
What two bonds keep a water molecule together?
Answer
529.2k+ views
Hint :Here, the phrase “keep a water molecule together” can mean two things – that the bonds that keep a single molecule together as well as the bonds that keep a water molecule together with the other water molecules. Hence, we need to consider both cases and find the bonds that keep a molecule together in both cases.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider a water molecule as shown in the figure
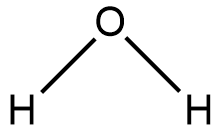
From the periodic table, we can understand that oxygen needs two electrons to achieve stable state and hydrogen needs one electron to reach stable state.
Hence, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom comes closer, but we can understand from the periodic trends that even though oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the electronegativity difference and the atomic size difference is very less to form an ionic bond.
Hence, the hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom forms two covalent oxygen-hydrogen bonds.
These are the bonds that keep a single molecule of water bonded and together.
Now, even though the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen is less, oxygen due to higher electronegativity pulls the electron pair towards itself.
Due to this a partial positive charge is set up on hydrogen and a partial negative charge is set up on oxygen.
Due to this phenomenon, hydrogen which is partially positively charged gets attracted by the oxygen of a nearby molecule that is partially negatively charged and has a lone pair of electrons.
Hence, hydrogen of one molecule forms a bond with oxygen of another molecule due to the opposite charges which is known as hydrogen bonding, as shown in the figure.
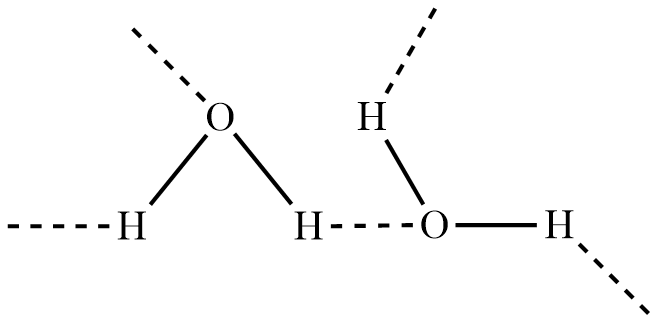
This bond is not exactly classified as a bond, but an attraction which is weaker than ionic or covalent bonding but stronger than Vander Waals dispersion forces.
Hence, this bond keeps the water molecule bonded with other molecules of water.
Hence, in water, there are two types of bond present that keep the molecule together, namely Covalent bond and Hydrogen bond.
Note :
The hydrogen bond that forms between the hydrogen of one molecule and oxygen of the adjacent molecule is responsible for some of the major properties of water like relatively high boiling point, adhesion, cohesion and its density. The hydrogen bond is only formed in the molecules in which there is high electronegativity difference between the parent atom and hydrogen i.e. Hydrogen Fluoride, Water, and Ammonia. The higher electronegative atoms form an ionic compound with hydrogen and thus hydrogen bond is not possible in those compounds.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider a water molecule as shown in the figure

From the periodic table, we can understand that oxygen needs two electrons to achieve stable state and hydrogen needs one electron to reach stable state.
Hence, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom comes closer, but we can understand from the periodic trends that even though oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the electronegativity difference and the atomic size difference is very less to form an ionic bond.
Hence, the hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom forms two covalent oxygen-hydrogen bonds.
These are the bonds that keep a single molecule of water bonded and together.
Now, even though the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen is less, oxygen due to higher electronegativity pulls the electron pair towards itself.
Due to this a partial positive charge is set up on hydrogen and a partial negative charge is set up on oxygen.
Due to this phenomenon, hydrogen which is partially positively charged gets attracted by the oxygen of a nearby molecule that is partially negatively charged and has a lone pair of electrons.
Hence, hydrogen of one molecule forms a bond with oxygen of another molecule due to the opposite charges which is known as hydrogen bonding, as shown in the figure.

This bond is not exactly classified as a bond, but an attraction which is weaker than ionic or covalent bonding but stronger than Vander Waals dispersion forces.
Hence, this bond keeps the water molecule bonded with other molecules of water.
Hence, in water, there are two types of bond present that keep the molecule together, namely Covalent bond and Hydrogen bond.
Note :
The hydrogen bond that forms between the hydrogen of one molecule and oxygen of the adjacent molecule is responsible for some of the major properties of water like relatively high boiling point, adhesion, cohesion and its density. The hydrogen bond is only formed in the molecules in which there is high electronegativity difference between the parent atom and hydrogen i.e. Hydrogen Fluoride, Water, and Ammonia. The higher electronegative atoms form an ionic compound with hydrogen and thus hydrogen bond is not possible in those compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




