
Vascular bundles in dicot stems are:
(a)Open, collateral, endarch
(b)Closed, collateral, endarch
(c)Open, collateral, exarch
(d)Closed, collateral, exarch
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Vascular bundles are a collection of tube-like tissues that flow through plants and are a part of the transport system, transporting critical substances to various parts of the plant. The vascular bundle consists of two forms: xylem and phloem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Xylem transports water and nutrients and phloem transports organic molecules, these, in addition, will include supporting and protective tissues, phloem on the outer surface, and xylem on the inside. Because of the presence of cambium the vascular bundles of dicot stem are open. In the dicot stem, vascular bundles are arranged in a ring around the pith and the pith is concentrated at the core of the stem.
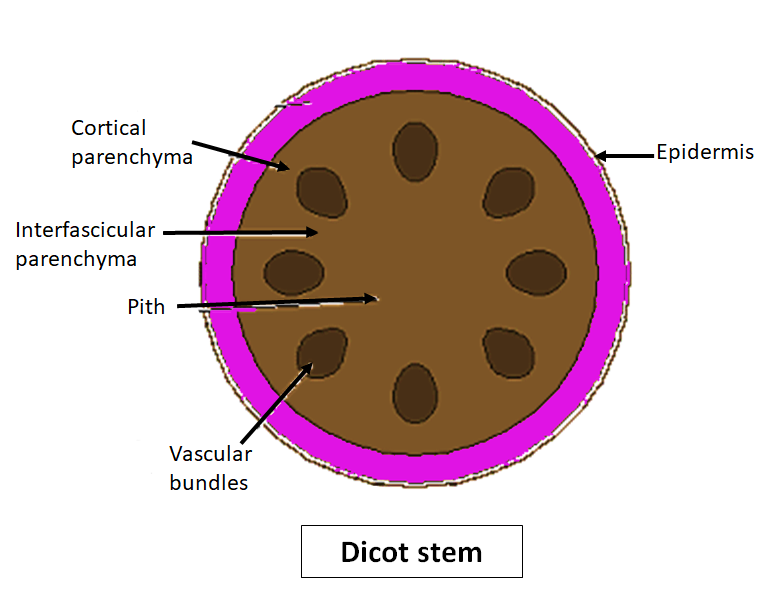
Xylem is described as an endarch and is used when there is more than one strand of primary xylem in a stem or root. The xylem develops from the inside towards the periphery, i.e., centrifugally. The protoxylem is closest to the center of the stem or root and the metaxylem closest to the periphery of the stem. The stems of dicot plants typically have endarch development and the roots are normally considered to have exarch development. Closed vascular bundles are present in monocots as they lack cambium. Vascular bundles in monocot stems are closed, collateral, and endarch.
So, the correct answer is ‘open, collateral, endarch’.
Note: The stems of dicot plants have a well-defined epidermis with a cuticle, a layer of dermis along with multicellular stem hair. Examples are sunflower and Cucurbita. Cambium separates xylem and phloem, and all the tissue from the cambium layer outward is considered bark, while all the tissue inside the cambium layer to the center of the tree is wood.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Xylem transports water and nutrients and phloem transports organic molecules, these, in addition, will include supporting and protective tissues, phloem on the outer surface, and xylem on the inside. Because of the presence of cambium the vascular bundles of dicot stem are open. In the dicot stem, vascular bundles are arranged in a ring around the pith and the pith is concentrated at the core of the stem.

Xylem is described as an endarch and is used when there is more than one strand of primary xylem in a stem or root. The xylem develops from the inside towards the periphery, i.e., centrifugally. The protoxylem is closest to the center of the stem or root and the metaxylem closest to the periphery of the stem. The stems of dicot plants typically have endarch development and the roots are normally considered to have exarch development. Closed vascular bundles are present in monocots as they lack cambium. Vascular bundles in monocot stems are closed, collateral, and endarch.
So, the correct answer is ‘open, collateral, endarch’.
Note: The stems of dicot plants have a well-defined epidermis with a cuticle, a layer of dermis along with multicellular stem hair. Examples are sunflower and Cucurbita. Cambium separates xylem and phloem, and all the tissue from the cambium layer outward is considered bark, while all the tissue inside the cambium layer to the center of the tree is wood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




