
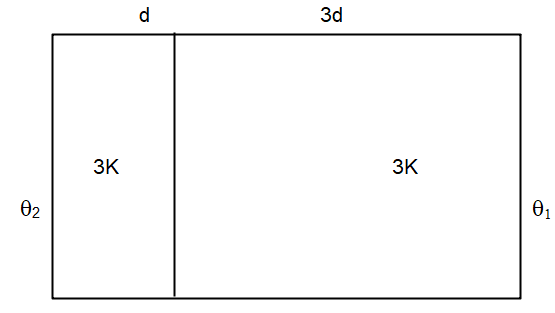
Two materials having coefficients of thermal conductivity ′3K′ and ′K′ and thickness 'd' and ′3d′, respectively, are joined to form a slab as shown in the figure. The temperature of the outer surfaces are $ \prime {\theta _2}\prime $ and $ \prime {\theta _1}\prime \; $ respectively, $ \left( {{\theta _2} > {\theta _1}} \right). $ . The temperature at the interface is?
A) $ \dfrac{{{\theta _1} + {\theta _2}}}{2} $
B) $ \dfrac{{{\theta _1}}}{{10}} + \dfrac{{9{\theta _2}}}{{10}} $
C) $ \dfrac{{{\theta _1}}}{3} + \dfrac{{2{\theta _2}}}{3} $
D) $ \dfrac{{{\theta _1}}}{6} + \dfrac{{5{\theta _2}}}{6} $

Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint : In this solution, we will assume that the system has been in a steady-state for a long time. Then both the slabs will have the same rate of heat transfer and we will use this to determine the solution of the interface.
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formula:
Rate of heat transfer in a slab with different temperatures: $ Q = \dfrac{{kA\Delta T}}{L} $ where $ A $ is the area of the surface, $ \Delta T $ is the temperature difference, and $ L $ is the length of the slab.
Complete step by step answer
In the system given to us, we will assume that the system has been left in this situation for a long time. This implies that the heat transfer will have occurred over a long time and the system can be said to have achieved a steady-state.
In this steady-state situation, we can say that the heat transfer in both the slabs will be the same. Let us assume that the temperature of the surface is $ \theta $ . Then since the heat flow rate is constant for both the surfaces will be the same and we can write
$ \dfrac{{3kA({\theta _2} - \theta )}}{d} = \dfrac{{kA(\theta - {\theta _1})}}{{3d}} $
Dividing both sides by $ kA/d $ and cross multiplying the denominators, we get
$ 9{\theta _2} - 9\theta = \theta - {\theta _1} $
Solving for $ \theta $ , we get
$\Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{{9{\theta _2}}}{{10}} + \dfrac{{{\theta _1}}}{{10}} $ which corresponds to option (B).
Note
Unless mentioned otherwise, we must take such systems to be in a steady-state i.e. the system has been in this state for a long time. Only with this assumption can we assume that both the slabs will have the same rate of heat transfer.
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formula:
Rate of heat transfer in a slab with different temperatures: $ Q = \dfrac{{kA\Delta T}}{L} $ where $ A $ is the area of the surface, $ \Delta T $ is the temperature difference, and $ L $ is the length of the slab.
Complete step by step answer
In the system given to us, we will assume that the system has been left in this situation for a long time. This implies that the heat transfer will have occurred over a long time and the system can be said to have achieved a steady-state.
In this steady-state situation, we can say that the heat transfer in both the slabs will be the same. Let us assume that the temperature of the surface is $ \theta $ . Then since the heat flow rate is constant for both the surfaces will be the same and we can write
$ \dfrac{{3kA({\theta _2} - \theta )}}{d} = \dfrac{{kA(\theta - {\theta _1})}}{{3d}} $
Dividing both sides by $ kA/d $ and cross multiplying the denominators, we get
$ 9{\theta _2} - 9\theta = \theta - {\theta _1} $
Solving for $ \theta $ , we get
$\Rightarrow \theta = \dfrac{{9{\theta _2}}}{{10}} + \dfrac{{{\theta _1}}}{{10}} $ which corresponds to option (B).
Note
Unless mentioned otherwise, we must take such systems to be in a steady-state i.e. the system has been in this state for a long time. Only with this assumption can we assume that both the slabs will have the same rate of heat transfer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




