
What is stellar evolution?
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: An evolutionary phase of a star formation depending upon the mass of the star. Its formation starts with the gravitational collapse and giant molecular cloud and while collapsing there are releases of gravitational potential energy as heat.
Complete step by step answer:
A star is a hot ball of mostly hydrogen gas; mostly earth is an example of a typical ordinary star. As we know gravity keeps the gas evaporating into space and pressure due to the star’s high temperature and density keeps the ball from shrinking.
In the case of the core of the star, the temperature and densities are very high and that is enough to sustain nuclear fusion reactions. This reaction releases lots of energy as heat and light.
When the fuel for the fusion reaction is depleted ,the structure of the star changes depending upon the mass of star’s and the star’s fuel for energy generation is the stuff they are made of –hydrogen ,helium ,carbon etc. which they burn by converting these element into heavier element it is called nuclear burning in which the nuclei of atoms fuse into nuclei for heavier atoms.
The process of building up heavier elements from lighter ones by nuclear reactions, and adjusting the internal structure to balance gravity and pressure is called stellar evolution or study of how the star changes over time.
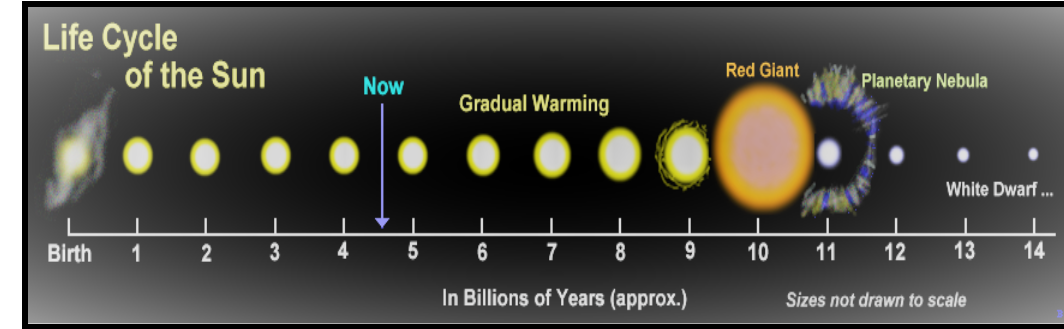
Note: A star starts its life as a cloud of dust and gas called a nebula .The stages in the life cycle of stars are: nebula ,main sequence star, red giant and either with dwarf followed by black dwarf ,neutron star or black hole. Stars played an important role in religion and proved vital to navigation. Astronomy is also called the study of heavens in ancient science.
Complete step by step answer:
A star is a hot ball of mostly hydrogen gas; mostly earth is an example of a typical ordinary star. As we know gravity keeps the gas evaporating into space and pressure due to the star’s high temperature and density keeps the ball from shrinking.
In the case of the core of the star, the temperature and densities are very high and that is enough to sustain nuclear fusion reactions. This reaction releases lots of energy as heat and light.
When the fuel for the fusion reaction is depleted ,the structure of the star changes depending upon the mass of star’s and the star’s fuel for energy generation is the stuff they are made of –hydrogen ,helium ,carbon etc. which they burn by converting these element into heavier element it is called nuclear burning in which the nuclei of atoms fuse into nuclei for heavier atoms.
The process of building up heavier elements from lighter ones by nuclear reactions, and adjusting the internal structure to balance gravity and pressure is called stellar evolution or study of how the star changes over time.
Note: A star starts its life as a cloud of dust and gas called a nebula .The stages in the life cycle of stars are: nebula ,main sequence star, red giant and either with dwarf followed by black dwarf ,neutron star or black hole. Stars played an important role in religion and proved vital to navigation. Astronomy is also called the study of heavens in ancient science.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





