
When the velocity of a satellite increases, its kinetic energy increases. The satellite revolves in an orbit of.
A. Smaller radius
B. Longer radius
C. Same radius
D. Data insufficient
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: A satellite possesses potential as well as kinetic energy. Both the energies can be added up to form a single term. This single term provides a relation between the velocity of the satellite and its orbital radius. Using this expression, we can find the relation between the net energy and radius.
Formula used:
$U=-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{0}}^{2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us suppose a satellite of mass ‘m’ revolving around a planet, of mass M and radius R, at a distance of r from its centre with an orbital velocity of ${{v}_{0}}$
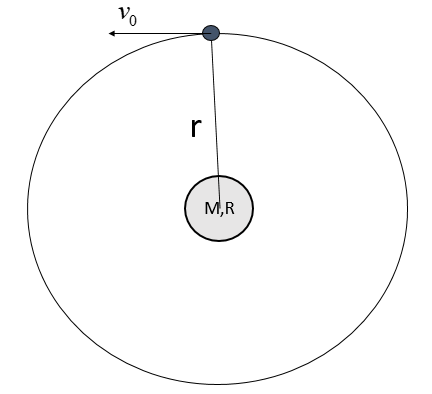
Here, we know that,
The Potential energy of Satellite = $-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$ --- (i)
The Kinetic energy of Satellite = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{0}}^{2}$ ---(ii)
Hence,
Total energy of satellite = potential energy + kinetic energy
= $-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$ + $\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{0}}^{2}$
We know, the orbital velocity of a satellite is given by: ${{v}_{0}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{GM}{r}}$
Putting this value in above equation, we get:
Total energy of satellite = $-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$ + $\dfrac{1}{2}m\dfrac{GM}{r}$
= $-\dfrac{GMm}{2r}$ ----(iii)
Clearly, it can be seen that with the increase in the velocity of the satellite, its kinetic energy increases. This increased kinetic energy when added to potential energy, decreases the total energy of the satellite (magnitude).
Here, $G,M,m$ are constants. Hence, it can be seen that the total energy is inversely proportional to the radius of the orbit, i.e.,
Total energy = $\dfrac{\text{Constant}}{r}$ ---(iv)
Hence, as we increase the velocity of a satellite, its total energy (magnitude) decreases. And from equation (iv) it can be seen that total energy is inversely proportional to the radius.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Satellites are objects travelling at speeds more than 27000 kmph. Global Positioning system (GPS), are a group of more than 20 satellites that helps us detect the precise location of an object.
Note:
Whenever you want to compare the total energy with any of its parameters, always take the magnitude of the expression before comparison. This will eliminate the negative sign and avoid any type of confusion. Further we can assume other parameters, which we are not comparing, as constants and hence create a proportionality relation between the required parameters.
Formula used:
$U=-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{0}}^{2}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let us suppose a satellite of mass ‘m’ revolving around a planet, of mass M and radius R, at a distance of r from its centre with an orbital velocity of ${{v}_{0}}$

Here, we know that,
The Potential energy of Satellite = $-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$ --- (i)
The Kinetic energy of Satellite = $\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{0}}^{2}$ ---(ii)
Hence,
Total energy of satellite = potential energy + kinetic energy
= $-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$ + $\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}_{0}}^{2}$
We know, the orbital velocity of a satellite is given by: ${{v}_{0}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{GM}{r}}$
Putting this value in above equation, we get:
Total energy of satellite = $-\dfrac{GMm}{r}$ + $\dfrac{1}{2}m\dfrac{GM}{r}$
= $-\dfrac{GMm}{2r}$ ----(iii)
Clearly, it can be seen that with the increase in the velocity of the satellite, its kinetic energy increases. This increased kinetic energy when added to potential energy, decreases the total energy of the satellite (magnitude).
Here, $G,M,m$ are constants. Hence, it can be seen that the total energy is inversely proportional to the radius of the orbit, i.e.,
Total energy = $\dfrac{\text{Constant}}{r}$ ---(iv)
Hence, as we increase the velocity of a satellite, its total energy (magnitude) decreases. And from equation (iv) it can be seen that total energy is inversely proportional to the radius.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Satellites are objects travelling at speeds more than 27000 kmph. Global Positioning system (GPS), are a group of more than 20 satellites that helps us detect the precise location of an object.
Note:
Whenever you want to compare the total energy with any of its parameters, always take the magnitude of the expression before comparison. This will eliminate the negative sign and avoid any type of confusion. Further we can assume other parameters, which we are not comparing, as constants and hence create a proportionality relation between the required parameters.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




