
What is used, produced, and accomplished by the Calvin-Benson cycle?
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The Calvin cycle or Calvin-Benson cycle is a metabolic pathway by which carbon dioxide is combined into carbohydrates. The plants used Calvin cycle to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into sugars. The cycle consists of chemical reactions which depend indirectly on light, but not directly.
Complete answer:
The Calvin cycle consists of three stages. Every organism on the Earth is dependent on Calvin cycle, plants are directly dependent on it whereas other organisms depend indirectly upon Calvin cycle.
The plants and algae use Calvin cycle to produce their food by converting atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbohydrates, basically sugars. It is one of the parts of photosynthesis and included in dark reactions of photosynthesis. The Calvin cycle is said to be light independent as energy carriers ATP and NADPH are produced during light dependent reactions. These energy carriers act as fuel for producing sugars during the Calvin cycle.
The site for Calvin cycle is stroma in the chloroplast of a plant cell. It is the same site where carbon dioxide diffuses, which enters into plants through tiny pores on leafs named as stomata. The Calvin cycle is a series of chemical reactions, which are divided into three stages, namely carbon fixation, reduction and regeneration.
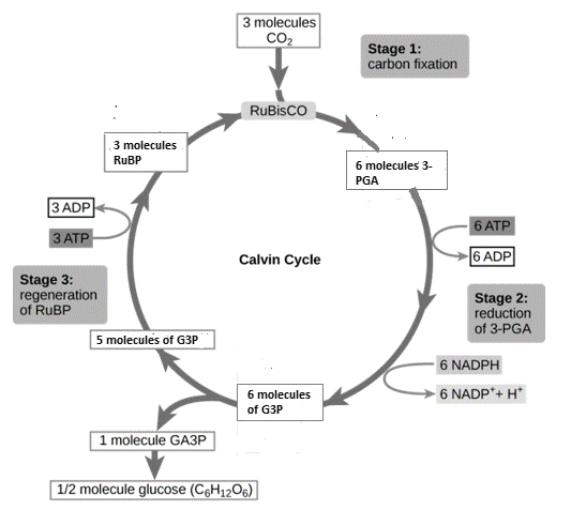
In the first step of carbon fixation, the reaction between carbon dioxide and ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) occurs in presence of catalyst ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCo). Here, RuBP is a molecule consisting of 5 carbon atoms and 2 phosphate groups whereas, RuBisCo is an enzyme. For each carbon dioxide molecule reacting with RuBP, 2 molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA) form. Each turn of the step 1 in the Calvin cycle involves a reaction between only one molecule each of carbon dioxide and RuBP. This step is referred to as the carbon fixation step because atmospheric carbon is fixed from its inorganic form to organic form.
In step of reduction, the conversion of 6 molecules of into 6 molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) occurs. This step is a reduction step as 3-PGA gains electrons from NADPH. The second stage of the Calvin cycle uses energy from ATP and NADPH. The ATP molecule is converted to Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) by losing its one of the phosphate groups. The NADPH molecule loses both hydrogen atom and electrons and gets converted into $NAD{P^ + }$. Both ADP and $NAD{P^ + }$molecules are then reused in other light-dependent reactions.
In the third step of the Calvin cycle that is regeneration, one of the molecules of G3P leaves the Calvin cycle to produce glucose molecules, while the rest of G3P molecules contribute in the formation of RuBP so that the process of carbon fixation can continue further. As glucose, a carbohydrate with chemical formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ contains six carbon atoms, the Calvin cycle must be repeated 6 times in order to create a single molecule of glucose. Also, the regeneration process is quite complex and it requires 3 ATP molecules. Given below is the schematic diagram for Calvin cycle.
Note: As we are aware of the fact that, during photosynthesis energy from the sunlight is used up by plants to produce their food. Photosynthesis occurs in two stages in a cell, light dependent reactions and light independent reactions. In the first stage of light-dependent reactions, energy from sunlight is captured to produce energy carrier molecules ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle then utilizes energy from molecules of ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds by light-independent reactions. These organic compounds are used as food by other organisms.
Complete answer:
The Calvin cycle consists of three stages. Every organism on the Earth is dependent on Calvin cycle, plants are directly dependent on it whereas other organisms depend indirectly upon Calvin cycle.
The plants and algae use Calvin cycle to produce their food by converting atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbohydrates, basically sugars. It is one of the parts of photosynthesis and included in dark reactions of photosynthesis. The Calvin cycle is said to be light independent as energy carriers ATP and NADPH are produced during light dependent reactions. These energy carriers act as fuel for producing sugars during the Calvin cycle.
The site for Calvin cycle is stroma in the chloroplast of a plant cell. It is the same site where carbon dioxide diffuses, which enters into plants through tiny pores on leafs named as stomata. The Calvin cycle is a series of chemical reactions, which are divided into three stages, namely carbon fixation, reduction and regeneration.
In the first step of carbon fixation, the reaction between carbon dioxide and ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) occurs in presence of catalyst ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCo). Here, RuBP is a molecule consisting of 5 carbon atoms and 2 phosphate groups whereas, RuBisCo is an enzyme. For each carbon dioxide molecule reacting with RuBP, 2 molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA) form. Each turn of the step 1 in the Calvin cycle involves a reaction between only one molecule each of carbon dioxide and RuBP. This step is referred to as the carbon fixation step because atmospheric carbon is fixed from its inorganic form to organic form.
In step of reduction, the conversion of 6 molecules of into 6 molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) occurs. This step is a reduction step as 3-PGA gains electrons from NADPH. The second stage of the Calvin cycle uses energy from ATP and NADPH. The ATP molecule is converted to Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) by losing its one of the phosphate groups. The NADPH molecule loses both hydrogen atom and electrons and gets converted into $NAD{P^ + }$. Both ADP and $NAD{P^ + }$molecules are then reused in other light-dependent reactions.
In the third step of the Calvin cycle that is regeneration, one of the molecules of G3P leaves the Calvin cycle to produce glucose molecules, while the rest of G3P molecules contribute in the formation of RuBP so that the process of carbon fixation can continue further. As glucose, a carbohydrate with chemical formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$ contains six carbon atoms, the Calvin cycle must be repeated 6 times in order to create a single molecule of glucose. Also, the regeneration process is quite complex and it requires 3 ATP molecules. Given below is the schematic diagram for Calvin cycle.

Note: As we are aware of the fact that, during photosynthesis energy from the sunlight is used up by plants to produce their food. Photosynthesis occurs in two stages in a cell, light dependent reactions and light independent reactions. In the first stage of light-dependent reactions, energy from sunlight is captured to produce energy carrier molecules ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle then utilizes energy from molecules of ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds by light-independent reactions. These organic compounds are used as food by other organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




