
What is the hybridization of ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$?
Answer
527.4k+ views
Hint: We can find the hybridization of carbon atoms in the organic molecules by finding the number of bonds and bonds present around the carbon atom. The hybridization for the carbon atom will be $s{{p}^{3}}$, $s{{p}^{2}}$, or sp.
Complete answer:
When the mixing of orbitals takes place because the energies of the orbitals are different so that the redistribution of the orbitals can take place there will be the formation of new orbitals having the same energy and same shape that is used for the formation of compounds.
The given compound in the question is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$, this is known as ethane which is the second member of the alkanes group.
We can find the hybridization of carbon atoms in the organic molecules by finding the number of bonds and bonds present around the carbon atom. If the carbon atom has only single bonds then the hybridization will be $s{{p}^{3}}$, if the carbon atom has at least one double bond then the hybridization will be $s{{p}^{2}}$, if the carbon atom has at least one triple bond then the hybridization will be sp.
The structure of the ethane molecule is given below:
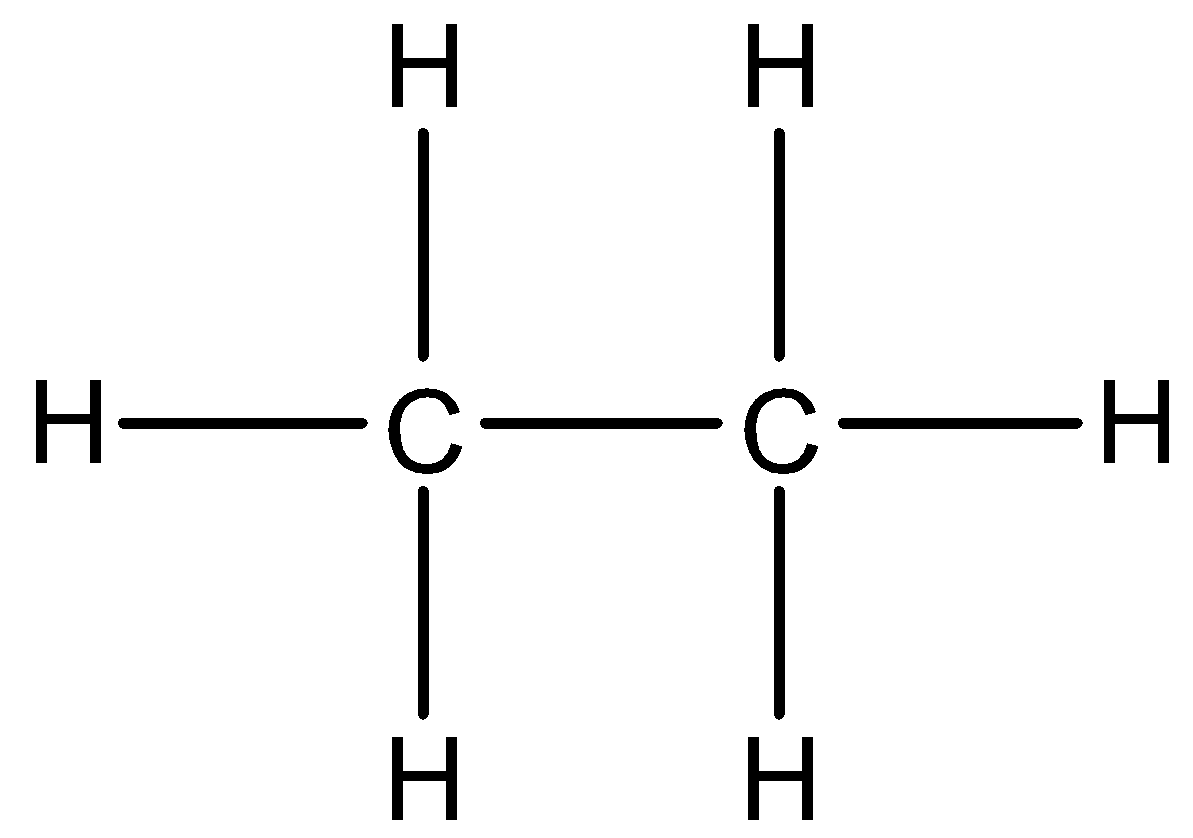
From the structure we can see that all the bonds around the carbon atoms are single, so the hybridization of this molecule will be $s{{p}^{3}}$.
So, the hybridization of ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note:
We can also find the hybridization of the molecule by using a formula:
$X=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ VE+MA-c+a \right]$
Where VE is the number of valence electrons of the central atom
MA is the number of monovalent atoms surrounding the central atom
c is the cationic charge and a is the anionic charge.
Complete answer:
When the mixing of orbitals takes place because the energies of the orbitals are different so that the redistribution of the orbitals can take place there will be the formation of new orbitals having the same energy and same shape that is used for the formation of compounds.
The given compound in the question is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$, this is known as ethane which is the second member of the alkanes group.
We can find the hybridization of carbon atoms in the organic molecules by finding the number of bonds and bonds present around the carbon atom. If the carbon atom has only single bonds then the hybridization will be $s{{p}^{3}}$, if the carbon atom has at least one double bond then the hybridization will be $s{{p}^{2}}$, if the carbon atom has at least one triple bond then the hybridization will be sp.
The structure of the ethane molecule is given below:

From the structure we can see that all the bonds around the carbon atoms are single, so the hybridization of this molecule will be $s{{p}^{3}}$.
So, the hybridization of ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note:
We can also find the hybridization of the molecule by using a formula:
$X=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ VE+MA-c+a \right]$
Where VE is the number of valence electrons of the central atom
MA is the number of monovalent atoms surrounding the central atom
c is the cationic charge and a is the anionic charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




