
What are septate hyphae?
Answer
499.8k+ views
Hint: Hyphae is the long filamentous structure of fungi. It is the means of vegetative growth in the case of fungi. The fungal hyphae can be septate or aseptate. The growth of the hyphae is regulated by the stimuli.
Complete answer:
The fungi are the eukaryotic organisms that have cell walls but do not produce their own food. They are heterotrophic in nature and obtain nutrition either through the saprophytic or parasitic mode of nutrition. The fungus body is not differentiated. It has a root-like structure called the hyphae and the body is called the thallus.
The function of the hyphae in the fungi is similar to that of the roots in the plants. They absorb the nutrients from the surroundings and transports them to the fungal body called the thallus. The hyphae contain the cytoplasm which has a definite nucleus and genetic material.
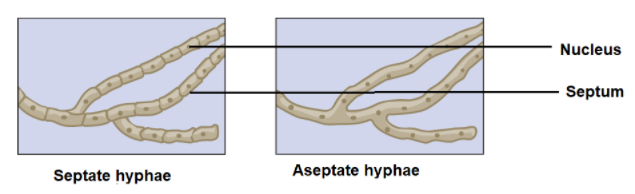
The hyphae are of two types-
1) Septate hyphae-In most of the fungi the hyphae are divided into cells with the help of internal walls. These are called the septum. The septa are porous walls that allow the organelles like ribosomes and mitochondria to move in between the cells.
2) Aseptate or coenocytic hyphae- The hyphae which do not have septum are called aseptate hyphae. They are multinuclear.
The advantage of the septa is that the fungi can close the septa in case of injury. This prevents the loss of fluid from the organism.
Note: The network of hyphae is known as mycelium. The fungal cell wall is made up of chitin. Basidiomycetes and Ascomycetes have septate hyphae. Fungi belonging to the class zygomycetes are aseptate.
Complete answer:
The fungi are the eukaryotic organisms that have cell walls but do not produce their own food. They are heterotrophic in nature and obtain nutrition either through the saprophytic or parasitic mode of nutrition. The fungus body is not differentiated. It has a root-like structure called the hyphae and the body is called the thallus.
The function of the hyphae in the fungi is similar to that of the roots in the plants. They absorb the nutrients from the surroundings and transports them to the fungal body called the thallus. The hyphae contain the cytoplasm which has a definite nucleus and genetic material.
The hyphae are of two types-
1) Septate hyphae-In most of the fungi the hyphae are divided into cells with the help of internal walls. These are called the septum. The septa are porous walls that allow the organelles like ribosomes and mitochondria to move in between the cells.
2) Aseptate or coenocytic hyphae- The hyphae which do not have septum are called aseptate hyphae. They are multinuclear.

The advantage of the septa is that the fungi can close the septa in case of injury. This prevents the loss of fluid from the organism.
Note: The network of hyphae is known as mycelium. The fungal cell wall is made up of chitin. Basidiomycetes and Ascomycetes have septate hyphae. Fungi belonging to the class zygomycetes are aseptate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




