
What is regelation?
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint- Regelation illustrates the idea of melting the ice and turning it into water under pressure and re-solidifies when the pressure is removed.
Complete step by step answer:
The phenomenon in which the ice melts to the water below 0°C on the application of pressure and refreezes back to ice on the removal of pressure is known as Regelation.
For pure substances that are crystalline substances such as ice, naphthalene, etc., the melting and freezing point coincide, whereas, in the case of amorphous substances like iron, glass, wax, etc., fusion and solidification take place over a short range of temperature, so that their melting and freezing point are not fixed with the definiteness. Since the melting and freezing points vary with the different substances.
The phenomenon of melting ice due to excess pressure and its re-solidification after the removal of the excess pressure is called regelation.
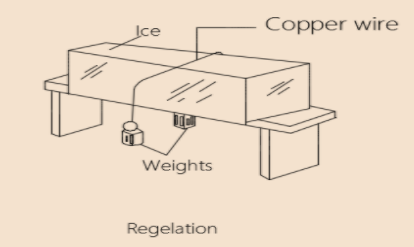
When a piece of wire loaded at both ends with equal weights is hanged across a block of ice. It is found that the wire cuts its way through the ice without however dividing the block into two pieces. The reason is that due to the pressure the ice immediately below the wire melts which enable the wire to sink through: but once the pressure is released, the water above the wire solidifies into ice again. It may be noted that the latent heat required to melt the ice below the wire comes from that evolved by the water solidifying above it. Hence, the copper wire will cut through the ice more quickly than an iron wire, because copper is a better conductor of heat than iron.
Additional information:
The quantity of heat required to convert the unit mass of solid at its melting point completely into liquid without change of temperature is called its latent heat of fusion.
The quantity of heat required to convert unit mass of a liquid at its boiling point completely into its vapour without change of temperature is called the latent heat of vaporization.
Note: Some of the examples of the regelation are as follows:
Glaciers act as a source of the river because of the regelation phenomena. The glacier exerts the pressure on the lower surface which lowers down the melting point of the ice at the base. This results in the melting of ice and the glacier sliding over the liquid.
Complete step by step answer:
The phenomenon in which the ice melts to the water below 0°C on the application of pressure and refreezes back to ice on the removal of pressure is known as Regelation.
For pure substances that are crystalline substances such as ice, naphthalene, etc., the melting and freezing point coincide, whereas, in the case of amorphous substances like iron, glass, wax, etc., fusion and solidification take place over a short range of temperature, so that their melting and freezing point are not fixed with the definiteness. Since the melting and freezing points vary with the different substances.
The phenomenon of melting ice due to excess pressure and its re-solidification after the removal of the excess pressure is called regelation.

When a piece of wire loaded at both ends with equal weights is hanged across a block of ice. It is found that the wire cuts its way through the ice without however dividing the block into two pieces. The reason is that due to the pressure the ice immediately below the wire melts which enable the wire to sink through: but once the pressure is released, the water above the wire solidifies into ice again. It may be noted that the latent heat required to melt the ice below the wire comes from that evolved by the water solidifying above it. Hence, the copper wire will cut through the ice more quickly than an iron wire, because copper is a better conductor of heat than iron.
Additional information:
The quantity of heat required to convert the unit mass of solid at its melting point completely into liquid without change of temperature is called its latent heat of fusion.
The quantity of heat required to convert unit mass of a liquid at its boiling point completely into its vapour without change of temperature is called the latent heat of vaporization.
Note: Some of the examples of the regelation are as follows:
Glaciers act as a source of the river because of the regelation phenomena. The glacier exerts the pressure on the lower surface which lowers down the melting point of the ice at the base. This results in the melting of ice and the glacier sliding over the liquid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




