
What is an electric cell?
Answer
552.9k+ views
Hint: An electric cell also known as an electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy to do useful work like power a load (i.e. bulbs, etc). Current flows from the positive terminal (cathode) via the external circuit to the negative terminal (anode).
Complete answer:
Electric cell is an electrical power supply to power the load. There are three types of cell referred to as an electrical cell, an electrochemical cell, a solar cell and an electrolytic cell. The process involved in each is similar and all are mainly used to produce current in the circuit and power the load. The figure below shows a typical electric cell, it has two metal electrodes immersed in an electrolyte solution.
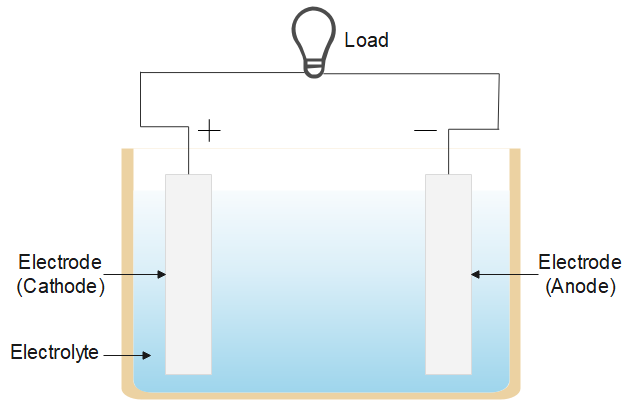
It converts chemical energy into electrical energy, the electrolyte (like, sodium chloride) is a solution of water and solvent containing dissolved ions. The ions get attracted to the electrode of opposite charge and chemical reactions (redox reactions) take place and an electric current is drawn in the circuit.
The maximum potential difference between the two electrodes is called electromotive force or the emf of the cell, it is the energy per unit charge.
Additional Information:
Galvanic cells are a type of electrochemical cell. It consists of two electrodes made of two different metals immersed in separate electrolyte solutions and a salt bridge to connect these two half cells.
Note:
Electric cells can be rechargeable or use and throw, non rechargeable electric cells are often referred to as primary cells (chemical reactions here are not reversible) and rechargeable electric cells are often referred to as secondary cells.
Complete answer:
Electric cell is an electrical power supply to power the load. There are three types of cell referred to as an electrical cell, an electrochemical cell, a solar cell and an electrolytic cell. The process involved in each is similar and all are mainly used to produce current in the circuit and power the load. The figure below shows a typical electric cell, it has two metal electrodes immersed in an electrolyte solution.

It converts chemical energy into electrical energy, the electrolyte (like, sodium chloride) is a solution of water and solvent containing dissolved ions. The ions get attracted to the electrode of opposite charge and chemical reactions (redox reactions) take place and an electric current is drawn in the circuit.
The maximum potential difference between the two electrodes is called electromotive force or the emf of the cell, it is the energy per unit charge.
Additional Information:
Galvanic cells are a type of electrochemical cell. It consists of two electrodes made of two different metals immersed in separate electrolyte solutions and a salt bridge to connect these two half cells.
Note:
Electric cells can be rechargeable or use and throw, non rechargeable electric cells are often referred to as primary cells (chemical reactions here are not reversible) and rechargeable electric cells are often referred to as secondary cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




