
What is tubular secretion? Name the substances secreted through the renal tubules.
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: This process is usually used to eliminate drugs, toxins, and poisons, or other natural compounds in excessive amounts. Materials that are secreted into the tubular fluid are for exclusion from the body.
Complete answer:
Tubular secretion is one of the numerous steps involved in the process of filtering blood to generate liquid waste in the form of urine. Inside the excretory system of many organisms, this is essential for both waste removal and acid-base balance.
The materials that are exuded into the tubular fluid for exclusion from the body include Potassium ions (${K^ + }$), Hydrogen ions (${H^ + }$), Ammonium ions ($N{H^ + }$), Creatinine, and Urea.
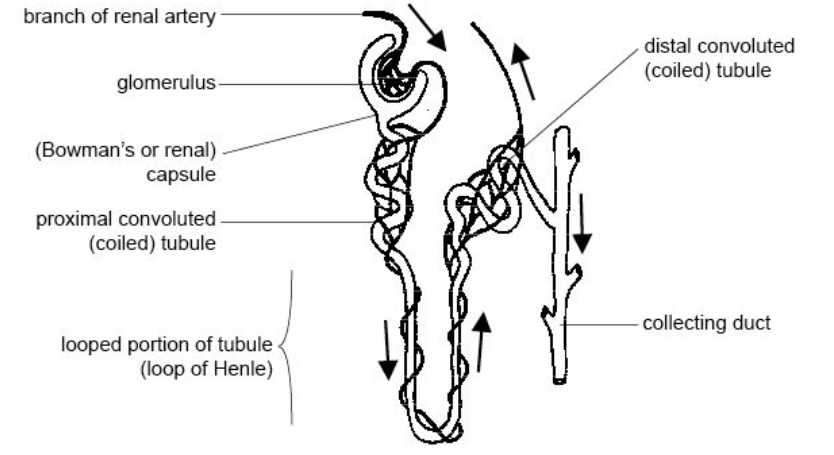
In humans and many vertebrates, tubular secretion takes place in the kidneys, where the blood is filtered in specific structures known as nephrons. These structures consist of an elongated tubule surrounded by extensive capillaries.
Additional information:
There can be two ways through which transport of nutrients can be made -
Diffusion—The movement of molecules from the peritubular capillaries to the interstitial fluid within the nephrons.
Active transport—The movement of molecules using ATPase pumps that carry the substance through the renal epithelial cell into the lumen of the nephron.
Note: Basically, the exuded substances come from the blood in peritubular capillaries and pass through the interstitial fluid before going through the wall of the tubule into the inside of the tubule (known as the lumen). There are many phases of secretion that occur in the proximal or distal parts of each tubule, but not in the region between them called the loop of Henle.
Complete answer:
Tubular secretion is one of the numerous steps involved in the process of filtering blood to generate liquid waste in the form of urine. Inside the excretory system of many organisms, this is essential for both waste removal and acid-base balance.
The materials that are exuded into the tubular fluid for exclusion from the body include Potassium ions (${K^ + }$), Hydrogen ions (${H^ + }$), Ammonium ions ($N{H^ + }$), Creatinine, and Urea.

In humans and many vertebrates, tubular secretion takes place in the kidneys, where the blood is filtered in specific structures known as nephrons. These structures consist of an elongated tubule surrounded by extensive capillaries.
Additional information:
There can be two ways through which transport of nutrients can be made -
Diffusion—The movement of molecules from the peritubular capillaries to the interstitial fluid within the nephrons.
Active transport—The movement of molecules using ATPase pumps that carry the substance through the renal epithelial cell into the lumen of the nephron.
Note: Basically, the exuded substances come from the blood in peritubular capillaries and pass through the interstitial fluid before going through the wall of the tubule into the inside of the tubule (known as the lumen). There are many phases of secretion that occur in the proximal or distal parts of each tubule, but not in the region between them called the loop of Henle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




