
What is Peltier effect $?$
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint Here, we explain the Peltier effect. We know that the Peltier effect is a phenomenon due to the dissimilarity in temperature at the junction of a circuit wire made of two different materials. Then the thermocouple of copper and iron, is a type of thermoelectric effect along with the Thomson and Seebeck effects.
Useful formula
Peltier efficiency,
$efficiency = \dfrac{{Energy\,used\,for\,cooling}}{{Input\,energy}}$
Complete step by step procedure
Given by,
Explain the impact of Peltier
The Peltier effect was first noticed and named after Jean Charles Athanase Peltier, a French physicist who discovered this effect in $1834$
In accordance with the provisions to this effect,
As an electrical current passes through a thermocouple circuit, heat at one junction develops and at the other junction is absorbed. This is called the consequence of Peltier.
For example,
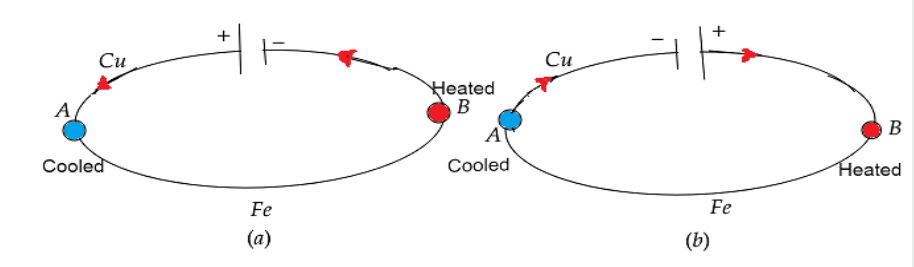
The junctions A and B are kept in the Cu-Fe thermocouple at the same temperature.
Let a battery current flow through the thermocouple. Figure a. Heat is absorbed in the A junction, where the current flows from Cu to Fe, and the A junction becomes cold.
At junction B, where the heat is released and it gets hot, the current flows from Fe to Cu. When the current direction is inverted, as shown in Figure b, junction A is heated and junction B is cooled.
Hence the Peltier effect is reversible.
On the other word, A cooling effect is observed in one junction when an electric current is passed through a circuit consisting of two separate conductors, while another junction experiences a temperature increase. The Peltier effect is referred to as this change in temperatures at the junctions.
When two separate semiconductors are used in place of conductors in the circuit, the impact is found to be even greater.
For example,
When in an electric circuit, copper wire and bismuth wire are connected, heat is produced at the point where current passes from copper to bismuth, and where the current passes from bismuth to copper, a drop in temperature occurs. In nature, this effect is reversible. By changing the direction of the current flow, the heating or cooling impact found at a junction can be reversed.
Note The phenomenon behind the Peltier effect is used in the application of thermoelectric heat pumps and thermoelectric cooling systems. It is also used when other methods for cooling computers and other electronic devices are not feasible. Here, when one-ampere current flows for one second, the amount of heat energy absorbed or generated at one of the junctions of a thermocouple.
Useful formula
Peltier efficiency,
$efficiency = \dfrac{{Energy\,used\,for\,cooling}}{{Input\,energy}}$
Complete step by step procedure
Given by,
Explain the impact of Peltier
The Peltier effect was first noticed and named after Jean Charles Athanase Peltier, a French physicist who discovered this effect in $1834$
In accordance with the provisions to this effect,
As an electrical current passes through a thermocouple circuit, heat at one junction develops and at the other junction is absorbed. This is called the consequence of Peltier.
For example,

The junctions A and B are kept in the Cu-Fe thermocouple at the same temperature.
Let a battery current flow through the thermocouple. Figure a. Heat is absorbed in the A junction, where the current flows from Cu to Fe, and the A junction becomes cold.
At junction B, where the heat is released and it gets hot, the current flows from Fe to Cu. When the current direction is inverted, as shown in Figure b, junction A is heated and junction B is cooled.
Hence the Peltier effect is reversible.
On the other word, A cooling effect is observed in one junction when an electric current is passed through a circuit consisting of two separate conductors, while another junction experiences a temperature increase. The Peltier effect is referred to as this change in temperatures at the junctions.
When two separate semiconductors are used in place of conductors in the circuit, the impact is found to be even greater.
For example,
When in an electric circuit, copper wire and bismuth wire are connected, heat is produced at the point where current passes from copper to bismuth, and where the current passes from bismuth to copper, a drop in temperature occurs. In nature, this effect is reversible. By changing the direction of the current flow, the heating or cooling impact found at a junction can be reversed.
Note The phenomenon behind the Peltier effect is used in the application of thermoelectric heat pumps and thermoelectric cooling systems. It is also used when other methods for cooling computers and other electronic devices are not feasible. Here, when one-ampere current flows for one second, the amount of heat energy absorbed or generated at one of the junctions of a thermocouple.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




