
Vegetative propagation refers to the formation of new plants from
(a) Stems, roots, and leaves
(b) Leaves, flowers, and seeds
(c) Stems, roots, and seeds
(d) Fruits, seeds, and spores
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: It is an asexual method of plant reproduction that occurs in its leaves, roots, and stem. This can happen through fragmentation and recovery of particular vegetative pieces of plants. The new plant is framed from the unusual roots creating from the cutting.
Complete answer:
The Vegetative propagation happens with the help of vegetative parts like root, stem, leaves. Blossoms are intended for sexual propagation in angiosperms.
Additional information: Different types of vegetative propagation include:
Natural Vegetative Propagation
This occurs when plants grow and develop naturally with none human interference. Natural vegetative propagation is often enabled by the event of adventitious roots. Consequently, new plants may rise up out of the roots, stem, and leaves of the parent plant.
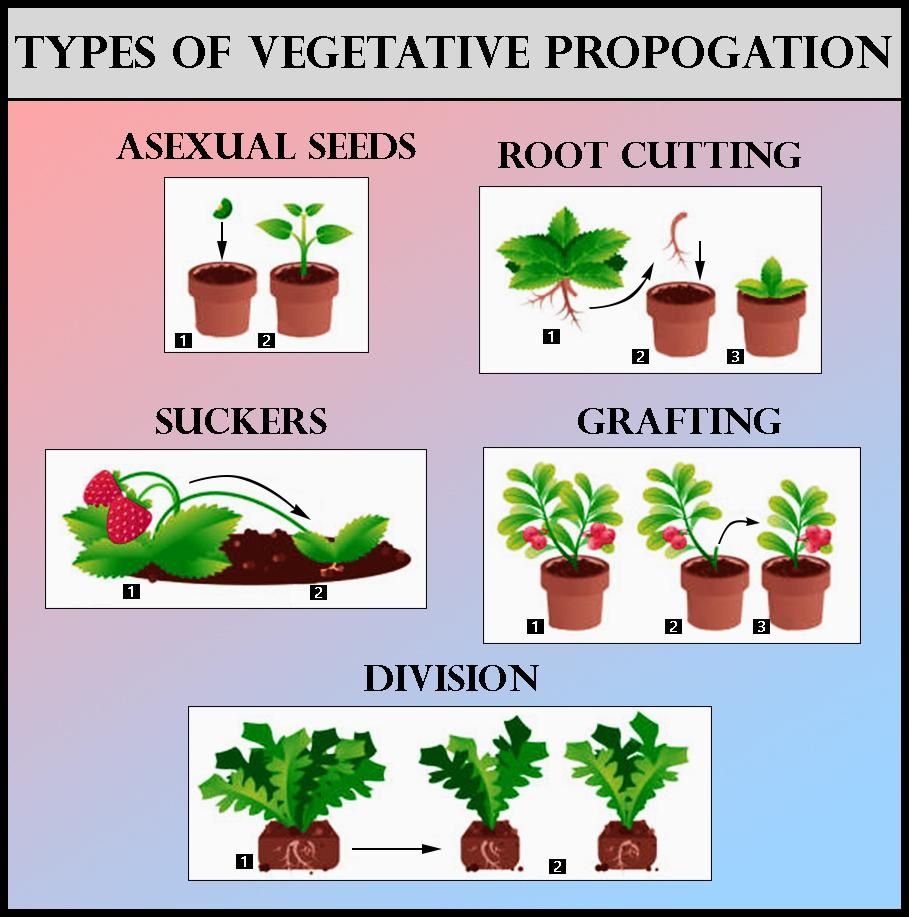
The vegetative plant structures emerging from the stem are alluded to as rhizomes, bulbs, sprinters, tubers, and so forth. The plants proliferated vegetatively are given below:
Stem
Runners grow horizontally above the ground. At the nodes of the runners, the buds are formed.
Roots
New plants emerge out of swollen, modified roots referred to as tubers. At the base of the stem, the formation of bud takes place.
Leaves
Leaves of a couple of plants get detached from the parent plant and become a replacement plant.
Bulbs
Bulbs have an underground stem to which the leaves are connected. These leaves are capable of storing food. The center of the bulb contains an apical bud that produces leaves and flowers. With the help of lateral buds, shoots are formed.
Artificial Vegetative Propagation
In the fields and laboratories, artificial vegetative reproduction carried out by humans.
So the correct answer is ‘(a) Stems, roots, and leaves’.
Note: In grafting, the cutting from some other plant is attached to the stem of the plant rooted in the ground. The tissues of the graft become coordinated with the tissues of the established plant and create a solitary plant over a long time.
In layering, the stem of the plant is bent to the ground and covered with soil. Adventitious roots arise out of the plant parts covered with the soil. This attached stem with developing roots is understood as a layer.
Complete answer:
The Vegetative propagation happens with the help of vegetative parts like root, stem, leaves. Blossoms are intended for sexual propagation in angiosperms.
Additional information: Different types of vegetative propagation include:
Natural Vegetative Propagation
This occurs when plants grow and develop naturally with none human interference. Natural vegetative propagation is often enabled by the event of adventitious roots. Consequently, new plants may rise up out of the roots, stem, and leaves of the parent plant.

The vegetative plant structures emerging from the stem are alluded to as rhizomes, bulbs, sprinters, tubers, and so forth. The plants proliferated vegetatively are given below:
Stem
Runners grow horizontally above the ground. At the nodes of the runners, the buds are formed.
Roots
New plants emerge out of swollen, modified roots referred to as tubers. At the base of the stem, the formation of bud takes place.
Leaves
Leaves of a couple of plants get detached from the parent plant and become a replacement plant.
Bulbs
Bulbs have an underground stem to which the leaves are connected. These leaves are capable of storing food. The center of the bulb contains an apical bud that produces leaves and flowers. With the help of lateral buds, shoots are formed.
Artificial Vegetative Propagation
In the fields and laboratories, artificial vegetative reproduction carried out by humans.
So the correct answer is ‘(a) Stems, roots, and leaves’.
Note: In grafting, the cutting from some other plant is attached to the stem of the plant rooted in the ground. The tissues of the graft become coordinated with the tissues of the established plant and create a solitary plant over a long time.
In layering, the stem of the plant is bent to the ground and covered with soil. Adventitious roots arise out of the plant parts covered with the soil. This attached stem with developing roots is understood as a layer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




