
What is the end product of Lipolysis?
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: This is a metabolic process through which the lipids break down and releases free fatty acids. Free fatty acids are the major oxidative fuel of the body. It involves the dietary lipids in the digestive tract and free lipids in our blood. It also uses the stored lipid in the adipose tissue or stored in our livers.
Complete answer:
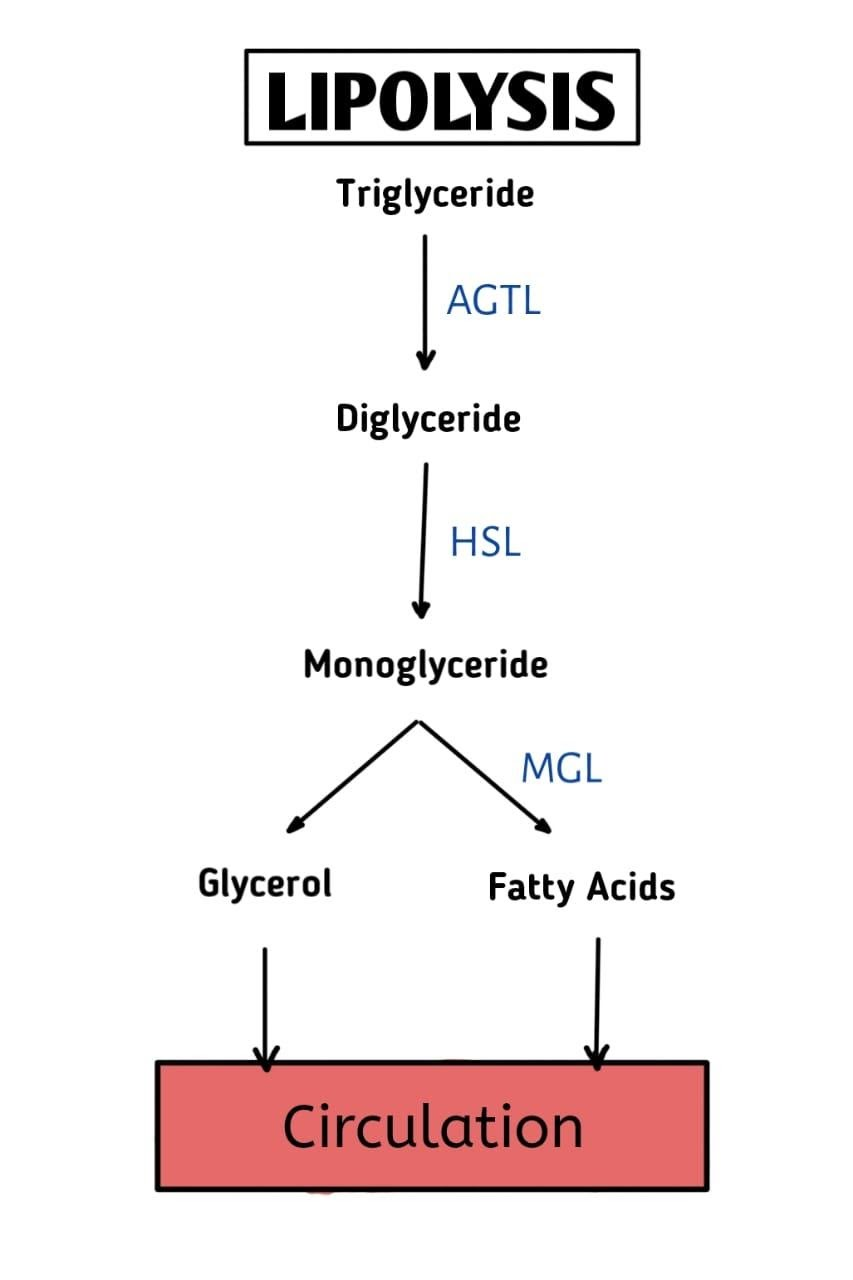
Lipolysis is a metabolic process. In this process the triacylglycerols (TAGs) collapse via hydrolysis into their basic component molecules: glycerol and free fatty acids (FFAs). Through adipose triacylglycerols, the fat is stored in the body and is utilized for heat, energy, and keeps them from spreading. The body uses the fat from the stores as it is the main source of energy during starvation, and conserves protein. Overall, fats are the most important fuel in the body. The amount of fat stored in the adipose tissue decides how long a person can survive without food. And for that reason, lipolysis is very important in the ‘fasting state’ of metabolism, because in that state the glucose level of our blood has decreased.
The end products of Lipolysis are Fatty acids and Glycerol.
Note:
Glycerol is a source of carbon for gluconeogenesis in the liver that is produced by lipolysis. fatty acids are transported in the blood, they are bound to the albumin. These are either oxidized in tissues by beta-oxidation or converted to ketone bodies. The offshoots of beta-oxidation Adenosine Triphosphate and NADH [nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) hydrogen (H)] promote gluconeogenesis. Fatty acids convert to ketone bodies in the liver which is an energy source of the brain. Fatty acids are utilized throughout the body for energy production called as biosynthetic pathways except in white adipose tissue (WAT), where the fatty acids are stored. In a metabolic "fasting" state when the body is poor in nutrients, white adipose tissue releases Fatty acids and glycerol to supply non-adipose tissues.
The major enzymes involved in lipolysis are adipose triglyceride lipase or ATGL, hormone-sensitive lipase or HSL, and monoglyceride lipase or MGL.
Complete answer:
Lipolysis is a metabolic process. In this process the triacylglycerols (TAGs) collapse via hydrolysis into their basic component molecules: glycerol and free fatty acids (FFAs). Through adipose triacylglycerols, the fat is stored in the body and is utilized for heat, energy, and keeps them from spreading. The body uses the fat from the stores as it is the main source of energy during starvation, and conserves protein. Overall, fats are the most important fuel in the body. The amount of fat stored in the adipose tissue decides how long a person can survive without food. And for that reason, lipolysis is very important in the ‘fasting state’ of metabolism, because in that state the glucose level of our blood has decreased.
The end products of Lipolysis are Fatty acids and Glycerol.

Note:
Glycerol is a source of carbon for gluconeogenesis in the liver that is produced by lipolysis. fatty acids are transported in the blood, they are bound to the albumin. These are either oxidized in tissues by beta-oxidation or converted to ketone bodies. The offshoots of beta-oxidation Adenosine Triphosphate and NADH [nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) hydrogen (H)] promote gluconeogenesis. Fatty acids convert to ketone bodies in the liver which is an energy source of the brain. Fatty acids are utilized throughout the body for energy production called as biosynthetic pathways except in white adipose tissue (WAT), where the fatty acids are stored. In a metabolic "fasting" state when the body is poor in nutrients, white adipose tissue releases Fatty acids and glycerol to supply non-adipose tissues.
The major enzymes involved in lipolysis are adipose triglyceride lipase or ATGL, hormone-sensitive lipase or HSL, and monoglyceride lipase or MGL.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




