
Two balls $A$ and $B$ are simultaneously thrown. $A$ is thrown from the ground level with a velocity of $20m{s^{ - 1}}$ in the upward direction $B$ is thrown from a height of $40m$ in the downward direction with the same velocity. Where will the two balls meet?
A. $15m$
B. $25m$
C. $35m$
D. $45m$
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: you can start by writing the second equation of motion, i.e. $S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$. Then use this equation for both balls $A$ and $B$, and add the equations you get to obtain the value of $t$. Then use the value of $t$ to find the height where the balls meet.
Complete answer:
Let’s assume that the balls meet at a Point R and are at a height $h$ from the ground and will meet in time $t$ .
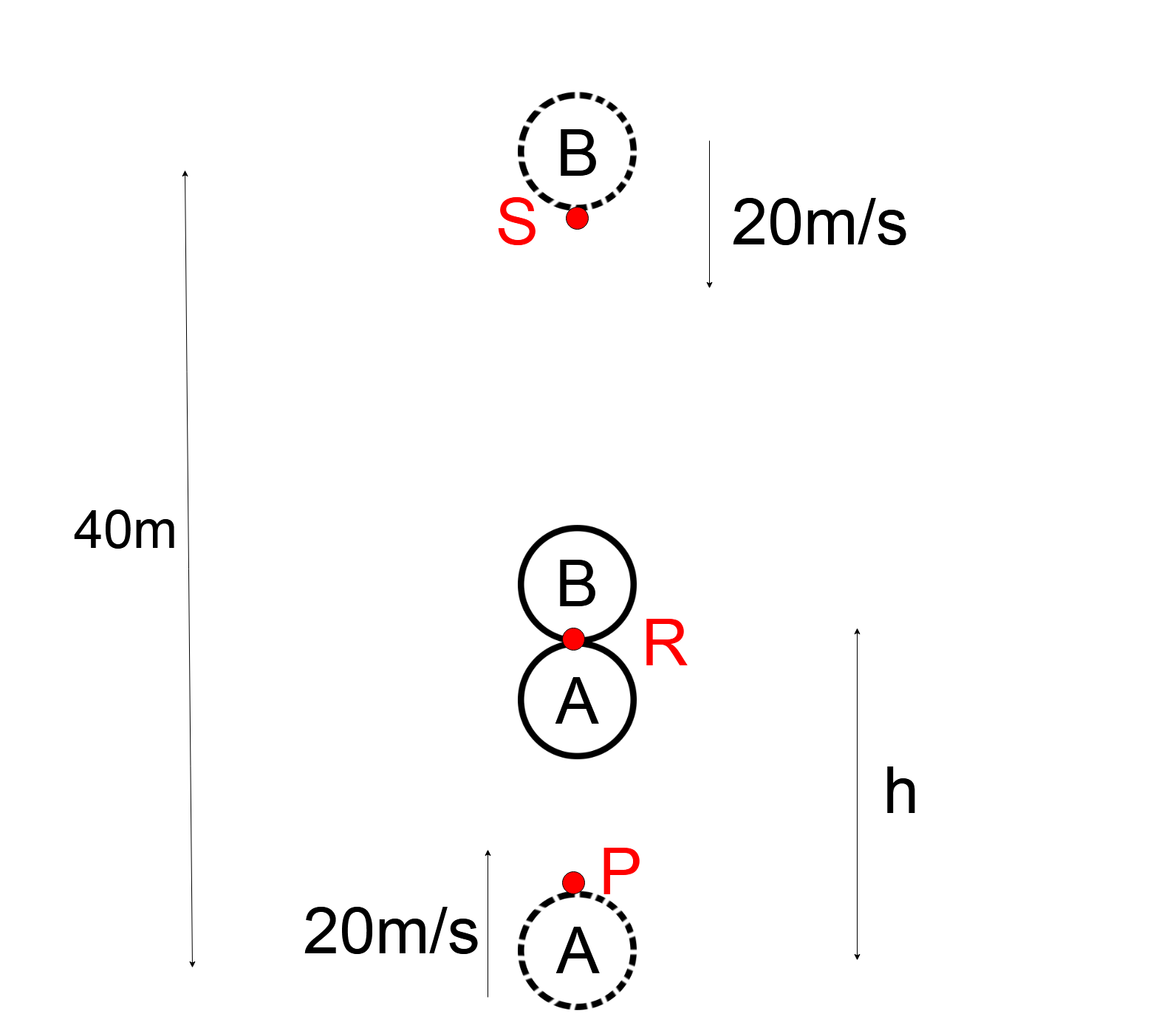
Given, the initial velocity of the ball that is thrown upwards is $20m/s$ from point P. The acceleration due to gravity acts in the downward direction ( $ - g$ ).
