
What does a frog’s trachea do?
Answer
480.3k+ views
Hint: The trachea is the main part of the respiratory system of vertebrates for the supply of air to the lungs. It also links the pharynx with the lungs. In a frog, the trachea is represented as a laryngotracheal chamber. Due to the absence of the neck in frogs, there is no distinct tracheal tract that exists. Air conduction is the function of the trachea. It provides an air passage to the lungs. It makes the lungs inhale oxygen-rich air and exhale carbon dioxide-filled air.
Complete answer:
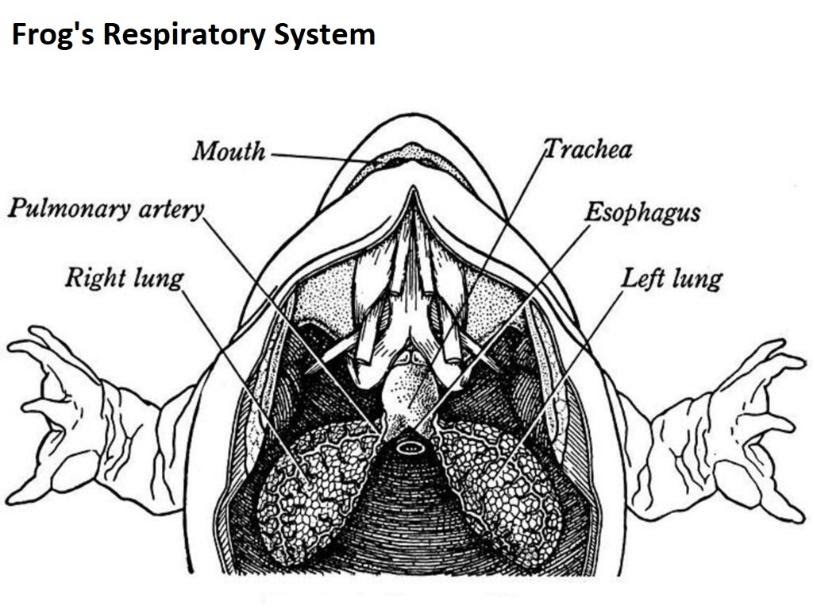
Fig.: Parts of a Respiratory System in Frog
The opening slit between the laryngotracheal chamber and the buccal cavity is depicted as the glottis. The airflow to the lungs is controlled by the glottis. Glottis closes off the trachea during swallowing.
Into a box-like larynx, the median slit-like glottis on the floor of the pharynx opens directly. Though the voice box is present in all amphibians, it is anatomically most complex in frogs. The larynx is a small sac, whose walls are supported by one cricoid and two arytenoid cartilages. The cricoid cartilage is a slender ring, which surrounds the larynx. The larynx exits into the trachea and the trachea bifurcates into the bronchi and subsequently to the lungs.
The laryngotracheal chamber serves as a precursor to the larynx and trachea. It is a thin-walled chamber. It initiates the supply of air to the lungs.
After the inhalation with the depressed buccal cavity and closed glottis, the glottis gets opened and the pulmonary air flows, leading to the respiration process.
Note:
The trachea serves as a passage for air. It moistens and warms the air when it passes into the lungs. Besides, it protects the respiratory surface from the accumulation of foreign particles. The trachea is lined with a moist mucous membrane layer, made of cells containing short hair-like projections known as cilia. Since both the digestive and respiratory systems lie in the same place, the glottis prevents the entry of the food material into the respiratory tract.
Complete answer:

Fig.: Parts of a Respiratory System in Frog
The opening slit between the laryngotracheal chamber and the buccal cavity is depicted as the glottis. The airflow to the lungs is controlled by the glottis. Glottis closes off the trachea during swallowing.
Into a box-like larynx, the median slit-like glottis on the floor of the pharynx opens directly. Though the voice box is present in all amphibians, it is anatomically most complex in frogs. The larynx is a small sac, whose walls are supported by one cricoid and two arytenoid cartilages. The cricoid cartilage is a slender ring, which surrounds the larynx. The larynx exits into the trachea and the trachea bifurcates into the bronchi and subsequently to the lungs.
The laryngotracheal chamber serves as a precursor to the larynx and trachea. It is a thin-walled chamber. It initiates the supply of air to the lungs.
After the inhalation with the depressed buccal cavity and closed glottis, the glottis gets opened and the pulmonary air flows, leading to the respiration process.
Note:
The trachea serves as a passage for air. It moistens and warms the air when it passes into the lungs. Besides, it protects the respiratory surface from the accumulation of foreign particles. The trachea is lined with a moist mucous membrane layer, made of cells containing short hair-like projections known as cilia. Since both the digestive and respiratory systems lie in the same place, the glottis prevents the entry of the food material into the respiratory tract.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




