
Two stones are thrown up simultaneously from the edge of a cliff $240m$high with initial speed $10m{{s}^{-1}}$and $40m{{s}^{-1}}$respectively. Which of the following graphs best represents the time variation of relative position of the second stone with respect to the first?
(Assume stones do not rebound after hitting the ground and neglect air resistance, take $g=10m{{s}^{-2}}$)
(The figures are schematic and not drawn to scale.)
A.

B.

C.

D.





Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint:We will apply the concept of relative motion to predict the nature of motion of one particle with respect to the other particle. By using the equations of motion we can calculate the time intervals where the two objects will come across and when one of the objects will touch the ground.
Formula used:
Equation of motion, $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Complete step by step solution:
When we throw an object vertically upwards, it will eventually fall back to the ground under the effect of earth’s gravity. The velocity of the object keeps on decreasing, that is, the object thrown vertically upwards decelerates under earth’s gravity. Its speed decreases till the time it attains a maximum height. At that point, the velocity of the object becomes zero. Then the object is accelerated uniformly downwards. The vertical motion under gravity can be described using the equations of motion.
Consider the two stones are thrown up simultaneously as shown in the below figure.
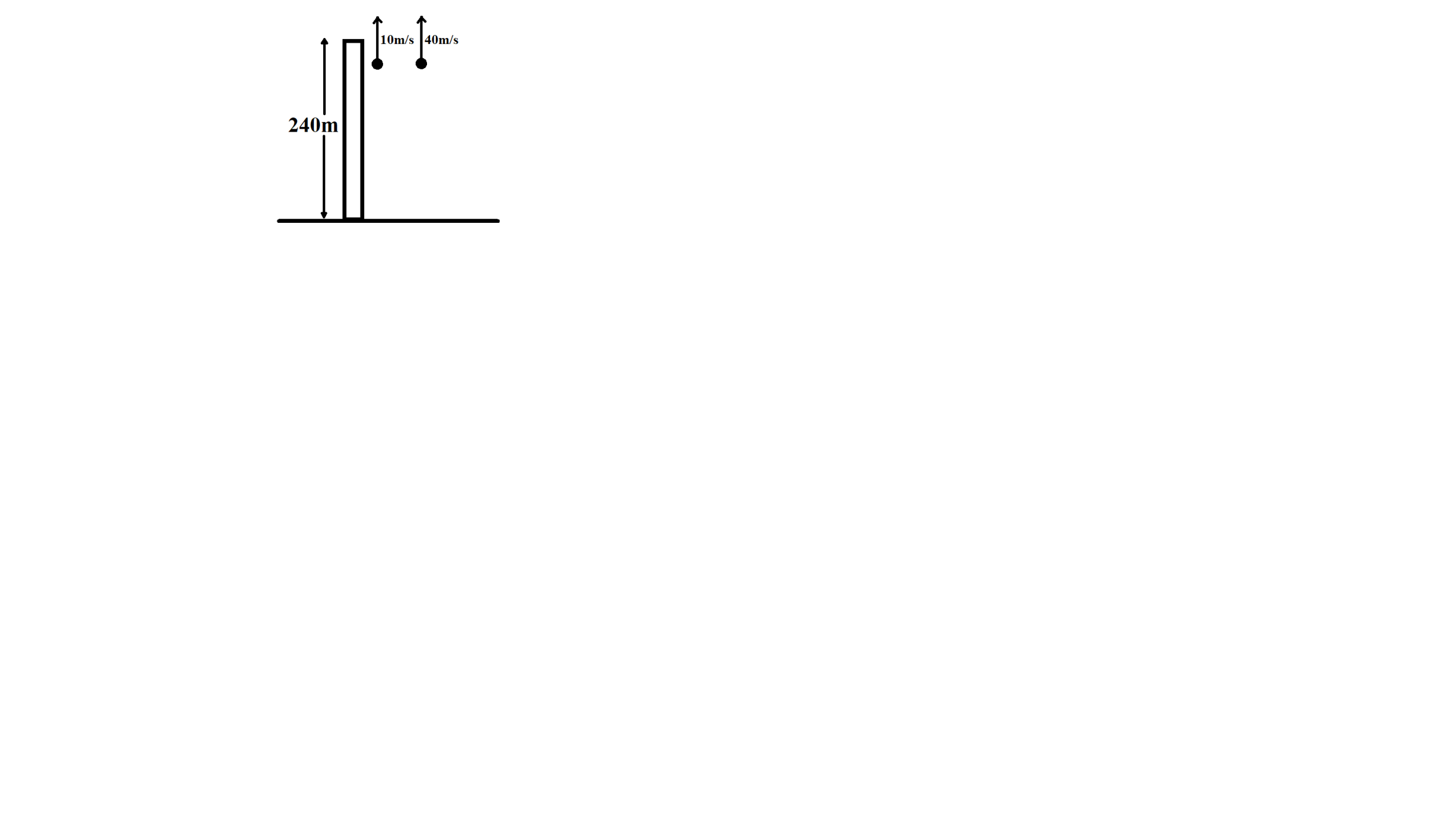
Let’s consider acceleration of particle first as ${{a}_{1}}$and acceleration of second particle as ${{a}_{2}}$
The magnitude of relative acceleration of second particle with respect to first particle is,
$\begin{align}
& \left| {{a}_{21}} \right|=\left| {{a}_{2}}-{{a}_{1}} \right| \\
& {{a}_{1}}={{a}_{2}}=g \\
\end{align}$
Therefore,
$\left| {{a}_{21}} \right|=0$
The motion of first particle is straight line with respect to second particle till the moment first particle strikes the ground at time$t$
Applying equation of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Putting values,
$\begin{align}
& s=-120m \\
& u=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& a=10m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& -120=10t-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{t}^{2}} \\
& {{t}^{2}}-2t-48=0 \\
& {{t}^{2}}-8t+6t-48=0 \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$t=8\text{ or }t=-6$
Since time cannot be negative. Therefore,
$t=8\sec $
Now, distance covered by second particle with respect to first particle with respect to second particle in $8\text{ seconds}$is,
${{s}_{12}}=\left( {{v}_{21}} \right)t$
Putting values,
$\begin{align}
& {{v}_{21}}={{v}_{2}}-{{v}_{1}}=40-10 \\
& {{v}_{21}}=30m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& t=8\sec \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$\begin{align}
& {{s}_{12}}=30\times 8=240 \\
& {{s}_{12}}=240m \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, time taken by second particle to strike the ground is given by,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Putting values,
$\begin{align}
& s=-240m \\
& u=40m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& a=10m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& -240=40t-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{t}^{2}} \\
& -240=40t-5{{t}^{2}} \\
& 5{{t}^{2}}-40t-240=0 \\
& {{t}^{2}}-8t-48=0 \\
& {{t}^{2}}-12t+4t-48=0 \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$t=12\text{ or}-4$
Since time cannot be negative. Therefore,
$t=12\sec $
Thus, after $8\sec $, the magnitude of relative velocity will increase up to $12\sec $ when the second particle strikes the ground.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: After being thrown upwards, when the object returns to the point of projection, it has the same speed as that at the instant of projection. Also, the duration of the upward is exactly the same as that of the downward motion. The effect of air resistance is neglected in these cases. Air resistance further opposes the motion of the object in free fall and decreases its acceleration.
Formula used:
Equation of motion, $s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Complete step by step solution:
When we throw an object vertically upwards, it will eventually fall back to the ground under the effect of earth’s gravity. The velocity of the object keeps on decreasing, that is, the object thrown vertically upwards decelerates under earth’s gravity. Its speed decreases till the time it attains a maximum height. At that point, the velocity of the object becomes zero. Then the object is accelerated uniformly downwards. The vertical motion under gravity can be described using the equations of motion.
Consider the two stones are thrown up simultaneously as shown in the below figure.

