
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
Answer
528k+ views
Hint: The filling of electrons is done into the orbitals which are s, p, d, f. There are four sets of quantum numbers. Pauli's exclusion principle tells us that these sets of quantum numbers should be different in the filling of electrons. It has made rules on accommodation of electrons in any orbital.
Complete answer:
According to Pauli’s exclusion principle, any atomic orbital can not accommodate more than 2 electrons with the opposite spin. This means that one orbital contains only two electrons that have opposite spin.
This principle can also be defined in another way as no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of all the four quantum numbers. There are 4 quantum numbers, principle (n), azimuthal (l), magnetic (m), and spin (s). The set of all these quantum numbers for electrons is different as electrons are present in an orbital with opposite spins. This means that one electron has an up spin of $+\dfrac{1}{2}$ , while the other electron has the down spin of $-\dfrac{1}{2}$ .
Here is the representation of the 1 s orbital of hydrogen (H) and helium (He):
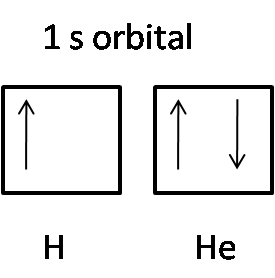
The hydrogen atom consists of only one electron in the 1 s orbital, so it has an upward arrow. The helium atom consists of 2 electrons in the 1 s orbital. One has an upward arrow showing up spin, other showing a downward arrow indicating down spin.
Hence, according to Pauli’s exclusion principle, the electrons in an orbital have opposite spin, and all the sets of quantum numbers of these electrons cannot be the same.
Note:
Pauli’s exclusion principle perfectly explains the fact that 2 electrons are filled in one orbital only. The sub – shells s, p, d, and f can have 1, 3, 5, 7 number or orbital respectively. These orbital, s, p, d, f can accommodate a maximum of 2, 6, 10, and 14 electrons respectively.
Complete answer:
According to Pauli’s exclusion principle, any atomic orbital can not accommodate more than 2 electrons with the opposite spin. This means that one orbital contains only two electrons that have opposite spin.
This principle can also be defined in another way as no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of all the four quantum numbers. There are 4 quantum numbers, principle (n), azimuthal (l), magnetic (m), and spin (s). The set of all these quantum numbers for electrons is different as electrons are present in an orbital with opposite spins. This means that one electron has an up spin of $+\dfrac{1}{2}$ , while the other electron has the down spin of $-\dfrac{1}{2}$ .
Here is the representation of the 1 s orbital of hydrogen (H) and helium (He):
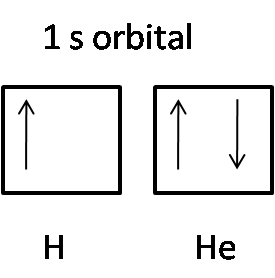
The hydrogen atom consists of only one electron in the 1 s orbital, so it has an upward arrow. The helium atom consists of 2 electrons in the 1 s orbital. One has an upward arrow showing up spin, other showing a downward arrow indicating down spin.
Hence, according to Pauli’s exclusion principle, the electrons in an orbital have opposite spin, and all the sets of quantum numbers of these electrons cannot be the same.
Note:
Pauli’s exclusion principle perfectly explains the fact that 2 electrons are filled in one orbital only. The sub – shells s, p, d, and f can have 1, 3, 5, 7 number or orbital respectively. These orbital, s, p, d, f can accommodate a maximum of 2, 6, 10, and 14 electrons respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




