
What is the back cross?
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: The crossing of heterozygous individuals with similar phenotypical and genotypical traits of parents results in knowing the genotype of a plant.
Complete step by step answer:
When the heterozygotes or ${ F }_{ 1 }$ individuals are crossed with any one of the parent organisms that are phenotypically similar and genotypically similar to the parents. This type of crossing is called a back cross.
A test cross is also a type of back cross
We can say the phenotype of the plant by observation but it is not possible to say the genotype of an organism just by observation.
to find the genotype of an organism back cross is used.
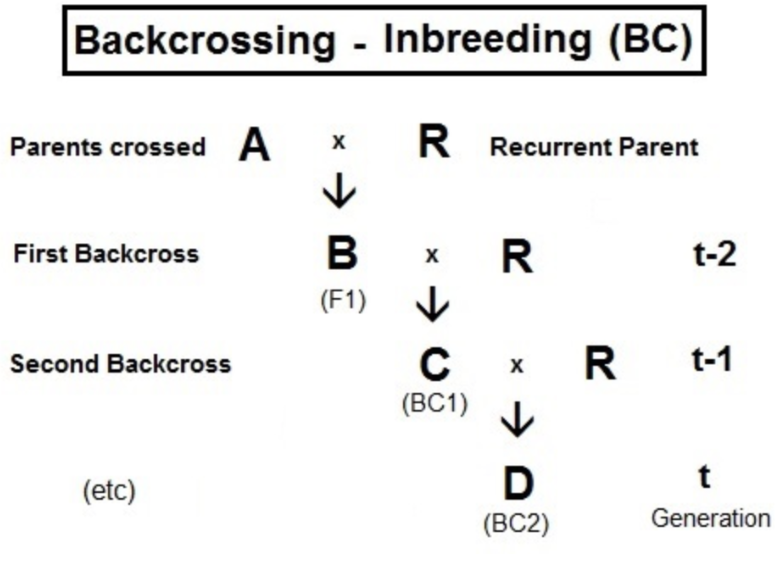
For example, consider a plant with a dominant trait as violet color and recessive trait as white color.
when a homozygous recessive trait is crossed with the dominant phenotype of an unknown genotype all the progeny formed are in violet color where the unknown flower is homozygous dominant. now take individuals of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation and they are crossed with a homozygous recessive individual. in the progeny half of the flowers are white and half of them are violet. here the unknown flower is heterogeneous.
Additional information:
- If the heterozygous individuals are crossed with the parents having a homozygous dominant trait, no recessive individuals are formed in ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation all plants show phenotypically dominant character
- Based on observations of monohybrid cross Mendal proposed two rules. they help in understanding the inheritance in a monohybrid cross. The two rules are the law of dominance and the law of segregation, these two principles are called laws of inheritance.
The Law of dominance is used to explain both the parental characters in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation but only one parental character in the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation.
An in-law of segregation, two heterozygous alleles of a gene do not fuse but they segregate during meiosis.
Note: Deviations from the Mendal concept of dominance are incomplete dominance shown by flower color of snapdragon and co-dominance shown by ABO blood cells in human beings.
the phenomenon in which the single gene may result in more than one character is called pleiotropy.
Complete step by step answer:
When the heterozygotes or ${ F }_{ 1 }$ individuals are crossed with any one of the parent organisms that are phenotypically similar and genotypically similar to the parents. This type of crossing is called a back cross.
A test cross is also a type of back cross
We can say the phenotype of the plant by observation but it is not possible to say the genotype of an organism just by observation.
to find the genotype of an organism back cross is used.

For example, consider a plant with a dominant trait as violet color and recessive trait as white color.
when a homozygous recessive trait is crossed with the dominant phenotype of an unknown genotype all the progeny formed are in violet color where the unknown flower is homozygous dominant. now take individuals of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation and they are crossed with a homozygous recessive individual. in the progeny half of the flowers are white and half of them are violet. here the unknown flower is heterogeneous.
Additional information:
- If the heterozygous individuals are crossed with the parents having a homozygous dominant trait, no recessive individuals are formed in ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation all plants show phenotypically dominant character
- Based on observations of monohybrid cross Mendal proposed two rules. they help in understanding the inheritance in a monohybrid cross. The two rules are the law of dominance and the law of segregation, these two principles are called laws of inheritance.
The Law of dominance is used to explain both the parental characters in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation but only one parental character in the ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation.
An in-law of segregation, two heterozygous alleles of a gene do not fuse but they segregate during meiosis.
Note: Deviations from the Mendal concept of dominance are incomplete dominance shown by flower color of snapdragon and co-dominance shown by ABO blood cells in human beings.
the phenomenon in which the single gene may result in more than one character is called pleiotropy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




