
What is the use of the kelvin double bridge?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint:Low resistance is defined as resistance that is less than or equal to $1\Omega $. Machine armature windings, cables, and ammeter shunts, for example, have a low resistance value.
The Kelvin double bridge is ideally suited for measuring extremely low resistances.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Kelvin's double bridge was used to measure four-terminal low resistances with precision. The resistance of four-terminal resistors is equal to the stated nominal value across two current leading terminals and two potential terminals. This is because the current must enter and exit the resistor in such a way that the current density distribution between the several equipotential surfaces used to determine the resistance is the same or equal. Any contact resistance at the current lead-in terminals is also reduced by the new points.
Additional information:
Circuit Diagram:
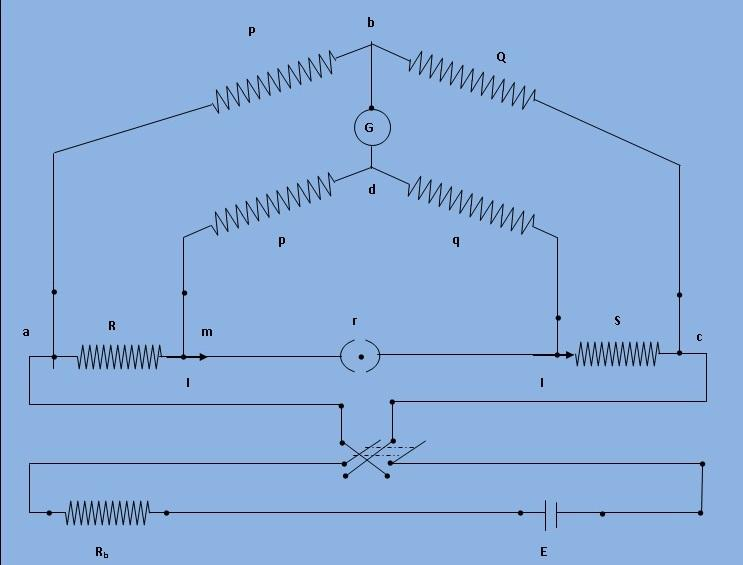
The kelvin double bridge has four terminal resistors for the low resistance arms and the second set of ratio arms (thus the name "double bridge"). The Kelvin bridge is depicted in Figure. P and Q represent the first ratio arms. To avoid the effect of connecting lead resistance r between the unknown resistance R and the standard resistance S, the second set of ratio arms p and q are employed to connect the galvanometer to a point d at the proper voltage between points m and n.
Note:
Advantages of Kelvin double bridge:
It can detect resistance values ranging from \[0.1\mu A\] to \[1.0{\text{ }}A\].
There is a reduction in the amount of energy used.
The construction is straightforward.
The level of sensitivity is really high.
The Kelvin double bridge is ideally suited for measuring extremely low resistances.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Kelvin's double bridge was used to measure four-terminal low resistances with precision. The resistance of four-terminal resistors is equal to the stated nominal value across two current leading terminals and two potential terminals. This is because the current must enter and exit the resistor in such a way that the current density distribution between the several equipotential surfaces used to determine the resistance is the same or equal. Any contact resistance at the current lead-in terminals is also reduced by the new points.
Additional information:
Circuit Diagram:

The kelvin double bridge has four terminal resistors for the low resistance arms and the second set of ratio arms (thus the name "double bridge"). The Kelvin bridge is depicted in Figure. P and Q represent the first ratio arms. To avoid the effect of connecting lead resistance r between the unknown resistance R and the standard resistance S, the second set of ratio arms p and q are employed to connect the galvanometer to a point d at the proper voltage between points m and n.
Note:
Advantages of Kelvin double bridge:
It can detect resistance values ranging from \[0.1\mu A\] to \[1.0{\text{ }}A\].
There is a reduction in the amount of energy used.
The construction is straightforward.
The level of sensitivity is really high.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




