
What type of graph will you get when PV is plotted against P at constant temperature?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: the fundamental units used in this question are pressure (P), volume(V) and temperature (T). We know that all these terms are correlated by certain laws like Boyle’s law, Charles’s law and Avogadro’s law. By using these three ideal gas equations were given.
Ideal gas equation: PV=nRT
Where, P=pressure
V=volume
n=number of moles
R=gas constant
T=temperature.
Complete answer:
Let us look at all the 3 laws in short and then come to the question.
Boyle’s law: Robert Boyle gave a law that states that pressure is inversely proportional to volume. That is $ P \propto \dfrac{1}{V} $ .
Charles’s law : Jacques Charles discovered that volume is directly proportional to temperature, that is $ V \propto T $ .
Avogadro’s law: Avogadro stated that volume is directly proportional to the number of moles of the compound. That is $ V \propto n $
Hence combined effect of these 3 laws gave the ideal gas equation:
$ V \propto \dfrac{{nT}}{P} $
Or, $ VP = RnT $
Where R is the gas constant (universal constant).It has various values based on units,
$ R = 8.3145Jmo{l^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}} $ or,
$ R = 0.082L.atm.mo{l^{ - 1}}.{K^{ - 1}} $
Hence we see that according to ideal gas equation,
$ PV = nRT $ , observe this equation, we see that R and n are constants. Now according to the question it has been given that temperature is constant , thus the R.H.S of the equation becomes constant.
Hence : PV=constant
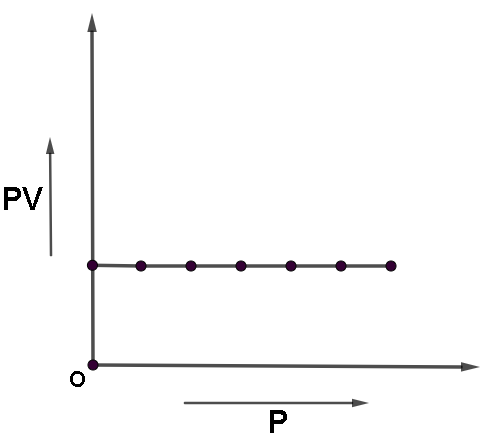
Let us now plot PV against P,
And take temperature constant
Hence we will get a straight line parallel to the x axis.
Note:
Note that temperature has been kept constant the line will be parallel to x-axis(P) and not y (PV). This is because PV here is taken as y axis. It means y=constant. And a graph for y=constant is always parallel to the x axis.
Ideal gas equation: PV=nRT
Where, P=pressure
V=volume
n=number of moles
R=gas constant
T=temperature.
Complete answer:
Let us look at all the 3 laws in short and then come to the question.
Boyle’s law: Robert Boyle gave a law that states that pressure is inversely proportional to volume. That is $ P \propto \dfrac{1}{V} $ .
Charles’s law : Jacques Charles discovered that volume is directly proportional to temperature, that is $ V \propto T $ .
Avogadro’s law: Avogadro stated that volume is directly proportional to the number of moles of the compound. That is $ V \propto n $
Hence combined effect of these 3 laws gave the ideal gas equation:
$ V \propto \dfrac{{nT}}{P} $
Or, $ VP = RnT $
Where R is the gas constant (universal constant).It has various values based on units,
$ R = 8.3145Jmo{l^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}} $ or,
$ R = 0.082L.atm.mo{l^{ - 1}}.{K^{ - 1}} $
Hence we see that according to ideal gas equation,
$ PV = nRT $ , observe this equation, we see that R and n are constants. Now according to the question it has been given that temperature is constant , thus the R.H.S of the equation becomes constant.
Hence : PV=constant

Let us now plot PV against P,
And take temperature constant
Hence we will get a straight line parallel to the x axis.
Note:
Note that temperature has been kept constant the line will be parallel to x-axis(P) and not y (PV). This is because PV here is taken as y axis. It means y=constant. And a graph for y=constant is always parallel to the x axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




