
What is ‘Skip distance’?
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: In sky wave propagation, the maximum angle made by transmitted radio waves with the horizontal, above which the radio waves are no longer reflected back by the ionosphere and further rays get escaped above the ionosphere. We can also say that above critical frequency, the waves are no longer reflected back.
Complete step-by-step solution -
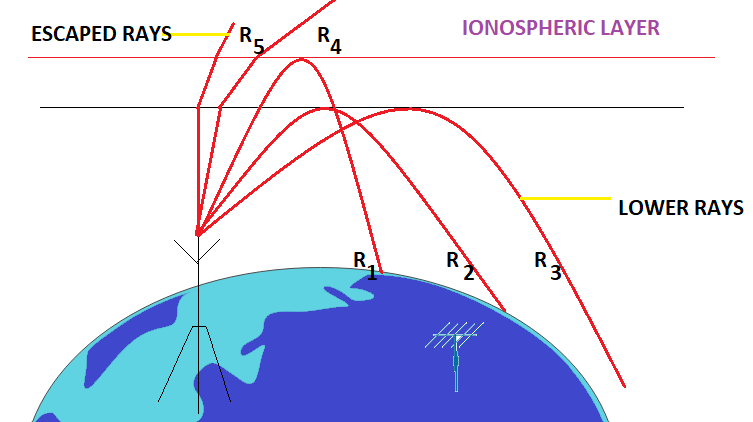
In the sky wave propagation, for a fixed frequency, the shortest distance between the point of transmission and point of reception along the surface is known as the skip distance. When the angle of distance is large for the ray R1 as shown in diagram, the sky wave returns to the ground at a long distance from the transmitter. As this angle is slowly reduced naturally the wave turns closer and closer to the transmitter as shown by the rays R2 and R3. If the angle of incidence is now made significantly less than that of ray R3, the ray will be very close to the normal to be returned to the earth. If the angle of incidence is reduced further the radio waves penetrate through the layer as shown by the rays R4 and R5. For a particular angle of incidence, the distance between point of transmission and point of reception is minimum. The minimum distance between the transmitter and ray like R3 which strikes the earth is called the skip distance. The region between the points where there is no reception of ground waves at the point where the Sky waves received is known as skip zone. In the skip zone there is no reception at all.
Note: To get a better understanding about skip distance, students should also know the following terms so that you won’t get confused. Angle of radiation is defined as the maximum angle made by transmitted radio waves with horizontal, above which radio waves will not be reflected back by the ionosphere. Critical frequency is defined as the maximum frequency of transmitted radio waves, above which the radio waves are no longer reflected back by the ionosphere. It is given by ${{f}_{c}}=g\sqrt{{{N}_{\max }}}\text{ where }{{N}_{\max }}$is maximum electron density of ionosphere. We should also know the meaning of fading which is defined as disappearance of a signal for a short time due to vibration in height and density of ionisation of ionosphere.
Complete step-by-step solution -

In the sky wave propagation, for a fixed frequency, the shortest distance between the point of transmission and point of reception along the surface is known as the skip distance. When the angle of distance is large for the ray R1 as shown in diagram, the sky wave returns to the ground at a long distance from the transmitter. As this angle is slowly reduced naturally the wave turns closer and closer to the transmitter as shown by the rays R2 and R3. If the angle of incidence is now made significantly less than that of ray R3, the ray will be very close to the normal to be returned to the earth. If the angle of incidence is reduced further the radio waves penetrate through the layer as shown by the rays R4 and R5. For a particular angle of incidence, the distance between point of transmission and point of reception is minimum. The minimum distance between the transmitter and ray like R3 which strikes the earth is called the skip distance. The region between the points where there is no reception of ground waves at the point where the Sky waves received is known as skip zone. In the skip zone there is no reception at all.
Note: To get a better understanding about skip distance, students should also know the following terms so that you won’t get confused. Angle of radiation is defined as the maximum angle made by transmitted radio waves with horizontal, above which radio waves will not be reflected back by the ionosphere. Critical frequency is defined as the maximum frequency of transmitted radio waves, above which the radio waves are no longer reflected back by the ionosphere. It is given by ${{f}_{c}}=g\sqrt{{{N}_{\max }}}\text{ where }{{N}_{\max }}$is maximum electron density of ionosphere. We should also know the meaning of fading which is defined as disappearance of a signal for a short time due to vibration in height and density of ionisation of ionosphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




