
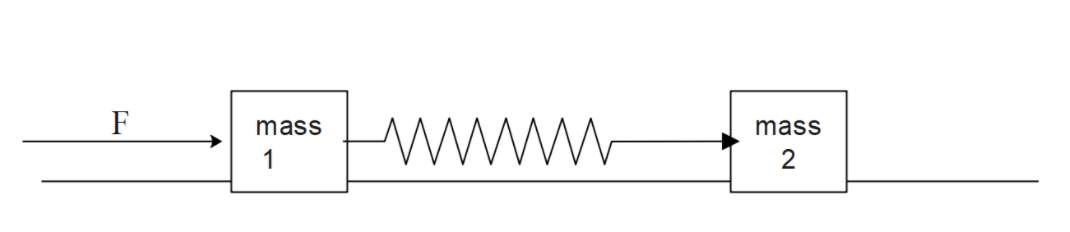
Two blocks of masses ${{m}_{1}}$, ${{m}_{2}}$ are connected by a spring of stiffness k. The coefficient of friction between the blocks and the surface is $\mu $. Find the minimum constant force F to be applied to ${{m}_{1}}$ in order to just slide the mass ${{m}_{2}}$ .

Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Let us first find the external force acting on the body when force F is applied. Work done by the net external force is calculated. Also, the spring force is calculated in terms of mass and acceleration. Finally, the change in kinetic energy of the total system is zero, work done is equal to the change in kinetic energy, therefore, we can find the force F on mass 1 so that it just slides on mass 2.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& W=\Delta K.E \\
& W=\int{{{F}^{1}}dx} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us find the net external force acting at any position x,
We know the masses ${{m}_{1}},{{m}_{2}}$, spring constant k,
The force acting is,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}^{1}}=F-(\mu {{m}_{1}}g+kx) \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Work done by the net external force in displacing the block m, through a length ${{x}_{0}}$will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{W}_{ext}}=\int{{{F}^{1}}dx} \\
& {{W}_{ext}}=\int\limits_{0}^{{{x}_{0}}}{(F-(\mu mg+kx))dx} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Also, they spring force required to just move the mass 2 will be,
$\begin{align}
& k{{x}_{0}}=\mu {{m}_{2}}g \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{0}}=\dfrac{\mu {{m}_{2}}g}{k} \\
\end{align}$as the change in kinetic energy of the system is zero, the work done is equal to change in kinetic energy,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta K.E=0 \\
& \Rightarrow W=\Delta K.E \\
& \Rightarrow F=\mu {{m}_{1}}g+\dfrac{k{{x}_{0}}}{2} \\
& \therefore F=\mu {{m}_{1}}g+\dfrac{\mu {{m}_{2}}g}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can find the force acted on the mass 1 so that it just slides on mass 2.
Additional Information:
A system of masses connected by springs is a classical system with several degrees of freedom. For example, a system consisting of two masses and three springs has two degrees of freedom. This means that its configuration can be described by two generalized coordinates, which can be chosen to be the displacements of the first and second mass from the equilibrium position.
Note:
Spring material plays an important role in the good functioning of the spring. Materials lie titanium, alloy steel, carbon steel etc. Are really good materials. We may experience spring problems if these springs are susceptible to harsh conditions. We need to coat a spring to prevent it from rusting.
Formula used:
$\begin{align}
& W=\Delta K.E \\
& W=\int{{{F}^{1}}dx} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us find the net external force acting at any position x,
We know the masses ${{m}_{1}},{{m}_{2}}$, spring constant k,
The force acting is,
$\begin{align}
& {{F}^{1}}=F-(\mu {{m}_{1}}g+kx) \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Work done by the net external force in displacing the block m, through a length ${{x}_{0}}$will be,
$\begin{align}
& {{W}_{ext}}=\int{{{F}^{1}}dx} \\
& {{W}_{ext}}=\int\limits_{0}^{{{x}_{0}}}{(F-(\mu mg+kx))dx} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Also, they spring force required to just move the mass 2 will be,
$\begin{align}
& k{{x}_{0}}=\mu {{m}_{2}}g \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{0}}=\dfrac{\mu {{m}_{2}}g}{k} \\
\end{align}$as the change in kinetic energy of the system is zero, the work done is equal to change in kinetic energy,
$\begin{align}
& \Delta K.E=0 \\
& \Rightarrow W=\Delta K.E \\
& \Rightarrow F=\mu {{m}_{1}}g+\dfrac{k{{x}_{0}}}{2} \\
& \therefore F=\mu {{m}_{1}}g+\dfrac{\mu {{m}_{2}}g}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can find the force acted on the mass 1 so that it just slides on mass 2.
Additional Information:
A system of masses connected by springs is a classical system with several degrees of freedom. For example, a system consisting of two masses and three springs has two degrees of freedom. This means that its configuration can be described by two generalized coordinates, which can be chosen to be the displacements of the first and second mass from the equilibrium position.
Note:
Spring material plays an important role in the good functioning of the spring. Materials lie titanium, alloy steel, carbon steel etc. Are really good materials. We may experience spring problems if these springs are susceptible to harsh conditions. We need to coat a spring to prevent it from rusting.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




