
How many unpaired electrons are there in \[{\left[ {V{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\]?
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: In the question you are given the coordination complex of vanadium. First find out the oxidation state of the central metal atom. This will give you the idea about the excited state of vanadium and then use the molecular orbital theory to find out the number of the unpaired electron. Remember that water is a weak ligand so there will not be any pairing taking place.
Complete answer:
For finding the number of unpaired electrons in the above compound we will have to use the molecular orbital theory.
First let us find out the oxidation state of Vanadium in the complex \[{\left[ {V{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\].
In the complex water is a neutral ligand it does not have any charge and so the oxidation state of vanadium becomes $ + 3$. This means that 3 electrons will be deducted in the excited state of vanadium ${V^{ + 3}}$. It is known that the electronic configuration of vanadium is \[[Ar]3{d^3}4{s^2}\]. And so in the excited state the electronic configuration of vanadium ${V^{ + 3}}$ will be \[[Ar]3{d^2}4{s^0}\].
Now we will draw the molecular orbital theory to find out the number of unpaired electrons in the complex.
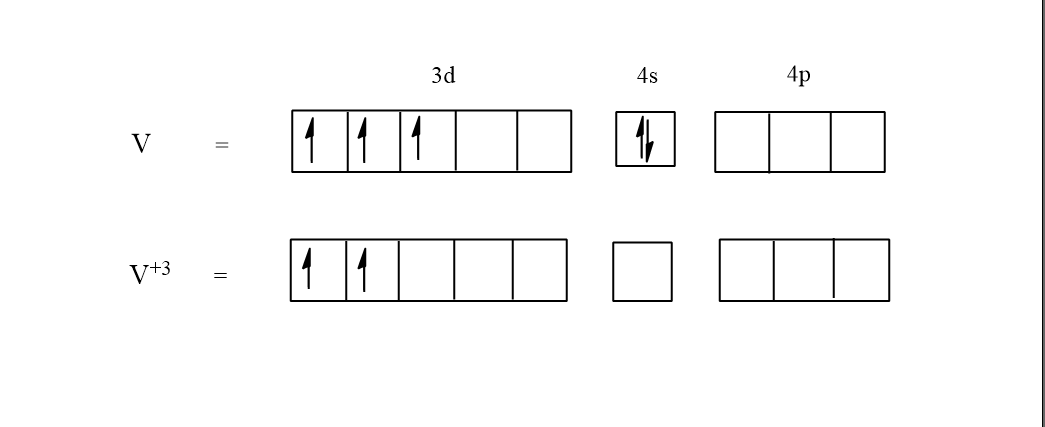
In the above molecular orbital theory, the normal state of the vanadium has $3$ electrons in the d orbital and $2$electrons in the s orbital. Here water is a weak ligand so there will not be any pairing of electrons taking place. In the excited state of vanadium $\left( {{V^{ + 3}}} \right)$, $3$ electrons are given out and so only $2$ electrons will be left in the d orbital.
Hence in the complex \[{\left[ {V{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] there are $2$ unpaired electrons.
Note:
water is a weak field ligand because the electronegative O atom is strongly electron-withdrawing, so there is poor orbital overlap between the electron pair on O and a metal d-orbital. But water can also act as a strong field ligand with $C{o^{ + 3}}$ and ions of ${2^{nd}}$ and ${3^{rd}}$ transition series.
Complete answer:
For finding the number of unpaired electrons in the above compound we will have to use the molecular orbital theory.
First let us find out the oxidation state of Vanadium in the complex \[{\left[ {V{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\].
In the complex water is a neutral ligand it does not have any charge and so the oxidation state of vanadium becomes $ + 3$. This means that 3 electrons will be deducted in the excited state of vanadium ${V^{ + 3}}$. It is known that the electronic configuration of vanadium is \[[Ar]3{d^3}4{s^2}\]. And so in the excited state the electronic configuration of vanadium ${V^{ + 3}}$ will be \[[Ar]3{d^2}4{s^0}\].
Now we will draw the molecular orbital theory to find out the number of unpaired electrons in the complex.

In the above molecular orbital theory, the normal state of the vanadium has $3$ electrons in the d orbital and $2$electrons in the s orbital. Here water is a weak ligand so there will not be any pairing of electrons taking place. In the excited state of vanadium $\left( {{V^{ + 3}}} \right)$, $3$ electrons are given out and so only $2$ electrons will be left in the d orbital.
Hence in the complex \[{\left[ {V{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}\] there are $2$ unpaired electrons.
Note:
water is a weak field ligand because the electronegative O atom is strongly electron-withdrawing, so there is poor orbital overlap between the electron pair on O and a metal d-orbital. But water can also act as a strong field ligand with $C{o^{ + 3}}$ and ions of ${2^{nd}}$ and ${3^{rd}}$ transition series.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




