
Two bodies of masses 4 kg and 9 kg are separated by distance of 60 cm. A 1 kg mass is placed in between these two masses. If the net force on 1 kg is zero, then its distance from 4 kg mass is
A: 26cm
B: 30cm
C: 28cm
D: 32 cm
E: 24cm
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We know that every particle attracts another particle that is kept at a distance, by the law of gravitation. We have to place the 1kg body somewhere in between the other two bodies, else both the bodies will exert an attractive force on the 1kg body in the same direction and the value of the net force on it will not be zero.
Formula used:
Law of gravitation:
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}$, where F is the gravitational force, G is the gravitational constant, M and m are the masses of two bodies and r is the distance between them.
Complete step by step answer:
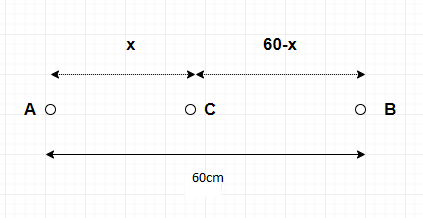
Let the 4kg masses body be A, 9 kg masses body be B and the 1kg massed body be C
Let us assume that the 1kg body is kept at a distance of $x$cm from the 4kg mass.
Hence, its distance from the 9kg mass would be $60-x$cm.
Let force due to A on C be \[{{\vec{F}}_{AC}}\]
From the law of gravitation,
\[{{\vec{F}}_{AC}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{C}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{G\times 4\times 1}{{{x}^{2}}}\]
Let force due to B on C be \[{{\vec{F}}_{BC}}\]
Hence, \[{{\vec{F}}_{BC}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{B}}{{m}_{C}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{G\times 9\times 1}{{{(60-x)}^{2}}}\]
We know that the net force on C is zero. Hence the sum of all the forces on C should be zero,
Since the forces \[{{\vec{F}}_{AC}}\]and \[{{\vec{F}}_{BC}}\]act in opposite directions, we can say that
$ {{{\vec{F}}}_{AC}}-{{{\vec{F}}}_{BC}}=0 \\ $
$\Rightarrow {{{\vec{F}}}_{AC}}={{{\vec{F}}}_{BC}} \\ $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4G}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{9G}{{{(60-x)}^{2}}} \\ $
$\Rightarrow 4{{(60-x)}^{2}}=9{{x}^{2}} \\$
Taking square on both sides,
$ 2(60-x)=3x \\ $
$\Rightarrow 120-2x=3x \\ $
$\Rightarrow 5x=120 \\ $
$\therefore x=\dfrac{120}{5}=24cm \\ $
Hence, C is to be kept at a distance of 24cm from A to retain net force as zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Gravitational force is a universal attractive force which obeys the inverse square law.
However it is considered to be the weakest force in nature in case of atomic and subatomic levels.
Formula used:
Law of gravitation:
$F=\dfrac{GMm}{{{r}^{2}}}$, where F is the gravitational force, G is the gravitational constant, M and m are the masses of two bodies and r is the distance between them.
Complete step by step answer:

Let the 4kg masses body be A, 9 kg masses body be B and the 1kg massed body be C
Let us assume that the 1kg body is kept at a distance of $x$cm from the 4kg mass.
Hence, its distance from the 9kg mass would be $60-x$cm.
Let force due to A on C be \[{{\vec{F}}_{AC}}\]
From the law of gravitation,
\[{{\vec{F}}_{AC}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{C}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{G\times 4\times 1}{{{x}^{2}}}\]
Let force due to B on C be \[{{\vec{F}}_{BC}}\]
Hence, \[{{\vec{F}}_{BC}}=\dfrac{G{{m}_{B}}{{m}_{C}}}{{{r}^{2}}}=\dfrac{G\times 9\times 1}{{{(60-x)}^{2}}}\]
We know that the net force on C is zero. Hence the sum of all the forces on C should be zero,
Since the forces \[{{\vec{F}}_{AC}}\]and \[{{\vec{F}}_{BC}}\]act in opposite directions, we can say that
$ {{{\vec{F}}}_{AC}}-{{{\vec{F}}}_{BC}}=0 \\ $
$\Rightarrow {{{\vec{F}}}_{AC}}={{{\vec{F}}}_{BC}} \\ $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4G}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{9G}{{{(60-x)}^{2}}} \\ $
$\Rightarrow 4{{(60-x)}^{2}}=9{{x}^{2}} \\$
Taking square on both sides,
$ 2(60-x)=3x \\ $
$\Rightarrow 120-2x=3x \\ $
$\Rightarrow 5x=120 \\ $
$\therefore x=\dfrac{120}{5}=24cm \\ $
Hence, C is to be kept at a distance of 24cm from A to retain net force as zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Gravitational force is a universal attractive force which obeys the inverse square law.
However it is considered to be the weakest force in nature in case of atomic and subatomic levels.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




