attached to the nitrogen. This makes the nitrogen either 1 – degree, 2 – degree, or 3 – degree depending on the number of hydrogens that have been substituted.
Complete step by step answer:
Treatment of ammonia with excess ethyl chloride will yield aliphatic amines. The nucleophilicity of ammonia depends upon the lone pair donating ability. With increasing the electron-donating group, the electron density on nitrogen increases as well as the nucleophilicity.
Now in presence of excess ethyl chloride, the following reaction will happen.
\[
N{H_3} + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {C_2}{H_5}N{H_2} + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {({C_2}H_5^{})_2}NH + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {({C_2}H_5^{})_3}N \\
{({C_2}{H_5})_3}N + {C_2}{H_5}Cl \to {({C_2}H_5^{})_4}{N^ + }{C^ - } \\
\]
In this reaction due to the addition of ethyl groups, the nucleophilicity of nitrogen increases with increases in the rate of the next step. Due to this, we get Tetraethyl ammonium chlorides at the end.
So, the correct option is D.
Additional information:
The parent compound in this given compound can be understood by the suffix added at the end of the name of the compound. As we can see, the name of the given compound ends with the suffix -amine.
Hence, the parent compound is A mine in this question. The structure of amine can be given as:

Now, while naming derivative compounds of amine, the rules that are followed include placing the corresponding replacing functional groups in alphabetical order followed by the suffix ‘amine’.
The name of the given compound is n – methylethanamine. This means that two of the hydrogen atoms are substituted from amine. The functional groups that have substituted these hydrogen atoms are ethyl and methyl. Hence the structure of n – methylethanamine can be given as:

Note: In the aqueous phase, if R is a methyl group then the order of basicity is secondary amine> primary amine > tertiary amine but if R is any group other than methyl group, then the order is secondary > tertiary > primary. The derivatives of amine are formed by substituting the hydrogen atoms that are attached to the nitrogen. This makes the nitrogen either 1 – degree, 2 – degree, or 3 – degree depending on the number of hydrogens that have been substituted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




