
Two vectors of equal magnitude have a resultant equal to either of them in magnitude. The angle between them is:
A. 60°
B. 90°
C. 105°
D. 120°
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: It is given that two vectors are equal in magnitude i.e. if A and B are two vectors then $\mid A \mid = \mid B \mid$. It is also mentioned that the magnitude of resultant is equal to the magnitude of either of them i.e. $\mid A \mid= \mid B \mid=\mid A+B \mid$. Find the resultant of both the vectors and then equate it with the magnitude of resultant of either of the vectors. After equating the equation, solve it and find the angle between them.
Formula used:
$|\overrightarrow { A+B } |=\sqrt { { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$
Complete answer:
Let the two vectors be $|\overrightarrow { A } |$ and $|\overrightarrow { B } |$.
$\theta$ be the angle between both the vectors.
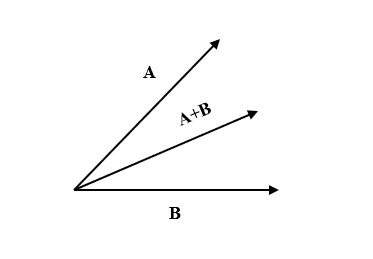
Both the vectors have the same magnitude.
$\therefore |\overrightarrow { A } |= |\overrightarrow { A } |$ …(1)
Let the resultant have magnitude equal to vector A.
Thus, the resultant is given by,
$|\overrightarrow { A } |=|\overrightarrow { B } |=|\overrightarrow { A+B } |$ …(2)
The magnitude of resultant of two vectors is given by,
$|\overrightarrow { A+B } |=\sqrt { { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$ …(3)
From the equation. (2) and equation. (3) we get,
$|\overrightarrow { A } |=\sqrt { { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$
Squaring both the sides we get,
$\Rightarrow { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$
Substituting equation. (1) in above equation we get,
${ |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { A } |\cos { \theta } }$
$\Rightarrow { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ { 2|\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { A } |\cos { \theta } }$
$\Rightarrow -{ |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ 2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { A } |\cos { \theta } }$
$\Rightarrow { \cos { \theta } =-\cfrac { 1 }{ 2 } }$
$\Rightarrow \theta =\cos ^{ -1 }{ \left( \cfrac { 1 }{ 2 } \right) }$
$\Rightarrow \theta= 120°$
Hence, the angle between the two vectors is 120°.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Students must remember that while adding two vectors don’t only consider the magnitude of the vectors but also consider the direction of both the vectors. If you don’t consider the direction then there might be an error in your calculation. If we double the resultant and reverse one of the vectors then the resultant gets doubled again.
Formula used:
$|\overrightarrow { A+B } |=\sqrt { { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$
Complete answer:
Let the two vectors be $|\overrightarrow { A } |$ and $|\overrightarrow { B } |$.
$\theta$ be the angle between both the vectors.

Both the vectors have the same magnitude.
$\therefore |\overrightarrow { A } |= |\overrightarrow { A } |$ …(1)
Let the resultant have magnitude equal to vector A.
Thus, the resultant is given by,
$|\overrightarrow { A } |=|\overrightarrow { B } |=|\overrightarrow { A+B } |$ …(2)
The magnitude of resultant of two vectors is given by,
$|\overrightarrow { A+B } |=\sqrt { { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$ …(3)
From the equation. (2) and equation. (3) we get,
$|\overrightarrow { A } |=\sqrt { { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$
Squaring both the sides we get,
$\Rightarrow { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { B } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { B } |\cos { \theta } }$
Substituting equation. (1) in above equation we get,
${ |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+{ |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { A } |\cos { \theta } }$
$\Rightarrow { |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ { 2|\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }+2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { A } |\cos { \theta } }$
$\Rightarrow -{ |\overrightarrow { A } | }^{ 2 }={ 2|\overrightarrow { A } ||\overrightarrow { A } |\cos { \theta } }$
$\Rightarrow { \cos { \theta } =-\cfrac { 1 }{ 2 } }$
$\Rightarrow \theta =\cos ^{ -1 }{ \left( \cfrac { 1 }{ 2 } \right) }$
$\Rightarrow \theta= 120°$
Hence, the angle between the two vectors is 120°.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Students must remember that while adding two vectors don’t only consider the magnitude of the vectors but also consider the direction of both the vectors. If you don’t consider the direction then there might be an error in your calculation. If we double the resultant and reverse one of the vectors then the resultant gets doubled again.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




