
What are the five common acids?
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: Out of the five common acids, three of them are inorganic acids and they contain sulphur, chlorine and nitrogen respectively. The rest two are organic acids and one of them is found in citrus fruits while the other is found in vinegar.
Complete answer:
There are three main theories which define an acid. Let us know about the theories first then we will find out the five common acids.
- Arrhenius Theory: According to Arrhenius, any compounds which can donate a proton or ${{H}^{+}}$ ion in an aqueous solution can be considered as an acid. For example:
\[\underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{HCl}}\,\rightleftharpoons \underset{\text{Proton}}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,+C{{l}^{-}}\]
- Bronsted Lowry Theory- It can be considered to be the extended version of Arrhenius theory. According to this, any substance which and donate a proton or ${{H}^{+}}$ ion to form a conjugate base can be considered as an acid. The conjugate base can accept a proton to form the acid. For example,
\[\begin{align}
& \underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{HF}}\,\rightleftharpoons \underset{\text{Proton}}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,+\underset{\text{Conjugate base}}{\mathop{{{F}^{-}}}}\, \\
& \underset{\text{Conjugate base}}{\mathop{{{F}^{-}}}}\,+\underset{\text{Proton}}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,\rightleftharpoons \underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{HF}}\, \\
\end{align}\]
- Lewis Theory: According to this theory, any substance which can accept a pair of electrons can be considered to be acids. For example:
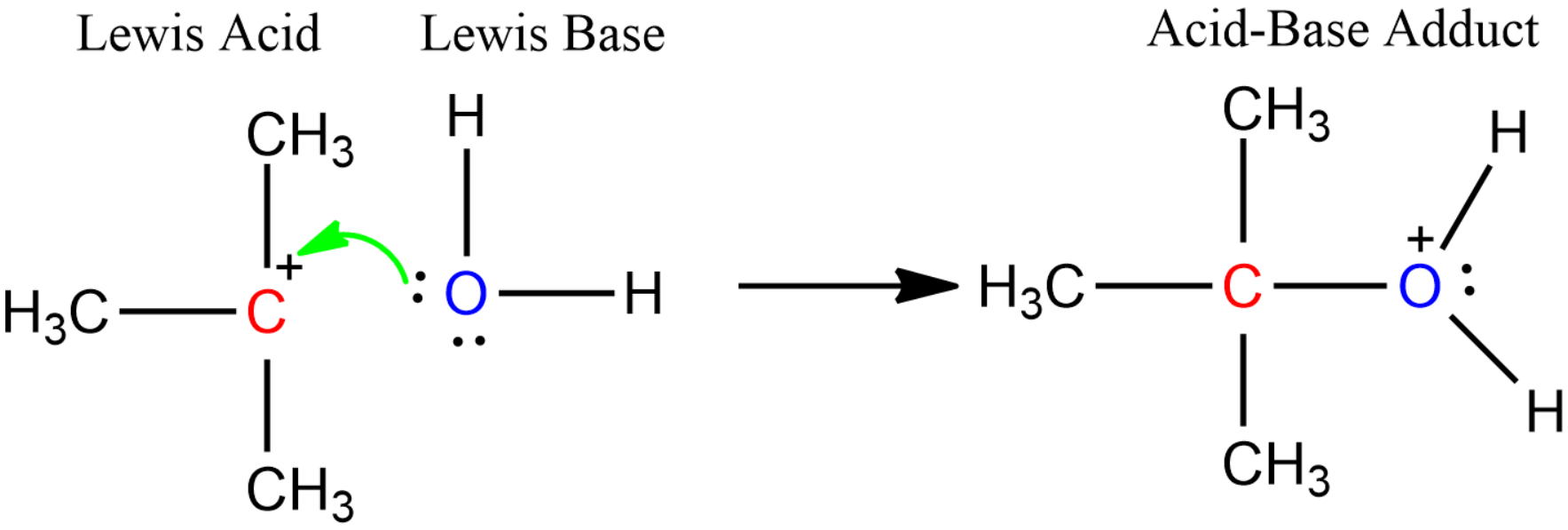
Among all these different theories of acid-base, the five common acids are: Sulphuric acid $\left( {{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} \right)$, Nitric acid $\left( HN{{O}_{3}} \right)$, Hydrochloric acid $\left( HCl \right)$, Acetic acid $\left( C{{H}_{3}}COOH \right)$ and Citric acid $\left( HOOC-C{{H}_{2}}-C(OH)COOH-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH \right)$
Sulphuric acid $\left( {{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} \right)$, Nitric acid $\left( HN{{O}_{3}} \right)$ and Hydrochloric acid $\left( HCl \right)$ are inorganic acids and they contain sulphur, chlorine and nitrogen respectively. Acetic acid $\left( C{{H}_{3}}COOH \right)$ and Citric acid $\left( HOOC-C{{H}_{2}}-C(OH)COOH-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH \right)$ are organic acids and the first one is found in vinegar while the second one is found in citrus fruits.
Note:
Acids are highly corrosive in nature. They can burn your skin and cause deep wounds. We should always handle acids with care and take protections while using them in the lab.
Complete answer:
There are three main theories which define an acid. Let us know about the theories first then we will find out the five common acids.
- Arrhenius Theory: According to Arrhenius, any compounds which can donate a proton or ${{H}^{+}}$ ion in an aqueous solution can be considered as an acid. For example:
\[\underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{HCl}}\,\rightleftharpoons \underset{\text{Proton}}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,+C{{l}^{-}}\]
- Bronsted Lowry Theory- It can be considered to be the extended version of Arrhenius theory. According to this, any substance which and donate a proton or ${{H}^{+}}$ ion to form a conjugate base can be considered as an acid. The conjugate base can accept a proton to form the acid. For example,
\[\begin{align}
& \underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{HF}}\,\rightleftharpoons \underset{\text{Proton}}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,+\underset{\text{Conjugate base}}{\mathop{{{F}^{-}}}}\, \\
& \underset{\text{Conjugate base}}{\mathop{{{F}^{-}}}}\,+\underset{\text{Proton}}{\mathop{{{H}^{+}}}}\,\rightleftharpoons \underset{\text{Acid}}{\mathop{HF}}\, \\
\end{align}\]
- Lewis Theory: According to this theory, any substance which can accept a pair of electrons can be considered to be acids. For example:

Among all these different theories of acid-base, the five common acids are: Sulphuric acid $\left( {{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} \right)$, Nitric acid $\left( HN{{O}_{3}} \right)$, Hydrochloric acid $\left( HCl \right)$, Acetic acid $\left( C{{H}_{3}}COOH \right)$ and Citric acid $\left( HOOC-C{{H}_{2}}-C(OH)COOH-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH \right)$
Sulphuric acid $\left( {{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} \right)$, Nitric acid $\left( HN{{O}_{3}} \right)$ and Hydrochloric acid $\left( HCl \right)$ are inorganic acids and they contain sulphur, chlorine and nitrogen respectively. Acetic acid $\left( C{{H}_{3}}COOH \right)$ and Citric acid $\left( HOOC-C{{H}_{2}}-C(OH)COOH-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH \right)$ are organic acids and the first one is found in vinegar while the second one is found in citrus fruits.
Note:
Acids are highly corrosive in nature. They can burn your skin and cause deep wounds. We should always handle acids with care and take protections while using them in the lab.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




