
What is inside an atom?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: The atom is the smallest known particle of any object on this earth. Being a smallest particle it is important to study the inside of an atom. Inside the atom there are subatomic particles which are known as electrons, protons and neutrons. Every atom must contain these three sub-particle. We will discuss these subatomic particles in brief.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
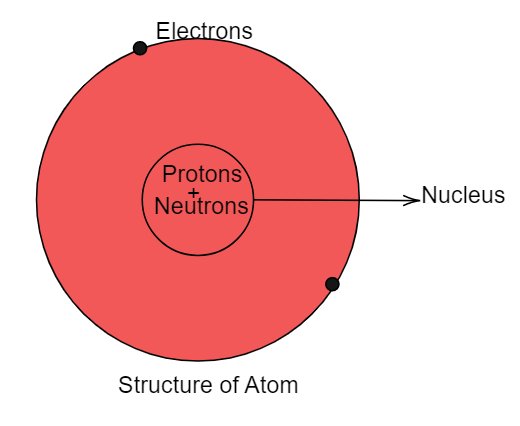
An atom is the smallest known particle of the element which can exist on its own. Like in the case of iron metal the smallest particle is an atom of iron. Hence the size of the atom is nearly to $ {10^{ - 10}}{\text{ m}} $ . The atom consists of three subatomic particles which are:
$ (i) $ Electrons:
Inside the atom electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom in a fixed circular path which is known as a shell. The number of electrons present in a shell is given by the rule of $ 2{n^2} $ where the value of n starts from one. The electrons are responsible for the atomic number of elements. The number of electrons present inside the atom is equal to its atomic number. Electrons are negatively charged particles.
$ (ii) $ Protons:
Protons are positively charged particles and they are present inside the nucleus of the atom. Protons of the atom constitute the atomic mass of the element. Protons do not revolve like electrons. They are stationary subatomic particles.
$ (iii) $ Neutrons:
Inside the nucleus of the atom protons and neutrons are present collectively and they are known as nucleons collectively. The atomic mass of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. Neutrons are neutral particles. They do not carry any charge.
Note:
The charge electronic charge present on electron is $ - 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}{\text{ C}} $ while that of proton is $ + 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}{\text{ C}} $ whereas neutron are neutral particle and it do not carry any charge. The mass of an electron is $ 9.1 \times {10^{ - 31}}{\text{ kg}} $ while that of proton is $ 1.6 \times {10^{ - 27}}{\text{ kg}} $ whereas neutron has rest mass equal to mass of proton.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
An atom is the smallest known particle of the element which can exist on its own. Like in the case of iron metal the smallest particle is an atom of iron. Hence the size of the atom is nearly to $ {10^{ - 10}}{\text{ m}} $ . The atom consists of three subatomic particles which are:
$ (i) $ Electrons:
Inside the atom electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom in a fixed circular path which is known as a shell. The number of electrons present in a shell is given by the rule of $ 2{n^2} $ where the value of n starts from one. The electrons are responsible for the atomic number of elements. The number of electrons present inside the atom is equal to its atomic number. Electrons are negatively charged particles.
$ (ii) $ Protons:
Protons are positively charged particles and they are present inside the nucleus of the atom. Protons of the atom constitute the atomic mass of the element. Protons do not revolve like electrons. They are stationary subatomic particles.
$ (iii) $ Neutrons:
Inside the nucleus of the atom protons and neutrons are present collectively and they are known as nucleons collectively. The atomic mass of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. Neutrons are neutral particles. They do not carry any charge.

Note:
The charge electronic charge present on electron is $ - 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}{\text{ C}} $ while that of proton is $ + 1.6 \times {10^{ - 19}}{\text{ C}} $ whereas neutron are neutral particle and it do not carry any charge. The mass of an electron is $ 9.1 \times {10^{ - 31}}{\text{ kg}} $ while that of proton is $ 1.6 \times {10^{ - 27}}{\text{ kg}} $ whereas neutron has rest mass equal to mass of proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




