
What is the centre of symmetry?
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint :Centre of symmetry is a symmetry element used to measure the extent to which a given compound or structure is symmetrical. Unlike axes and planes, the centre of symmetry is just a single point that is usually present in all regular shapes.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Covalent molecules as well as ionic compounds in their crystal lattices have a definite arrangement which imparts symmetry to them.
A point in any molecule or crystal lattice is nothing but an atom of the molecule or an ion present in an ionic lattice.
A centre of symmetry in covalent molecules is a point or an atom that lies exactly in the middle of the plain. All bonds formed with this atom reflect each other which means that for each bond formed in a particular direction there is a same bond (between the central atom and another atom of the same element as that of the first bond) that exists in a direction opposite to it.
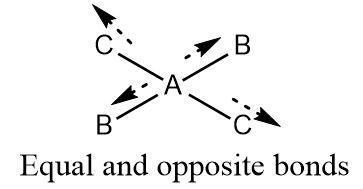
A molecule containing a centre of symmetry tends to have zero dipole moment even if the bonds are polar as dipole moment in one direction is cancelled by another dipole moment of equal magnitude but opposite direction.
A centre of symmetry in a solid lattice can be the centre of a unit cell. The atom that lies in the body centre is known as the centre of symmetry.
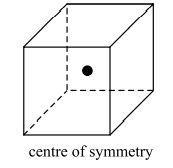
A cube can also have a centre of symmetry which is defined by a point in its exact centre such that each corner or vertex of the cube is equidistant to that point.
Note :
A centre of symmetry may not be confused with an alternate axis of symmetry that involves rotation followed by reflection. Structures or geometries that have a centre of symmetry also contain an axis or plane of symmetry in most cases.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Covalent molecules as well as ionic compounds in their crystal lattices have a definite arrangement which imparts symmetry to them.
A point in any molecule or crystal lattice is nothing but an atom of the molecule or an ion present in an ionic lattice.
A centre of symmetry in covalent molecules is a point or an atom that lies exactly in the middle of the plain. All bonds formed with this atom reflect each other which means that for each bond formed in a particular direction there is a same bond (between the central atom and another atom of the same element as that of the first bond) that exists in a direction opposite to it.

A molecule containing a centre of symmetry tends to have zero dipole moment even if the bonds are polar as dipole moment in one direction is cancelled by another dipole moment of equal magnitude but opposite direction.
A centre of symmetry in a solid lattice can be the centre of a unit cell. The atom that lies in the body centre is known as the centre of symmetry.
A cube can also have a centre of symmetry which is defined by a point in its exact centre such that each corner or vertex of the cube is equidistant to that point.

Note :
A centre of symmetry may not be confused with an alternate axis of symmetry that involves rotation followed by reflection. Structures or geometries that have a centre of symmetry also contain an axis or plane of symmetry in most cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




