
What is the function of SER?
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: It is a membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It is organized in a mesh-like branching structure of flattened sacs and tubules which is extended to the cytosol.
Complete answer:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum or SER is made up of a three-dimensional network of tubules near the cell periphery, called cisternae. This SER is connected to the nuclear envelope. Because of the absence of ribosomes in its surface, it appears smooth and hence, known as the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The internal part of the SER is called the lumen which is enclosed by a phospholipid membrane, just like the membrane that encloses the whole cell. In the endoplasmic reticulum, the transport of vesicles occurs to the Golgi apparatus that contain lipids and proteins made in the ER. It is not involved in protein synthesis due to the absence of ribosomes.
Functions of smooth endoplasmic reticulum:
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum plays an important role in the synthesis of lipids such as cholesterol and phospholipids.
- Apart from the synthesis of cholesterol and phospholipids it also helps in secretion of steroid hormones from lipid precursors.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is also involved in carbohydrate metabolism.
- Since the presence of a glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme, the final reaction of gluconeogenesis is completed in the lumen of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
- It also detoxifies the liver by removing a number of substances from the liver through urine.
- It regulates the calcium ion concentrations in muscle cells.
- It allows for an increased surface area to be dedicated to the storage of key enzymes and the products of these enzymes.
Note:
> The endoplasmic reticulum is not present in red blood cells and spermatozoa.
> Smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a specialized membrane structure in skeletal muscle cells known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum which is a critical storage site for calcium ions.
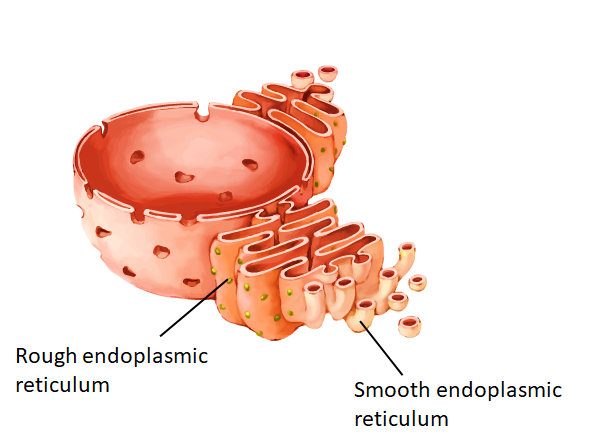
Figure: Structure of endoplasmic reticulum
Complete answer:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum or SER is made up of a three-dimensional network of tubules near the cell periphery, called cisternae. This SER is connected to the nuclear envelope. Because of the absence of ribosomes in its surface, it appears smooth and hence, known as the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The internal part of the SER is called the lumen which is enclosed by a phospholipid membrane, just like the membrane that encloses the whole cell. In the endoplasmic reticulum, the transport of vesicles occurs to the Golgi apparatus that contain lipids and proteins made in the ER. It is not involved in protein synthesis due to the absence of ribosomes.
Functions of smooth endoplasmic reticulum:
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum plays an important role in the synthesis of lipids such as cholesterol and phospholipids.
- Apart from the synthesis of cholesterol and phospholipids it also helps in secretion of steroid hormones from lipid precursors.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is also involved in carbohydrate metabolism.
- Since the presence of a glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme, the final reaction of gluconeogenesis is completed in the lumen of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
- It also detoxifies the liver by removing a number of substances from the liver through urine.
- It regulates the calcium ion concentrations in muscle cells.
- It allows for an increased surface area to be dedicated to the storage of key enzymes and the products of these enzymes.
Note:
> The endoplasmic reticulum is not present in red blood cells and spermatozoa.
> Smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a specialized membrane structure in skeletal muscle cells known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum which is a critical storage site for calcium ions.

Figure: Structure of endoplasmic reticulum
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




