
Two bodies of mass 10kg and 20kg respectively kept on a smooth, horizontal surface are tied to the ends of a light string. A horizontal force F=600N is applied to (i) A, (ii) B along the direction of the string. What is the tension in the string in each case?
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: Apply Newton’s second law of motion. That is force is equal to the product of mass and acceleration. Thus by rearranging the equation, calculate the acceleration. Then in the case of body A and consider the forces acting on the body and formulate the equation of motion for A and rearrange the equation for calculating the tension. Similarly find the tension in the second case for B.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Total mass of the system, $m={{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}$
That is,
$\begin{align}
& m=10+20 \\
& \Rightarrow m=30kg \\
\end{align}$
According to Newton’s second law of motion,
F=ma
Here we have to find the acceleration. Thus by rearranging the equation we get,
$a=\dfrac{F}{m}$
Also given that,
F=600N
Substituting in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{600}{30} \\
& \Rightarrow a=20\dfrac{m}{{{s}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
(i) When force is applied on A,
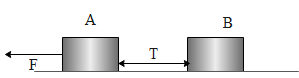
The equation of motion for A can be written as,
$F-T={{m}_{1}}a$
Hence $T=F-{{m}_{1}}a$
Substituting the values above equation becomes,
$\begin{align}
& T=600-10\times 20 \\
& \Rightarrow T=400N \\
\end{align}$
(ii) When the force is applied on B.
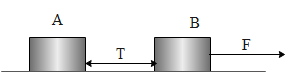
The equation of motion becomes,
$F-T={{m}_{2}}a$
Again substituting the values and rearranging the above equation becomes,
$\begin{align}
& T=F-{{m}_{2}}a \\
& \Rightarrow T=600-20\times 20 \\
& \therefore T=200N \\
\end{align}$
Note: Newton's second law of motion can be applied in a variety of fields. For example, a cricketer in cricket ground draws his hand backward while the ball is coming with high speed to avoid the injury on hand by reducing the velocity of the ball.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Total mass of the system, $m={{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}$
That is,
$\begin{align}
& m=10+20 \\
& \Rightarrow m=30kg \\
\end{align}$
According to Newton’s second law of motion,
F=ma
Here we have to find the acceleration. Thus by rearranging the equation we get,
$a=\dfrac{F}{m}$
Also given that,
F=600N
Substituting in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{600}{30} \\
& \Rightarrow a=20\dfrac{m}{{{s}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
(i) When force is applied on A,

The equation of motion for A can be written as,
$F-T={{m}_{1}}a$
Hence $T=F-{{m}_{1}}a$
Substituting the values above equation becomes,
$\begin{align}
& T=600-10\times 20 \\
& \Rightarrow T=400N \\
\end{align}$
(ii) When the force is applied on B.

The equation of motion becomes,
$F-T={{m}_{2}}a$
Again substituting the values and rearranging the above equation becomes,
$\begin{align}
& T=F-{{m}_{2}}a \\
& \Rightarrow T=600-20\times 20 \\
& \therefore T=200N \\
\end{align}$
Note: Newton's second law of motion can be applied in a variety of fields. For example, a cricketer in cricket ground draws his hand backward while the ball is coming with high speed to avoid the injury on hand by reducing the velocity of the ball.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




