
What type of lever is the seesaw ?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, we will be brushing up some basic concepts related to the lever. We will also be classifying the different types of levers.A lever is the simplest of the machines made. A lever can be demonstrated as a simple machine which consists of a beam or a rigid rod which is pivoted at a fixed hinge or a fulcrum.
Complete step by step answer:
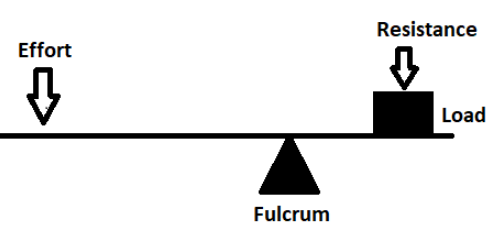
As we can see from the above figure, there are three basic parts in all levers. They are the fulcrum, a force or effort and a resistance. The force or effort and the resistance can be considered on either side of the fulcrum in the above figure.
Now, we will be looking at the types of levers. The levers can be classified on the basis of the relative position of the fulcrum, effort and the resistance. According to this, levers are classified into three types: the first class lever, the second class lever and the third class lever.
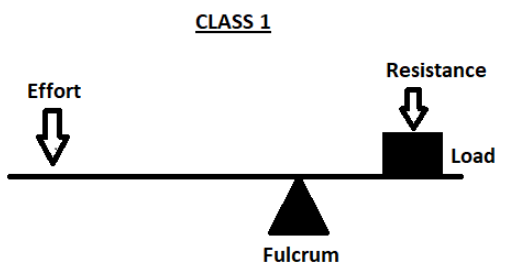
First class lever: In the first class lever, the fulcrum is placed in between the effort and the resistance. The similarity is shown in the above figure.
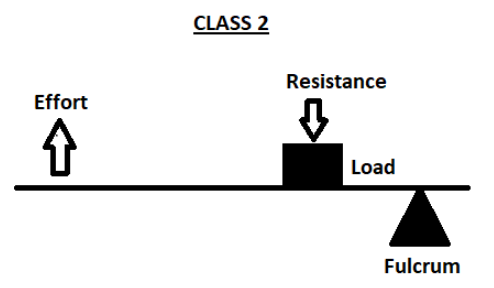
Second class lever: In the second class lever, the fulcrum is placed at one end and the effort is applied at the other end. The resistance is located somewhere in between these two.
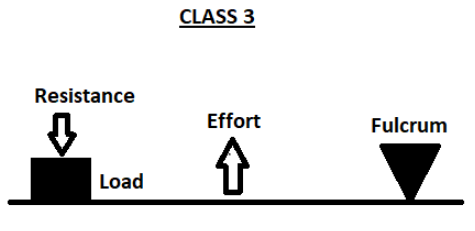
Third class lever: In the third class lever, the fulcrum is placed at one end and the resistance is located at the other end. The effort in this type of lever, is applied at some point in between the fulcrum and the resistance.
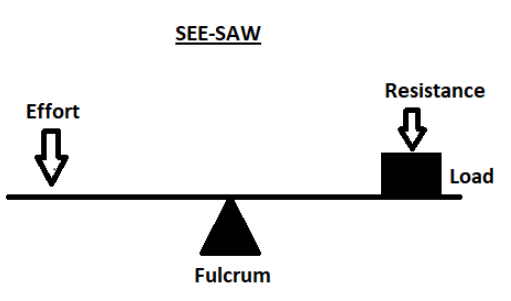
Based on the data we described about a lever, we can now easily classify that a seesaw is a special case of the first class lever where the fulcrum is placed in between the effort and the resistance.
Note:We have to note here that a seesaw is a case of the first class lever. The fulcrum can be placed anywhere in between the effort and the resistance in a first class lever.Crowbars, shears and pliers are also a good example of this class of levers.
Complete step by step answer:

As we can see from the above figure, there are three basic parts in all levers. They are the fulcrum, a force or effort and a resistance. The force or effort and the resistance can be considered on either side of the fulcrum in the above figure.
Now, we will be looking at the types of levers. The levers can be classified on the basis of the relative position of the fulcrum, effort and the resistance. According to this, levers are classified into three types: the first class lever, the second class lever and the third class lever.



First class lever: In the first class lever, the fulcrum is placed in between the effort and the resistance. The similarity is shown in the above figure.
Second class lever: In the second class lever, the fulcrum is placed at one end and the effort is applied at the other end. The resistance is located somewhere in between these two.
Third class lever: In the third class lever, the fulcrum is placed at one end and the resistance is located at the other end. The effort in this type of lever, is applied at some point in between the fulcrum and the resistance.

Based on the data we described about a lever, we can now easily classify that a seesaw is a special case of the first class lever where the fulcrum is placed in between the effort and the resistance.
Note:We have to note here that a seesaw is a case of the first class lever. The fulcrum can be placed anywhere in between the effort and the resistance in a first class lever.Crowbars, shears and pliers are also a good example of this class of levers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




