
What types of organisms were later placed in the kingdom Protista?
Answer
476.1k+ views
Hint: The six kingdom division includes Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Eubacteria, and Archaebacteria. Most of the Protists live in moist soil, water, and in the body of humans and plants as parasites. Amoeba, slime molds, giant kelp, and paramecium are kept under Protista. General characteristic features of kingdom Protista are the same as that of simple eukaryotic organisms like unicellular, colonial, and multicellular organisms like algae.
Complete answer
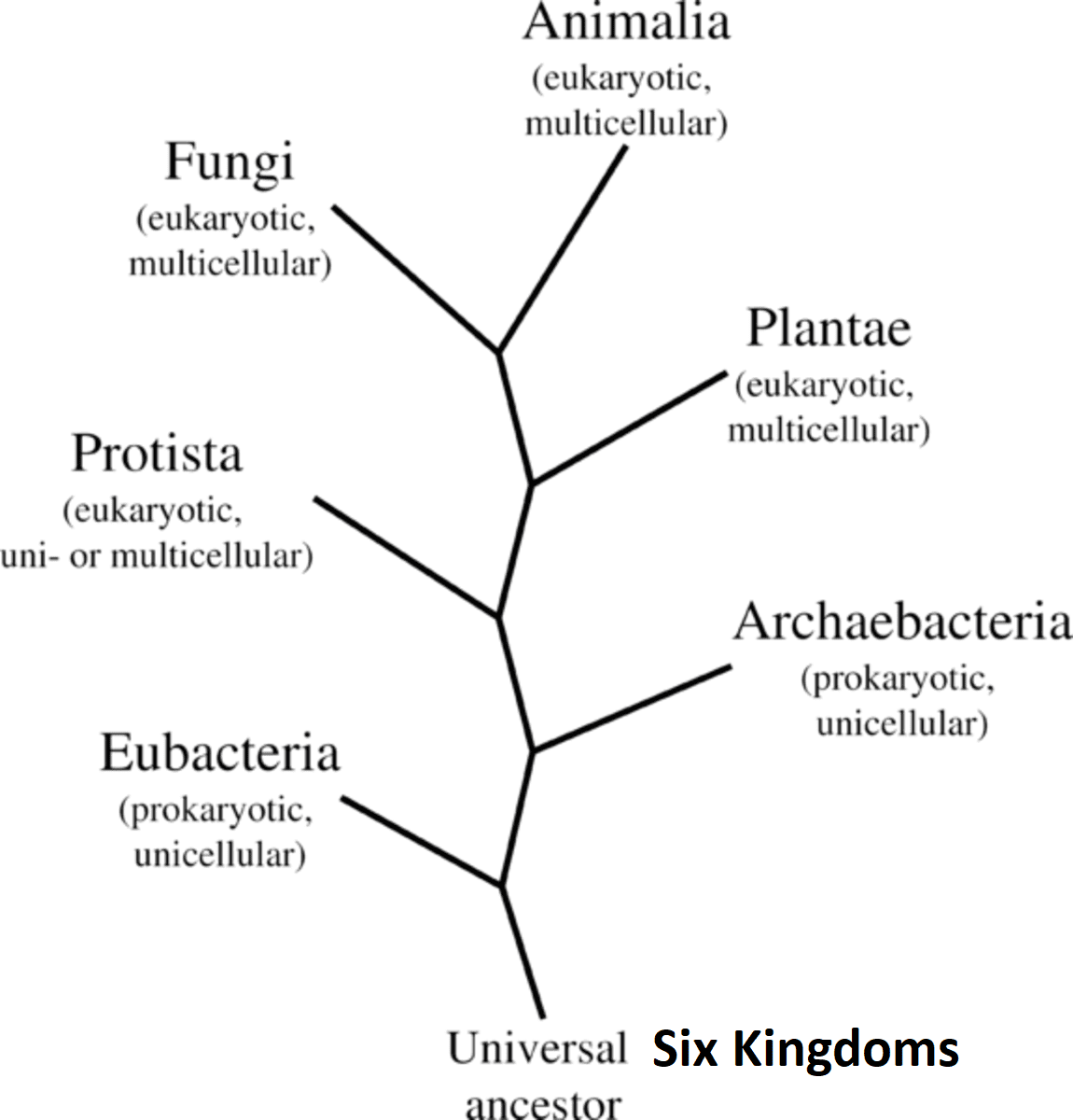
Fig.: Six Kingdom Classification
The classification system not only reflects physiological, morphological, and reproductive similarities but is also based on phylogenetic and evolutionary relationships. Microorganisms were later placed in the kingdom of Protista. Eukaryotic simple organisms are placed later in the kingdom. All single-celled eukaryotes are placed under the kingdom Protista, though the boundaries of the kingdom are not defined well. A photosynthetic protist to one biologist looks like a plant to another biologist. Protozoans, Euglenoids, Slime Moulds, Dinoflagellates, and Chrysophytes are generally placed under Protista.
The kingdom forms a link with other kingdoms' plants, fungi, and animals. The members of Protista are mainly aquatic. As a eukaryote, the cell body of the protist contains well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Some possess cilia or flagella. Protists reproduce sexually and asexually through the process of zygote formation and cell fusion respectively. The cell wall is present in some protists and absent in some organisms. The mode of nutrition is autotrophic in some organisms, while some protists undertake heterotrophic or non-photosynthetic nutrition.
Note:
Chlorella and Chlamydomonas possess cell walls and were placed within plants earlier. Amoeba and paramecium lack cell walls and were placed in the animal kingdom earlier. But the kingdom Protista has put together chlorella, Chlamydomonas, amoeba, and paramecium together. This occurred as the criteria for classification changed. Depending on the improvement in the understanding of evolutionary relationships and characteristics, these kinds of changes will happen in the future too.
Complete answer

Fig.: Six Kingdom Classification
The classification system not only reflects physiological, morphological, and reproductive similarities but is also based on phylogenetic and evolutionary relationships. Microorganisms were later placed in the kingdom of Protista. Eukaryotic simple organisms are placed later in the kingdom. All single-celled eukaryotes are placed under the kingdom Protista, though the boundaries of the kingdom are not defined well. A photosynthetic protist to one biologist looks like a plant to another biologist. Protozoans, Euglenoids, Slime Moulds, Dinoflagellates, and Chrysophytes are generally placed under Protista.
The kingdom forms a link with other kingdoms' plants, fungi, and animals. The members of Protista are mainly aquatic. As a eukaryote, the cell body of the protist contains well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Some possess cilia or flagella. Protists reproduce sexually and asexually through the process of zygote formation and cell fusion respectively. The cell wall is present in some protists and absent in some organisms. The mode of nutrition is autotrophic in some organisms, while some protists undertake heterotrophic or non-photosynthetic nutrition.
Note:
Chlorella and Chlamydomonas possess cell walls and were placed within plants earlier. Amoeba and paramecium lack cell walls and were placed in the animal kingdom earlier. But the kingdom Protista has put together chlorella, Chlamydomonas, amoeba, and paramecium together. This occurred as the criteria for classification changed. Depending on the improvement in the understanding of evolutionary relationships and characteristics, these kinds of changes will happen in the future too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




