
What is the importance of Cori’s cycle?
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Cori’s cycle is a metabolic pathway named after the name of its discoverers, Carl Ferdinand Cori and Gerty Cori.
Complete Answer:
Cori’s cycle:
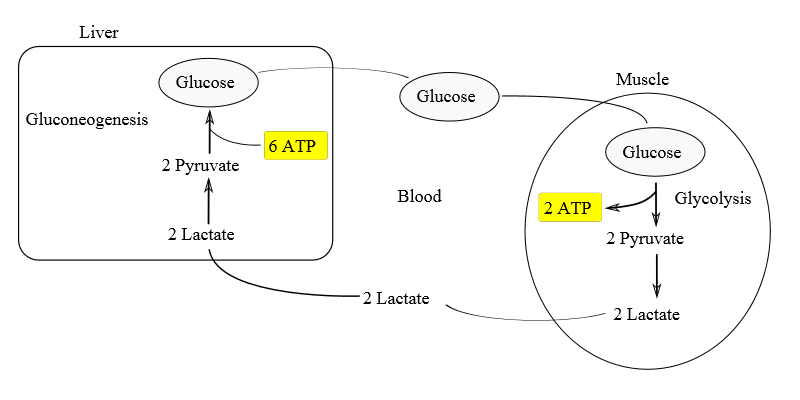
- The Cori’s cycle is also called the Lactic acid cycle or glucose-lactate cycle.
- It is a metabolic pathway in which lactate which is produced by anaerobic glycolysis is transported to the liver and converted to glucose, which then returns to the muscles and is cyclically metabolized back to lactate.
Summarised process of Cori’s cycle:
- First the conversion of glucose to lactic acid takes place by anaerobic glycolysis in skeletal muscle cells.
- Lactate or lactic acid diffused from muscle cells to the bloodstream by which it is transported to the liver.
- In the liver lactate gets converted to glucose by the process called hepatic gluconeogenesis.
- Glucose diffuses from the hepatocytes into the bloodstream by which it is transported back to the skeletal muscles and hence closing the cycle.
Note: Importances of Cori’s cycle:
- This cycle is important for the prevention of lactic acidosis in the muscles during anaerobic conditions.
- This cycle produces ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) , which is the energy rich molecule during muscle activity.
- This cycle is the more important source for gluconeogenesis than food.
Complete Answer:
Cori’s cycle:
- The Cori’s cycle is also called the Lactic acid cycle or glucose-lactate cycle.
- It is a metabolic pathway in which lactate which is produced by anaerobic glycolysis is transported to the liver and converted to glucose, which then returns to the muscles and is cyclically metabolized back to lactate.
Summarised process of Cori’s cycle:
- First the conversion of glucose to lactic acid takes place by anaerobic glycolysis in skeletal muscle cells.
- Lactate or lactic acid diffused from muscle cells to the bloodstream by which it is transported to the liver.
- In the liver lactate gets converted to glucose by the process called hepatic gluconeogenesis.
- Glucose diffuses from the hepatocytes into the bloodstream by which it is transported back to the skeletal muscles and hence closing the cycle.

Note: Importances of Cori’s cycle:
- This cycle is important for the prevention of lactic acidosis in the muscles during anaerobic conditions.
- This cycle produces ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) , which is the energy rich molecule during muscle activity.
- This cycle is the more important source for gluconeogenesis than food.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