The ball $B$ is initially at a point S. The initial height of the ball that is thrown in the downward direction is $40m$ and the velocity of the ball is $20m{s^{ - 1}}$ .
The diagram of the following situation is as follows
We know that the second equation of motion is
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Here, $s = $ Height
$u = $ The initial velocity of the body
$v = $ The final velocity of the body
$a = $ Acceleration of the body
$t = $ Time
So, using the second equation of motion, for the motion of the ball $A$ from point P to point R, we get
$h = 20 \times t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( { - g} \right) \times {t^2}$
$h = 20t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ (Equation 1)
And, using the second equation of motion, for the motion of ball $B$ from point S to point R, we get
$40 - h = 20 \times t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times g \times {t^2}$
$40 - h = 20t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ (Equation 2)
Adding equation 1 and equation 2, we get
$h + 40 - h = 20t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2} + 20t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
$40 = 40t$
$t = 1\sec $
Substituting the value of $t$ in equation 2, we get
$40 - h = 20 \times 1 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {\left( 1 \right)^2}$ (Assuming $g = 10m/{s^2}$ )
$h = 40 - 25$
$h = 15m$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
In this type of problems, we usually ignore possible interfering factors such as air resistance, and the gravitational pull of other celestial objects, unless stated otherwise. In practice, the balls would face these ignored factors and this will if not greatly, to some extent cause variability in the results obtained.
Complete answer:
Let’s assume that the balls meet at a Point R and are at a height $h$ from the ground and will meet in time $t$ .

Given, the initial velocity of the ball that is thrown upwards is $20m/s$ from point P. The acceleration due to gravity acts in the downward direction ( $ - g$ ).
The ball $B$ is initially at a point S. The initial height of the ball that is thrown in the downward direction is $40m$ and the velocity of the ball is $20m{s^{ - 1}}$ .
The diagram of the following situation is as follows
We know that the second equation of motion is
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Here, $s = $ Height
$u = $ The initial velocity of the body
$v = $ The final velocity of the body
$a = $ Acceleration of the body
$t = $ Time
So, using the second equation of motion, for the motion of the ball $A$ from point P to point R, we get
$h = 20 \times t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( { - g} \right) \times {t^2}$
$h = 20t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ (Equation 1)
And, using the second equation of motion, for the motion of ball $B$ from point S to point R, we get
$40 - h = 20 \times t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times g \times {t^2}$
$40 - h = 20t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ (Equation 2)
Adding equation 1 and equation 2, we get
$h + 40 - h = 20t - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2} + 20t + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$
$40 = 40t$
$t = 1\sec $
Substituting the value of $t$ in equation 2, we get
$40 - h = 20 \times 1 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {\left( 1 \right)^2}$ (Assuming $g = 10m/{s^2}$ )
$h = 40 - 25$
$h = 15m$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
In this type of problems, we usually ignore possible interfering factors such as air resistance, and the gravitational pull of other celestial objects, unless stated otherwise. In practice, the balls would face these ignored factors and this will if not greatly, to some extent cause variability in the results obtained.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




