
What is the Isothermal process?
Answer
527k+ views
Hint: Any process in which temperature remains the constant is called an Isothermal process or we can say the process in which $\Delta T = 0$ is called an Isothermal process.
Where $\Delta T$ is the change in temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Isothermal Process: An isothermal process may be defined as a thermodynamic process in which the temperature remains constant.
In an isothermal process $\Delta T = 0$ always, where $\Delta T$ is the change in temperature.
The P-V diagram of an isothermal process is shown below -
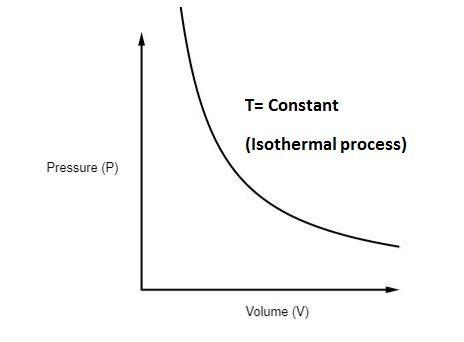
Some examples of isothermal process are as follows:
All the processes which are taking place inside a refrigerator are isothermal processes as there is no change in its internal temperature.
The melting of ice at zero degrees Celsius is also an isothermal process.
An ideal Carnot engine also works on an isothermal process.
The amount of work done during an isothermal process is given by :
$W = nRT\, \ln \, \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} = 2.303\, nRT\, \log \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}}$
Since ${P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$ (Boyle’s law)
Therefore work done can also be written as,
$W = nRT\, \ln\, \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}} = 2.303\, nRT\, \log \, \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}}$
Where $n$ is the number of moles of a gas, $R$ is the universal gas constant, $T$ is the temperature, ${P_1}$ and ${P_2}$ are the initial and final pressures respectively & ${V_1}$ and ${V_2}$ are the initial and final volumes respectively.
Note:
Keep in mind that in an isothermal process only temperature remains constant i.e. $\Delta T = 0$. If the gas is an ideal gas then change Internal energy also becomes zero in the isothermal process i.e. $\Delta U = 0$ but the change in heat will never equal to zero i.e. $\Delta Q \ne 0$. Moreover, the process in which heat remains the constant i.e. $\Delta Q = 0$ is called as an adiabatic process.
Where $\Delta T$ is the change in temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Isothermal Process: An isothermal process may be defined as a thermodynamic process in which the temperature remains constant.
In an isothermal process $\Delta T = 0$ always, where $\Delta T$ is the change in temperature.
The P-V diagram of an isothermal process is shown below -

Some examples of isothermal process are as follows:
All the processes which are taking place inside a refrigerator are isothermal processes as there is no change in its internal temperature.
The melting of ice at zero degrees Celsius is also an isothermal process.
An ideal Carnot engine also works on an isothermal process.
The amount of work done during an isothermal process is given by :
$W = nRT\, \ln \, \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}} = 2.303\, nRT\, \log \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{V_1}}}$
Since ${P_1}{V_1} = {P_2}{V_2}$ (Boyle’s law)
Therefore work done can also be written as,
$W = nRT\, \ln\, \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}} = 2.303\, nRT\, \log \, \dfrac{{{P_1}}}{{{P_2}}}$
Where $n$ is the number of moles of a gas, $R$ is the universal gas constant, $T$ is the temperature, ${P_1}$ and ${P_2}$ are the initial and final pressures respectively & ${V_1}$ and ${V_2}$ are the initial and final volumes respectively.
Note:
Keep in mind that in an isothermal process only temperature remains constant i.e. $\Delta T = 0$. If the gas is an ideal gas then change Internal energy also becomes zero in the isothermal process i.e. $\Delta U = 0$ but the change in heat will never equal to zero i.e. $\Delta Q \ne 0$. Moreover, the process in which heat remains the constant i.e. $\Delta Q = 0$ is called as an adiabatic process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




