
What is Chromatid?
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: When a cell divides, it has to take its DNA and duplicate it, and then pass half of it into one cell and a half into the other. DNA is arranged in chromosomes, so it gives rise to two strands as a chromosome replicates, or makes a duplicate of itself. A chromosome is a genetic material which has all the characteristics and features of an organism.
Complete answer:
A chromatid is half a chromosome that has been replicated. Chromosomes are replicated before cell division, and similar chromosome copies are fused at their centromeres. Every strand of one such chromosome is a chromatid. Chromatids that are joined are known as sister chromatids. Once connected sister chromatids separate each other during mitosis anaphase, each is known as a daughter chromosome. A Chromatid is one of two copied chromosome strands. Those are genetically identical chromatids.
Additional Information: A copy of each chromosome is inherited from a male parent and a female parent and this explains the characteristic features that their offspring exhibits (such as facial features that reflect parents).
Although sister chromatids are each other's exact copies, non-sister chromatids derive from homologous chromosomes. They code for the same genes but they are not similar in genetic terms. During meiosis, genetic material is periodically shared between non-sister chromatids, allowing new gene structures to be passed on to the progeny. This is called recombination or crossing over.
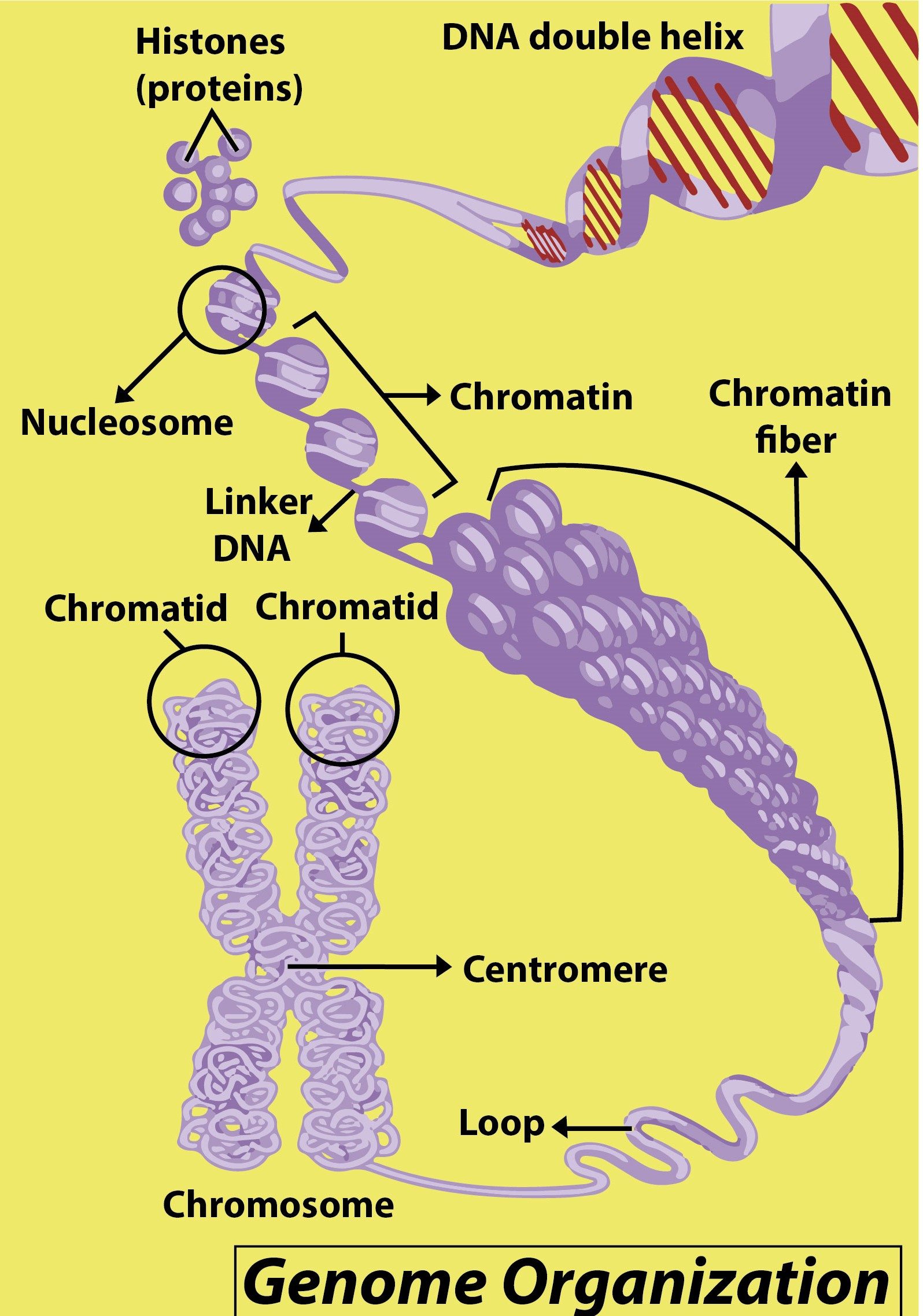
Note: Chromatids are produced by mitosis and meiosis in both the cell division processes. A chromosome will appear as a single-stranded chromatid before replication. A chromosome appears in an X-shaped form after replication. Chromosomes are first replicated, and their sister chromatids are then segregated during cell division to ensure that the required number of chromosomes is obtained by each daughter cell.
Complete answer:
A chromatid is half a chromosome that has been replicated. Chromosomes are replicated before cell division, and similar chromosome copies are fused at their centromeres. Every strand of one such chromosome is a chromatid. Chromatids that are joined are known as sister chromatids. Once connected sister chromatids separate each other during mitosis anaphase, each is known as a daughter chromosome. A Chromatid is one of two copied chromosome strands. Those are genetically identical chromatids.
Additional Information: A copy of each chromosome is inherited from a male parent and a female parent and this explains the characteristic features that their offspring exhibits (such as facial features that reflect parents).
Although sister chromatids are each other's exact copies, non-sister chromatids derive from homologous chromosomes. They code for the same genes but they are not similar in genetic terms. During meiosis, genetic material is periodically shared between non-sister chromatids, allowing new gene structures to be passed on to the progeny. This is called recombination or crossing over.

Note: Chromatids are produced by mitosis and meiosis in both the cell division processes. A chromosome will appear as a single-stranded chromatid before replication. A chromosome appears in an X-shaped form after replication. Chromosomes are first replicated, and their sister chromatids are then segregated during cell division to ensure that the required number of chromosomes is obtained by each daughter cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




