
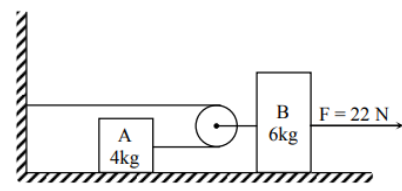
Two blocks are connected by a massless string through an ideal pulley as shown. A force of $22\,N$ is applied on block $B$ when initially the blocks are at rest. Then acceleration of centre of mass of block $A$ and block $B$, $2\,s$, after the application of force is $($ masses of $A$ and $B$ are $4\,kg$ and $6\,kg$ respectively and surfaces are smooth $)$
A. $1.4\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
B. $1\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
C. $2\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
D. None of these.

Answer
519.3k+ views
Hint:The point where the whole mass is assumed to be concentrated is known as the centre of mass and it is relative to an object or the system of objects and also the average position of all parts of the system, weighted according to their masses. The tension is nothing but the pulling force in the string and the direction of the string will be away from the load.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Force exerted on the block $B$ when the blocks are at rest is $ = 22\,N$
$F = 22\,N$
Mass of block $A = 4\,kg$
Mass of block $A = 6\,kg$
We need to find acceleration of centre of mass of blocks $A$ and $B$ after $2s$ from the application of force
Let the tension in the string be $T$ , then;
$F - 2T = 6a$ ……….. $\left( 1 \right)$
$\Rightarrow T = 4 \times 2a$
$\Rightarrow T = 8a$ ……….. $\left( 2 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 2 \right)$ in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get
$F - 16a = 6a$
Therefore, $a = \dfrac{F}{{22}}$
Substituting the value of $F$ in above equation we get acceleration as
$a = 1\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
Then the acceleration of the centre of mass will be
${a_{cm}} = \dfrac{{\left( {6 \times acceleration{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}A} \right) + \left( {4 \times acceleration{\text{ }}of{\text{ B}}} \right)}}{{6 + 4}}$
${a_{cm}} = \dfrac{{\left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {4 \times 2} \right)}}{{10}}$
\[\therefore {a_{cm}} = 1.4\,m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:By using acceleration of the centre of mass we can find speed of centre of mass that is speed of centre of mass = acceleration $ \times $ time $ = 1.4 \times 2 = 2.8m{s^{ - 1}}$ because the acceleration is defined as rate of change of velocity. Is is a vector quantity and its $S.I$ unit is $m{s^{ - 2}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Force exerted on the block $B$ when the blocks are at rest is $ = 22\,N$
$F = 22\,N$
Mass of block $A = 4\,kg$
Mass of block $A = 6\,kg$
We need to find acceleration of centre of mass of blocks $A$ and $B$ after $2s$ from the application of force
Let the tension in the string be $T$ , then;
$F - 2T = 6a$ ……….. $\left( 1 \right)$
$\Rightarrow T = 4 \times 2a$
$\Rightarrow T = 8a$ ……….. $\left( 2 \right)$
Substituting equation $\left( 2 \right)$ in equation $\left( 1 \right)$ we get
$F - 16a = 6a$
Therefore, $a = \dfrac{F}{{22}}$
Substituting the value of $F$ in above equation we get acceleration as
$a = 1\,m{s^{ - 2}}$
Then the acceleration of the centre of mass will be
${a_{cm}} = \dfrac{{\left( {6 \times acceleration{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}A} \right) + \left( {4 \times acceleration{\text{ }}of{\text{ B}}} \right)}}{{6 + 4}}$
${a_{cm}} = \dfrac{{\left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {4 \times 2} \right)}}{{10}}$
\[\therefore {a_{cm}} = 1.4\,m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:By using acceleration of the centre of mass we can find speed of centre of mass that is speed of centre of mass = acceleration $ \times $ time $ = 1.4 \times 2 = 2.8m{s^{ - 1}}$ because the acceleration is defined as rate of change of velocity. Is is a vector quantity and its $S.I$ unit is $m{s^{ - 2}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




