
Type of aestivation shown in Pisum
(a)Imbricate
(b)Vexillary
(c)Twisted
(d)Quincuncial
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Aestivation is a mode of arrangement of flower petals and sepals in a whorl. Aestivation is of considerable importance in classifying plants.
Complete answer:
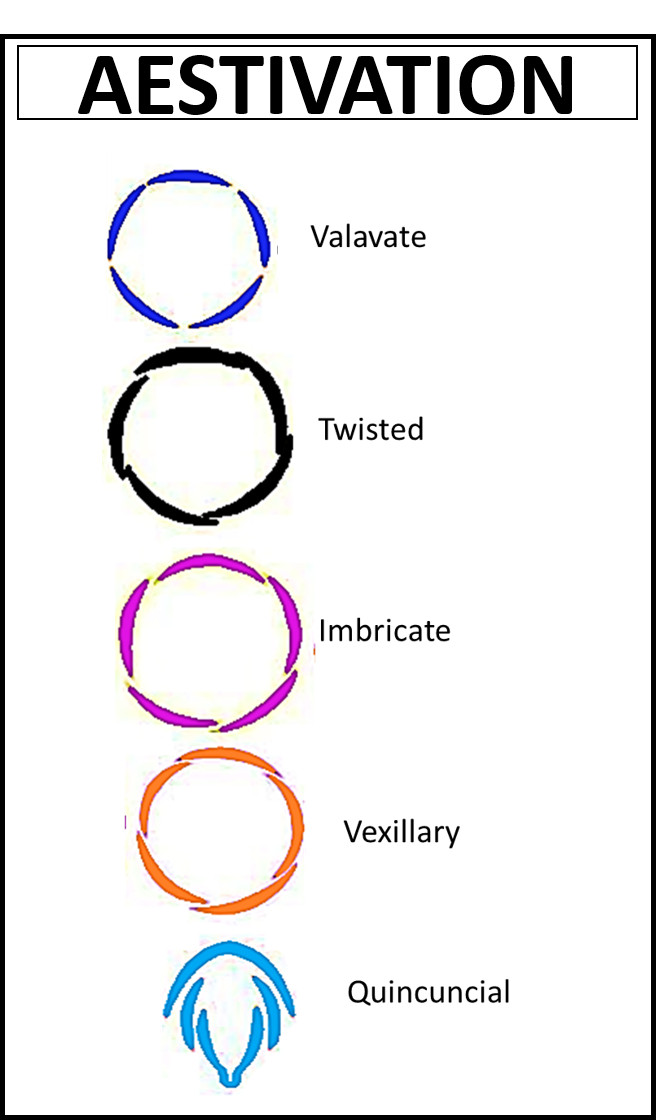
Vexillary aestivation- in this type of aestivation the five petals are differentiated into one large petal called as vexillum, it overlaps two smaller petals known as wings which then overlaps the smallest petals known as keels. This aestivation is usually found in the papilionaceous family.
Additional Information: -Imbricate aestivation- in this type of aestivation the margins overlap one another in no particular order. The flower petals do not lie in the single whorl. Example- Gulmohar and cassia.
-Twisted aestivation- it is also known as contorted aestivation. In this type of aestivation one side of the petal overlaps the adjacent side of the petal. The overlapping is in continuous order so the petals appear to be twisted. Examples: china rose, cotton etc.
-Quincuncial aestivation- this type of aestivation occurs when petals are not in a whorl but are spirally arranged. The petals are arranged in such a way that two petals are completely out of the whorl and two are completely inside the whorl. The fifth petal has its one side inside the whorl and the other side is outside the whorl. This aestivation can be spotted in Ranunculus family.
-Valvate aestivation- in this type of aestivation the sepals and petals are arranged in a whorl and their petals touch the margin of one another without any overlapping. This aestivation is usually found in Calotropis.
So, the answer is ‘vexillary’.
Note: Perianth is a non-reproductive part of the plant that envelops the reproductive part of the plant. It consists of calyx and corolla. The perianth is found in the Liliaceae family.
Complete answer:
Vexillary aestivation- in this type of aestivation the five petals are differentiated into one large petal called as vexillum, it overlaps two smaller petals known as wings which then overlaps the smallest petals known as keels. This aestivation is usually found in the papilionaceous family.
Additional Information: -Imbricate aestivation- in this type of aestivation the margins overlap one another in no particular order. The flower petals do not lie in the single whorl. Example- Gulmohar and cassia.
-Twisted aestivation- it is also known as contorted aestivation. In this type of aestivation one side of the petal overlaps the adjacent side of the petal. The overlapping is in continuous order so the petals appear to be twisted. Examples: china rose, cotton etc.
-Quincuncial aestivation- this type of aestivation occurs when petals are not in a whorl but are spirally arranged. The petals are arranged in such a way that two petals are completely out of the whorl and two are completely inside the whorl. The fifth petal has its one side inside the whorl and the other side is outside the whorl. This aestivation can be spotted in Ranunculus family.
-Valvate aestivation- in this type of aestivation the sepals and petals are arranged in a whorl and their petals touch the margin of one another without any overlapping. This aestivation is usually found in Calotropis.
So, the answer is ‘vexillary’.

Note: Perianth is a non-reproductive part of the plant that envelops the reproductive part of the plant. It consists of calyx and corolla. The perianth is found in the Liliaceae family.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




