
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer
576k+ views
Hint:Xylem is a specialised tissue found in vascular plants that transports water and nutrients from the roots to stems and leaves. It also provides mechanical support and storage. In its transitional stages, the plants with secondary growth usually contain a vascular bundle with primary xylem only.
Complete step by step answer:
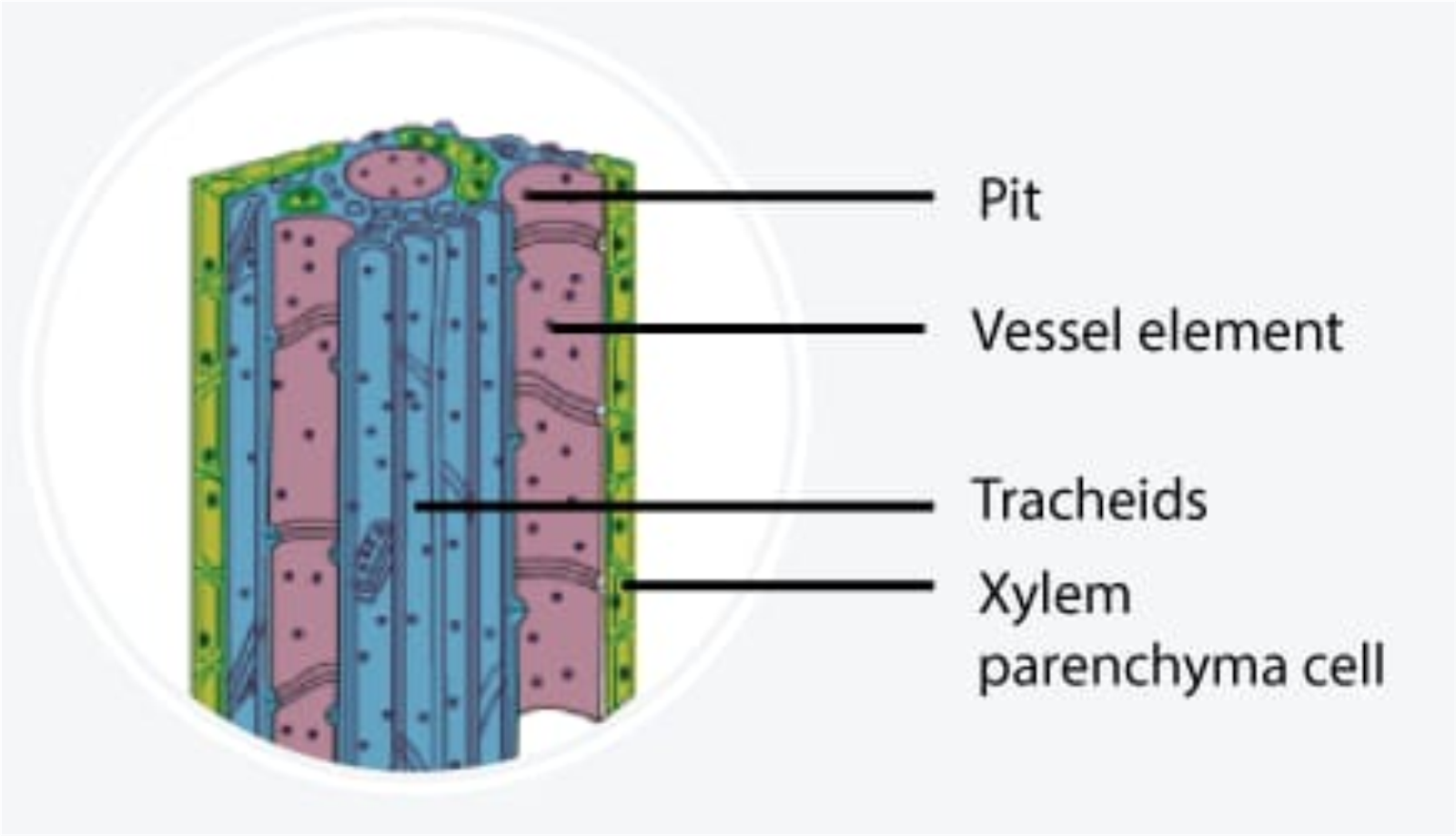
Xylem comprises of four different kinds of elements:
Tracheids: These are dead, tube-like cells with a tapering end.
Vessels: These are present in angiosperms.
Xylem Fibre: These are dead cells with lignified walls and a central lumen.
Xylem Parenchyma: These are only living cells of xylem and store starch and fat.
Among these, the most distinctive xylem cells are long tracheary elements that transport water. Their definitive shapes distinguish tracheids and vessel elements. Vessel elements are shorter and are connected to form long tubes that are called vessels.
Xylem also has two other cell types: parenchyma and fibres.
Xylem can be found in:
Vascular bundles are present in non-woody plants and non-woody parts of woody plants.
Secondary xylem, it is laid down by a meristem called the vascular cambium in woody plants
In stelar arrangement which is not divided into bundles, as in some ferns.
The branching pattern in xylem follows Murray's law.
Additional Information:
Primary and secondary xylem:
Primary xylem: It is formed during the primary growth from procambium. It is composed of protoxylem and metaxylem. Metaxylem develops after protoxylem but before the secondary xylem. Metaxylem contains wider vessels and tracheids than in the protoxylem.
Secondary xylem: It is formed from vascular cambium during secondary growth. Secondary xylem is found in members of gymnosperm groups Gnetophyta and Ginkgophyta.
Note:
Xylem and phloem are the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. The primary function of xylem is to transport water from the roots to stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant. It also transports nutrients. The term "xylem" is derived from the Greek word xylon, which means wood. The best-known xylem tissue is wood, although it is found throughout a plant. Carl Nägeli first introduced the term in 1858.
Complete step by step answer:
Xylem comprises of four different kinds of elements:
Tracheids: These are dead, tube-like cells with a tapering end.
Vessels: These are present in angiosperms.
Xylem Fibre: These are dead cells with lignified walls and a central lumen.
Xylem Parenchyma: These are only living cells of xylem and store starch and fat.
Among these, the most distinctive xylem cells are long tracheary elements that transport water. Their definitive shapes distinguish tracheids and vessel elements. Vessel elements are shorter and are connected to form long tubes that are called vessels.
Xylem also has two other cell types: parenchyma and fibres.
Xylem can be found in:
Vascular bundles are present in non-woody plants and non-woody parts of woody plants.
Secondary xylem, it is laid down by a meristem called the vascular cambium in woody plants
In stelar arrangement which is not divided into bundles, as in some ferns.
The branching pattern in xylem follows Murray's law.

Additional Information:
Primary and secondary xylem:
Primary xylem: It is formed during the primary growth from procambium. It is composed of protoxylem and metaxylem. Metaxylem develops after protoxylem but before the secondary xylem. Metaxylem contains wider vessels and tracheids than in the protoxylem.
Secondary xylem: It is formed from vascular cambium during secondary growth. Secondary xylem is found in members of gymnosperm groups Gnetophyta and Ginkgophyta.
Note:
Xylem and phloem are the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. The primary function of xylem is to transport water from the roots to stems, leaves, and other parts of the plant. It also transports nutrients. The term "xylem" is derived from the Greek word xylon, which means wood. The best-known xylem tissue is wood, although it is found throughout a plant. Carl Nägeli first introduced the term in 1858.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




