
Water storage tissues have
(a) Large-sized thin-walled cells
(b) Mucilage
(c) Large-sized vacuoles
(d) All of the above
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: They are simple permanent tissues which make a major part of the ground tissues in plants and are embedded in the vascular tissues. They are of various types based on their location and functions differently.
Complete answer:
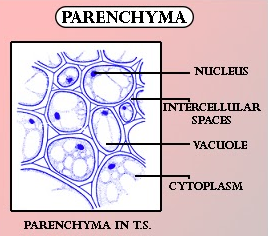
Parenchyma cells are relatively unspecified and thin-walled. The water storage tissue in desert plants are also parenchymatous cells named aquiferous parenchyma having a thin-walled, large-sized structure with a large vacuole inside it that helps them to store water. The vacuole or the cytoplasm contains the mucilage that helps them in increasing the capacity of the water retention or water storage.
Parenchyma is round or oval-shaped cells having spaces between them and they are simple tissues are tissues composed of cells that are structurally and functionally similar i.e. they are made up of the same type of cells. They are found in the leaves, stems, fruits, etc, and help in food storage. Chlorenchyma is the type of parenchyma that consists of chloroplast and helps during the process of photosynthesis. The aerenchyma is the type of parenchyma found in aquatic plants having large air spaces that helps them in floating. The parenchyma performs various functions that include photosynthesis, gaseous exchange, storage of food, etc. They are the main plant tissue that composes mostly the whole plant body.
Types of parenchyma:
There are four sorts of parenchyma consistent with their function:
-Photosynthetic parenchyma of camellia leaf.
-Storage parenchyma of the buttercup root cortex.
-Aquiferous parenchyma of a cactus.
-Aeriferous parenchyma of a rush stem.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note:
The parenchyma cells were discovered in the seventeenth century for the first time by Robert Hooke. The chloroplast is composed of the parenchyma cells that are composed of two parts, the outer part is called the cortex while the inner layer is the pith. The soft tissues of the fruits are also formed by the parenchyma cells.
Complete answer:
Parenchyma cells are relatively unspecified and thin-walled. The water storage tissue in desert plants are also parenchymatous cells named aquiferous parenchyma having a thin-walled, large-sized structure with a large vacuole inside it that helps them to store water. The vacuole or the cytoplasm contains the mucilage that helps them in increasing the capacity of the water retention or water storage.
Parenchyma is round or oval-shaped cells having spaces between them and they are simple tissues are tissues composed of cells that are structurally and functionally similar i.e. they are made up of the same type of cells. They are found in the leaves, stems, fruits, etc, and help in food storage. Chlorenchyma is the type of parenchyma that consists of chloroplast and helps during the process of photosynthesis. The aerenchyma is the type of parenchyma found in aquatic plants having large air spaces that helps them in floating. The parenchyma performs various functions that include photosynthesis, gaseous exchange, storage of food, etc. They are the main plant tissue that composes mostly the whole plant body.
Types of parenchyma:
There are four sorts of parenchyma consistent with their function:
-Photosynthetic parenchyma of camellia leaf.
-Storage parenchyma of the buttercup root cortex.
-Aquiferous parenchyma of a cactus.
-Aeriferous parenchyma of a rush stem.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.

Note:
The parenchyma cells were discovered in the seventeenth century for the first time by Robert Hooke. The chloroplast is composed of the parenchyma cells that are composed of two parts, the outer part is called the cortex while the inner layer is the pith. The soft tissues of the fruits are also formed by the parenchyma cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




