
What does xylem mean?
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: Functions of xylem-
Food material is stored as carbohydrates, lipids, tannins, and crystals.
The ray parenchymatous cell is responsible for water radial conduction.
Tyloses are outgrowths from xylem parenchyma cells that connect them to vessels or tracheids.
These tyloses protect vascular tissues from harm during drought or infection.
The maintenance of xylem transport capacity is aided by xylem parenchyma cells.
Complete answer:
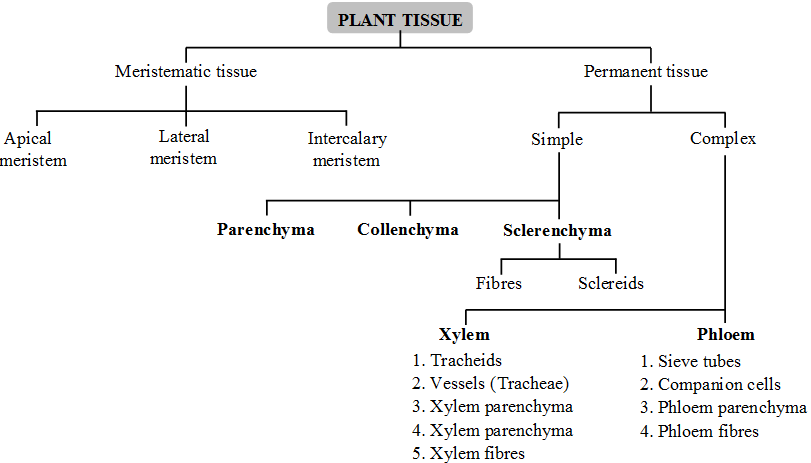
The word "xylem" comes from the Greek word "xylon", which means "wood". The term xylem was coined by Carl Nägeli. Plants have xylem, which is a form of vascular tissue that transfers water and nutrients from the roots to the stem and leaves. They also give the plants mechanical strength.
The xylem is a type of plant structure. This complex tissue is present in vascular plants and has an important role in providing support as well as the transport of nutrients, minerals, and water from the roots to all sections of the plant.The parenchyma is made up of vessels, tracheids, woody fibres, and parenchyma cells. In vascular plants, it is one of the forms of transport tissue. Phloem is the other one.
Note:
Characteristics of xylem parenchyma-
Only xylem cells are alive.
The cell wall is thin and cellulose.
The nucleus and protoplast are conspicuous.
Cells have huge vacuoles and are colourless.
Both primary and secondary xylem contain living parenchyma cells.
Seasonally, the fat and storage protein composition of parenchyma cells varies.
Septa can be used to separate parenchyma cells that contain crystals and have lignified walls with secondary thickening.
Food material is stored as carbohydrates, lipids, tannins, and crystals.
The ray parenchymatous cell is responsible for water radial conduction.
Tyloses are outgrowths from xylem parenchyma cells that connect them to vessels or tracheids.
These tyloses protect vascular tissues from harm during drought or infection.
The maintenance of xylem transport capacity is aided by xylem parenchyma cells.
Complete answer:
The word "xylem" comes from the Greek word "xylon", which means "wood". The term xylem was coined by Carl Nägeli. Plants have xylem, which is a form of vascular tissue that transfers water and nutrients from the roots to the stem and leaves. They also give the plants mechanical strength.
The xylem is a type of plant structure. This complex tissue is present in vascular plants and has an important role in providing support as well as the transport of nutrients, minerals, and water from the roots to all sections of the plant.The parenchyma is made up of vessels, tracheids, woody fibres, and parenchyma cells. In vascular plants, it is one of the forms of transport tissue. Phloem is the other one.

Note:
Characteristics of xylem parenchyma-
Only xylem cells are alive.
The cell wall is thin and cellulose.
The nucleus and protoplast are conspicuous.
Cells have huge vacuoles and are colourless.
Both primary and secondary xylem contain living parenchyma cells.
Seasonally, the fat and storage protein composition of parenchyma cells varies.
Septa can be used to separate parenchyma cells that contain crystals and have lignified walls with secondary thickening.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




