
Wharton’s duct is the duct of
(a)Parotid gland
(b)Submaxillary gland
(c)Submandibular salivary gland
(d)Both B and C
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: The gland is present in the side of the lower jaw bone and this gland is smaller than the other salivary glands that are found in the human oral cavity.
Complete answer:
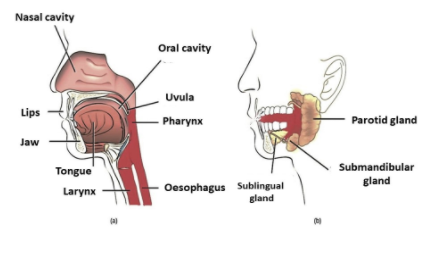
One of the salivary excretory ducts is the submandibular duct/ Wharton duct/submaxillary duct. It drains the saliva from each of the bilateral submandibular gland and sublingual gland to the sublingual caruncle present at the base of the tongue.
Additional Information: Human beings possess 3 major pairs of salivary glands that open into the mouth via the well-developed ducts.
Parotid gland: The parotid salivary gland is the largest gland amongst the other three glands. It is situated between the ear and the lower jaw’s ascending branch. Every gland has a major duct called Stensen’s duct which opens in the back of the mouth cavity.
submandibular gland: The second pair, the submaxillary glands/submandibular glands, is situated along the side of the lower jawbone. Wharton’s duct (major duct) opens into the mouth floor at the junction where the front of the tongue meets the floor of the mouth.
Sublingual gland: The third pair is called the sublingual glands, which is located beneath the mucous membrane of the mouth’s floor. Many ducts empty near the junction of the tongue and the floor of the mouth. Various ducts combine to form Bartholin’s duct. Bartholin is the major duct of the sublingual gland. It empties the saliva into or near the submaxillary duct. These glands secrete a mixed fluid that mainly consists of mucus.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Both B and C’.
Note: The saliva produced by the salivary gland mixes the food completely. Saliva possesses immunoglobulins and lysozymes which have antimicrobial activity and inhibits the growth of certain bacteria in our mouth. It has mucous that moistens the food and also buffers the food ph. Additionally, salivary amylase is abundantly present in the saliva. The salivary amylase converts the starch present in the food to simple disaccharide maltose sugar.
Complete answer:
One of the salivary excretory ducts is the submandibular duct/ Wharton duct/submaxillary duct. It drains the saliva from each of the bilateral submandibular gland and sublingual gland to the sublingual caruncle present at the base of the tongue.
Additional Information: Human beings possess 3 major pairs of salivary glands that open into the mouth via the well-developed ducts.
Parotid gland: The parotid salivary gland is the largest gland amongst the other three glands. It is situated between the ear and the lower jaw’s ascending branch. Every gland has a major duct called Stensen’s duct which opens in the back of the mouth cavity.
submandibular gland: The second pair, the submaxillary glands/submandibular glands, is situated along the side of the lower jawbone. Wharton’s duct (major duct) opens into the mouth floor at the junction where the front of the tongue meets the floor of the mouth.
Sublingual gland: The third pair is called the sublingual glands, which is located beneath the mucous membrane of the mouth’s floor. Many ducts empty near the junction of the tongue and the floor of the mouth. Various ducts combine to form Bartholin’s duct. Bartholin is the major duct of the sublingual gland. It empties the saliva into or near the submaxillary duct. These glands secrete a mixed fluid that mainly consists of mucus.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Both B and C’.
Note: The saliva produced by the salivary gland mixes the food completely. Saliva possesses immunoglobulins and lysozymes which have antimicrobial activity and inhibits the growth of certain bacteria in our mouth. It has mucous that moistens the food and also buffers the food ph. Additionally, salivary amylase is abundantly present in the saliva. The salivary amylase converts the starch present in the food to simple disaccharide maltose sugar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




