
What is the incentre of a triangle?
Answer
614.4k+ views
Hint- In this particular type of question we need to recall the definition of incentre and explain it to get the desired answer .
Complete step-by-step solution -
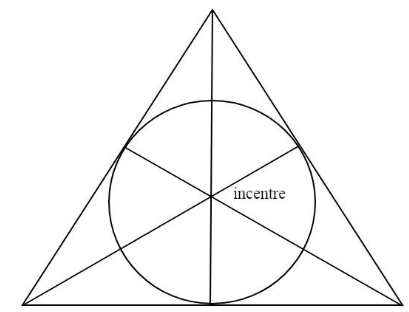
In geometry, the incentre of a triangle is a triangle center, a point defined for any triangle in a way that is independent of the triangle's placement or scale. The incentre may be equivalently defined as the point where the internal angle bisectors of the triangle cross, as the point equidistant from the triangle's sides, as the junction point of the medial axis and innermost point of the grassfire transform of the triangle, and as the center point of the inscribed circle of the triangle.
Note- It is important to note that together with the centroid, circumcenter, and orthocenter, it is one of the four triangle centers known to the ancient Greeks, and the only one that does not in general lie on the Euler line . Remember that for polygons with more than three sides, the incentre only exists for tangential polygons—those that have an incircle that is tangent to each side of the polygon. In this case the incentre is the center of this circle and is equally distant from all sides.
Complete step-by-step solution -

In geometry, the incentre of a triangle is a triangle center, a point defined for any triangle in a way that is independent of the triangle's placement or scale. The incentre may be equivalently defined as the point where the internal angle bisectors of the triangle cross, as the point equidistant from the triangle's sides, as the junction point of the medial axis and innermost point of the grassfire transform of the triangle, and as the center point of the inscribed circle of the triangle.
Note- It is important to note that together with the centroid, circumcenter, and orthocenter, it is one of the four triangle centers known to the ancient Greeks, and the only one that does not in general lie on the Euler line . Remember that for polygons with more than three sides, the incentre only exists for tangential polygons—those that have an incircle that is tangent to each side of the polygon. In this case the incentre is the center of this circle and is equally distant from all sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