Let’s consider acceleration of particle first as ${{a}_{1}}$and acceleration of second particle as ${{a}_{2}}$
The magnitude of relative acceleration of second particle with respect to first particle is,
$\begin{align}
& \left| {{a}_{21}} \right|=\left| {{a}_{2}}-{{a}_{1}} \right| \\
& {{a}_{1}}={{a}_{2}}=g \\
\end{align}$
Therefore,
$\left| {{a}_{21}} \right|=0$
The motion of first particle is straight line with respect to second particle till the moment first particle strikes the ground at time$t$
Applying equation of motion,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Putting values,
$\begin{align}
& s=-120m \\
& u=10m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& a=10m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& -120=10t-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{t}^{2}} \\
& {{t}^{2}}-2t-48=0 \\
& {{t}^{2}}-8t+6t-48=0 \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$t=8\text{ or }t=-6$
Since time cannot be negative. Therefore,
$t=8\sec $
Now, distance covered by second particle with respect to first particle with respect to second particle in $8\text{ seconds}$is,
${{s}_{12}}=\left( {{v}_{21}} \right)t$
Putting values,
$\begin{align}
& {{v}_{21}}={{v}_{2}}-{{v}_{1}}=40-10 \\
& {{v}_{21}}=30m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& t=8\sec \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$\begin{align}
& {{s}_{12}}=30\times 8=240 \\
& {{s}_{12}}=240m \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, time taken by second particle to strike the ground is given by,
$s=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}}$
Putting values,
$\begin{align}
& s=-240m \\
& u=40m{{s}^{-1}} \\
& a=10m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& -240=40t-\dfrac{1}{2}\times 10\times {{t}^{2}} \\
& -240=40t-5{{t}^{2}} \\
& 5{{t}^{2}}-40t-240=0 \\
& {{t}^{2}}-8t-48=0 \\
& {{t}^{2}}-12t+4t-48=0 \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$t=12\text{ or}-4$
Since time cannot be negative. Therefore,
$t=12\sec $
Thus, after $8\sec $, the magnitude of relative velocity will increase up to $12\sec $ when the second particle strikes the ground.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: After being thrown upwards, when the object returns to the point of projection, it has the same speed as that at the instant of projection. Also, the duration of the upward is exactly the same as that of the downward motion. The effect of air resistance is neglected in these cases. Air resistance further opposes the motion of the object in free fall and decreases its acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




