
What is the Vernier constant of a Vernier calliper.
Answer
527.3k+ views
Hint: The Vernier constant is something that is unique to a Vernier calliper, it is used in measurements.
Complete step by step answer:
A Vernier calliper is a measuring tool used to measure dimensions of a body like its width, height, radius etc… The Vernier scale on the main scale provides a more precise measurement compared to ordinary scale. Mechanical interpolation is the method used in the Vernier scale in order to improve measurements.
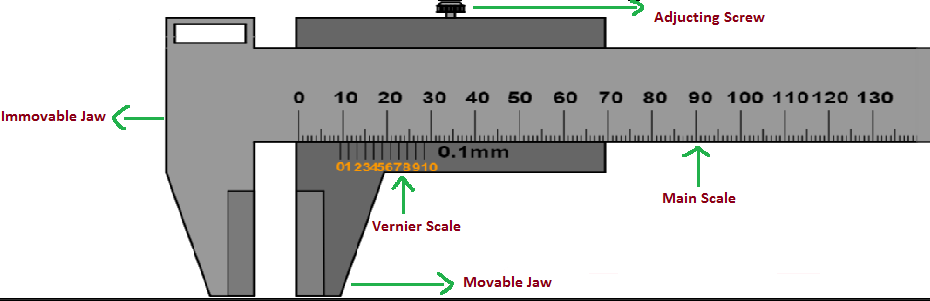
The Vernier constant is the least count of the Vernier callipers, it is defined as the difference between one main scale division and one Vernier scale division. So Vernier constant can be written as
$\text{Vernier Constant}=\text{One Main Scale Division (MSD)-One Vernier Scale Division (VSD)}$
Additional Information:
The modern Vernier calliper was invented by Joseph R. Brown in 1851. It was the first practical tool for exact measurements that could be sold at an affordable price to ordinary machinists. The Vernier Calliper consists of the main scale fitted with a jaw at one end. Another jaw, containing the vernier scale, moves over the main scale. When the two jaws are in contact, the zero of the main scale and the zero of the Vernier scale should coincide.
Note: The least count of the Vernier scale can also be found out by using the formula,
$\text{Least Count(LC)}=\dfrac{\text{One Main Scale Division}}{\text{Number divisions on the Vernier Scale}}$
There can be errors associated with the Vernier callipers when the main scale zero is not coinciding with Vernier scale zero when the jaws of the Vernier are in contact.
The errors can be positive or negative depending on the main scale zero coincidences with the point on the Vernier scale. The error correction in the final measurement is given by the formula,
$\text{Final Measurement}=\text{ Initial Measurement-Zero Error}$
Complete step by step answer:
A Vernier calliper is a measuring tool used to measure dimensions of a body like its width, height, radius etc… The Vernier scale on the main scale provides a more precise measurement compared to ordinary scale. Mechanical interpolation is the method used in the Vernier scale in order to improve measurements.

The Vernier constant is the least count of the Vernier callipers, it is defined as the difference between one main scale division and one Vernier scale division. So Vernier constant can be written as
$\text{Vernier Constant}=\text{One Main Scale Division (MSD)-One Vernier Scale Division (VSD)}$
Additional Information:
The modern Vernier calliper was invented by Joseph R. Brown in 1851. It was the first practical tool for exact measurements that could be sold at an affordable price to ordinary machinists. The Vernier Calliper consists of the main scale fitted with a jaw at one end. Another jaw, containing the vernier scale, moves over the main scale. When the two jaws are in contact, the zero of the main scale and the zero of the Vernier scale should coincide.
Note: The least count of the Vernier scale can also be found out by using the formula,
$\text{Least Count(LC)}=\dfrac{\text{One Main Scale Division}}{\text{Number divisions on the Vernier Scale}}$
There can be errors associated with the Vernier callipers when the main scale zero is not coinciding with Vernier scale zero when the jaws of the Vernier are in contact.
The errors can be positive or negative depending on the main scale zero coincidences with the point on the Vernier scale. The error correction in the final measurement is given by the formula,
$\text{Final Measurement}=\text{ Initial Measurement-Zero Error}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




