
Water absorption in root mainly takes place in which zone of root?
(a)Zone of elongation
(b)Root hair zone
(c)Root epidermis
(d)Maturation zone
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: These are tiny extensions of roots that help in keeping the plant firm and in the absorption of water and food. They are sometimes not visible to the naked eye. It is white in color and has very few meristematic cells.
Complete answer:
A single layer of Epiblema protects the roots. Root hairs are root epidermis extensions and are unicellular. To absorb water from the soil solution, the root hairs are specialized.
A tubular outgrowth of a trichoblast, a hair-forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root, is the root hair, or absorbent hair, the rhizoid of a vascular plant. They are visible to the naked eye and the light microscope since they are lateral extensions of a single cell and are rarely branched.
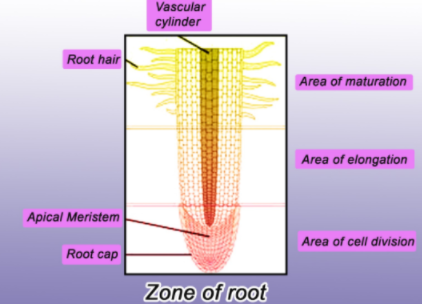
Additional Information: The elongation zone is where the length of the newly-formed cells increases, thereby lengthening the base. The zone of cell maturation where the root cells divide into specialized cell types starts with the first root hair. The apical meristem is separated by cells.
Hair and non-hair cells make up the epidermis of the roots. This epidermis patterning results from the spatially regulated differentiation of these types of cells. Genes with opposite functions have been identified in the production of shooting hair cells (trichomes) and root hair cells.
So, the correct answer is ‘root hair zone’.
Note: By having a large surface area to improve the rate of absorption, root hair cells are adapted to absorb water and mineral ions. They also contain loads of mitochondria, which, in order to provide the energy required for active transport, release energy from glucose during respiration.
Complete answer:
A single layer of Epiblema protects the roots. Root hairs are root epidermis extensions and are unicellular. To absorb water from the soil solution, the root hairs are specialized.
A tubular outgrowth of a trichoblast, a hair-forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root, is the root hair, or absorbent hair, the rhizoid of a vascular plant. They are visible to the naked eye and the light microscope since they are lateral extensions of a single cell and are rarely branched.
Additional Information: The elongation zone is where the length of the newly-formed cells increases, thereby lengthening the base. The zone of cell maturation where the root cells divide into specialized cell types starts with the first root hair. The apical meristem is separated by cells.
Hair and non-hair cells make up the epidermis of the roots. This epidermis patterning results from the spatially regulated differentiation of these types of cells. Genes with opposite functions have been identified in the production of shooting hair cells (trichomes) and root hair cells.
So, the correct answer is ‘root hair zone’.
Note: By having a large surface area to improve the rate of absorption, root hair cells are adapted to absorb water and mineral ions. They also contain loads of mitochondria, which, in order to provide the energy required for active transport, release energy from glucose during respiration.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




