
What is sigma and pi bond?
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: The bonds are classified on the basis of their overlapping. The overlapping takes place in either head to head or parallel to the axis, hence it affects the electron cloud, giving rise to different types of bonds.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to study about the types of overlapping and the nature of covalent bonds. When a covalent bond is formed, it involves the half filled atomic orbitals overlapping. The covalent bonds can be classified into two categories depending upon the type of overlapping. These are:
Sigma bond($\sigma $)- This type of covalent bond is formed when half filled atomic orbitals do axial overlapping. The atomic orbitals overlap along the internuclear axis and involve end to end or head on overlap.. The electrons constituting the sigma bond are called sigma electrons. The three types of overlapping that are possible are:
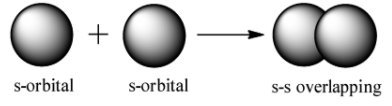
s-s overlap: It involves the overlapping of half filled s orbitals along the internuclear axis.
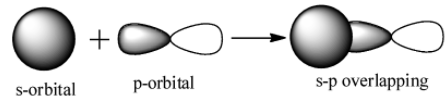
s-p overlap: It involves the overlapping of half filled s orbitals of one atom with the half filled p orbitals of other atoms.
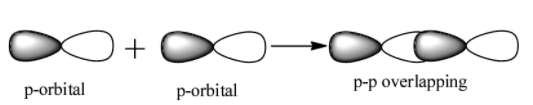
p-p overlap: It involves the co-axial overlapping between half filled p-orbitals of one atom with the half filled p orbitals of the other atom.
Pi bond($\pi $)- This type of covalent bond is formed when the atomic orbitals overlap in such a way that their axis remains parallel to each other and perpendicular to the internuclear axis. The orbitals formed due to sidewise overlapping consists of two saucer type charge clouds above and below the plane of the participating atoms. The electrons involved in $\pi $ bond formation are called pi-electrons.
Note:
Strength of a bond depends on the extent of overlapping. Sigma bond is stronger than pi bond. Pi bond between the two atoms is formed only in addition to a sigma bond. A single bond can never consist of pi bonds.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to study about the types of overlapping and the nature of covalent bonds. When a covalent bond is formed, it involves the half filled atomic orbitals overlapping. The covalent bonds can be classified into two categories depending upon the type of overlapping. These are:
Sigma bond($\sigma $)- This type of covalent bond is formed when half filled atomic orbitals do axial overlapping. The atomic orbitals overlap along the internuclear axis and involve end to end or head on overlap.. The electrons constituting the sigma bond are called sigma electrons. The three types of overlapping that are possible are:
s-s overlap: It involves the overlapping of half filled s orbitals along the internuclear axis.

s-p overlap: It involves the overlapping of half filled s orbitals of one atom with the half filled p orbitals of other atoms.

p-p overlap: It involves the co-axial overlapping between half filled p-orbitals of one atom with the half filled p orbitals of the other atom.

Pi bond($\pi $)- This type of covalent bond is formed when the atomic orbitals overlap in such a way that their axis remains parallel to each other and perpendicular to the internuclear axis. The orbitals formed due to sidewise overlapping consists of two saucer type charge clouds above and below the plane of the participating atoms. The electrons involved in $\pi $ bond formation are called pi-electrons.
Note:
Strength of a bond depends on the extent of overlapping. Sigma bond is stronger than pi bond. Pi bond between the two atoms is formed only in addition to a sigma bond. A single bond can never consist of pi bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




