
What is the Bohr model of potassium?
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: In an atom, there are various shells in which electrons orbit around the nucleus (containing protons and neutrons) of an atom, and these shells consist of various subshells, which further consist of various orbitals. The existence of these shells was proposed by Neils Bohr.
Complete answer:
Bohr's model of an atom says that the nucleus of an atom is located at the center of the atom and the electrons revolve around it in different orbits of various energy levels similar to how planets revolve around the sun.
Now we know that the atomic number Z of an element can be defined as the number of protons that are present in the nucleus of every atom of that element. Since each element has a different number of protons present, every element has a unique atomic number.
When there is no charge present on an atom, the number of electrons present in an atom is also equal to the atomic number.
So, the filling of electrons in an atom is governed by the Aufbau principle which states that the electrons are filled in the atomic orbitals in increasing order of the energy level of the orbital.
The energy levels of the shell can be given by the principal quantum number (n). n has an integer value starting from 1.
n=1,2,3,4…. or K, L, M, N…
The shell closest to the nucleus, K, has principal quantum number 1 and has the least energy.
Similarly, the shell next to K is L and has principal quantum number 2, and has energy a little higher than the 1st shell.
The shell which has the highest energy in an atom is the outermost shell and has the principal quantum number n.
Now, the principal quantum number can also be used to determine the maximum number of electrons that can be added to an electron shell.
The ${{n}^{th}}$ shell of an atom can have a maximum $2{{n}^{2}}$ number of electrons.
We know that potassium has an atomic number 19. So, its electronic configuration will be
\[K=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{1}}\]
We can see that K has 2 electrons in its 1st shell, 8 electrons in its 2nd shell, 8 electrons in its 3rd shell, and 1 electron in its 4th and last shell. s, p, d are the subshells in each shell.
So, the Bohr model of potassium will be
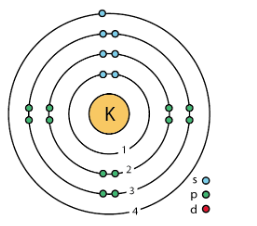
Note: It should be noted that a molecule may either gain an electron to form a positively charged ion or a cation, or lose an electron to form a negatively charged ion or an anion. This is done by the atom to achieve the most stable electron configuration by creating a full valence shell.
Complete answer:
Bohr's model of an atom says that the nucleus of an atom is located at the center of the atom and the electrons revolve around it in different orbits of various energy levels similar to how planets revolve around the sun.
Now we know that the atomic number Z of an element can be defined as the number of protons that are present in the nucleus of every atom of that element. Since each element has a different number of protons present, every element has a unique atomic number.
When there is no charge present on an atom, the number of electrons present in an atom is also equal to the atomic number.
So, the filling of electrons in an atom is governed by the Aufbau principle which states that the electrons are filled in the atomic orbitals in increasing order of the energy level of the orbital.
The energy levels of the shell can be given by the principal quantum number (n). n has an integer value starting from 1.
n=1,2,3,4…. or K, L, M, N…
The shell closest to the nucleus, K, has principal quantum number 1 and has the least energy.
Similarly, the shell next to K is L and has principal quantum number 2, and has energy a little higher than the 1st shell.
The shell which has the highest energy in an atom is the outermost shell and has the principal quantum number n.
Now, the principal quantum number can also be used to determine the maximum number of electrons that can be added to an electron shell.
The ${{n}^{th}}$ shell of an atom can have a maximum $2{{n}^{2}}$ number of electrons.
We know that potassium has an atomic number 19. So, its electronic configuration will be
\[K=1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{1}}\]
We can see that K has 2 electrons in its 1st shell, 8 electrons in its 2nd shell, 8 electrons in its 3rd shell, and 1 electron in its 4th and last shell. s, p, d are the subshells in each shell.
So, the Bohr model of potassium will be

Note: It should be noted that a molecule may either gain an electron to form a positively charged ion or a cation, or lose an electron to form a negatively charged ion or an anion. This is done by the atom to achieve the most stable electron configuration by creating a full valence shell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




