
What is budding?
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: In certain lower organisms, reproduction is done by an outgrowth that is capable in the formation of another organism. Yeast, corals etc are the organisms that reproduce by this method.
Complete answer:
The process of reproduction in which an outgrowth is observed on the body of an organism and after some time it detaches from the body and develops into an organism. It is a type of asexual reproduction commonly found in Hydra.
Let us see how budding occurs:
In Hydra, the bud is the result of the repeated cell division that occurs at one specific site. The bud forms many small tiny individuals which stay attached with the parent for sometime and eventually detach and develop itself into new organisms. The new individual is formed by mitosis. It is a common method of asexual reproduction observed in some protozoa and lower organisms.Sponges (Scypha), Coelenterates (Hydra), Annelids (Syllis), Yeast, and Tunicates (Salpa) are some of few examples..
Budding is of two types:
Exogenous budding: As the name suggests, the bud grows from the outer surface of the parent body. It is commonly seen in Hydra.
Endogenous budding: When the bud emerges from the inner side of the body it is known as endogenous budding. As practiced by Sponges.
Note: Some parasites also follow endodyogeny in which the two daughter cells are formed inside the mother cell, and when the time of the separation comes nearer the mother cell is consumed by the offspring. It is observed in Toxoplasma gondii.
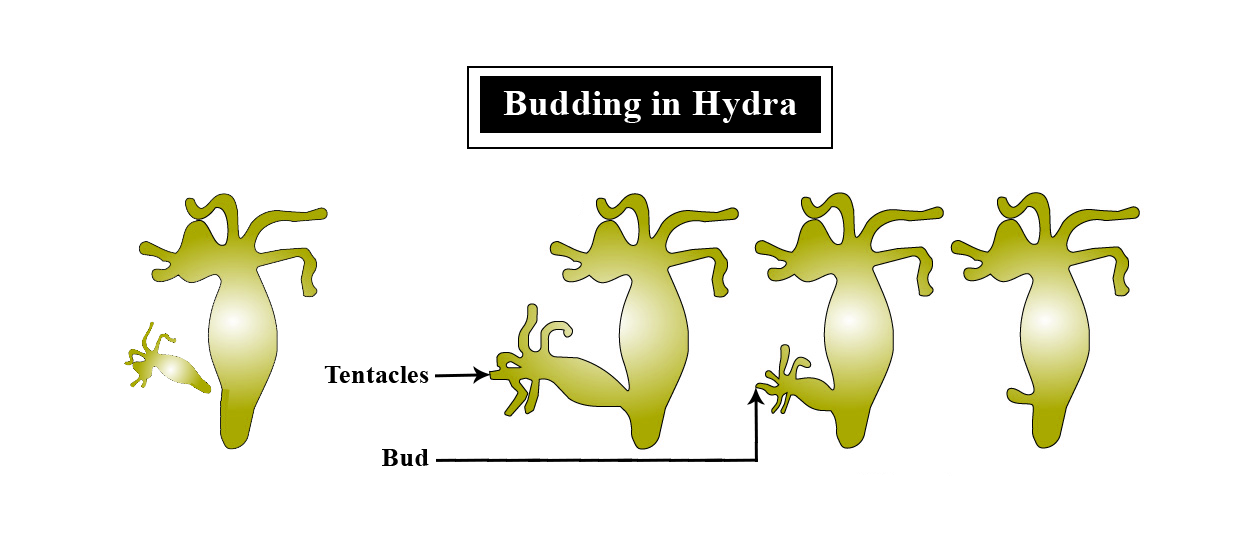
Complete answer:
The process of reproduction in which an outgrowth is observed on the body of an organism and after some time it detaches from the body and develops into an organism. It is a type of asexual reproduction commonly found in Hydra.
Let us see how budding occurs:
In Hydra, the bud is the result of the repeated cell division that occurs at one specific site. The bud forms many small tiny individuals which stay attached with the parent for sometime and eventually detach and develop itself into new organisms. The new individual is formed by mitosis. It is a common method of asexual reproduction observed in some protozoa and lower organisms.Sponges (Scypha), Coelenterates (Hydra), Annelids (Syllis), Yeast, and Tunicates (Salpa) are some of few examples..
Budding is of two types:
Exogenous budding: As the name suggests, the bud grows from the outer surface of the parent body. It is commonly seen in Hydra.
Endogenous budding: When the bud emerges from the inner side of the body it is known as endogenous budding. As practiced by Sponges.
Note: Some parasites also follow endodyogeny in which the two daughter cells are formed inside the mother cell, and when the time of the separation comes nearer the mother cell is consumed by the offspring. It is observed in Toxoplasma gondii.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




