
What is the principle of diffusion?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: It is the transfer of mass of an individual molecule of a substance caused by random molecular motion and associated with a driving force such as the concentration gradient. It is a time dependent process and the movement is based on the kinetic energy, the charge and also the mass of the molecule.
Complete answer:
To answer this question you must know about diffusion.
Diffusion is the process resulting from random motion of molecules by which there is net flow of matter from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration under the influence of concentration gradient. For example perfume of a flower that quickly permeates the still air of a room.
In the biological system it is a type of passive transport through a semipermeable membrane. Passive transport refers to the type of cellular transport where in the net movement of substances down their concentration gradient. In contrast, cellular transport where substances have to move to an area that is already saturated or high in concentration is called active transport. Because this movement of substances in passive transport does not go against the concentration gradient, therefore it does not require chemical energy (ATP) to proceed. Rather then it is derived from the kinetic and natural energy. Other examples of passive transport are filtration and osmosis.

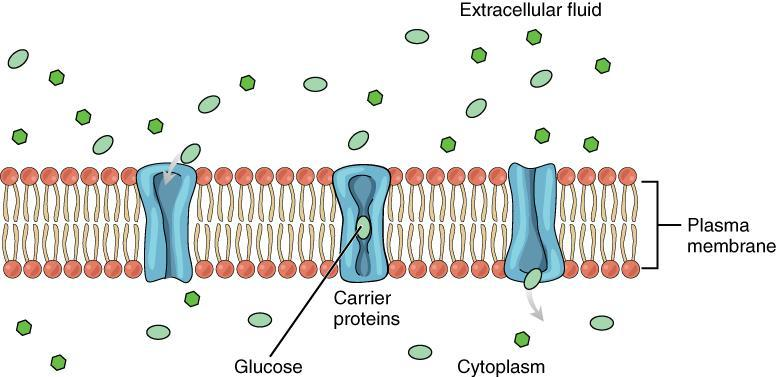 Some molecules such as polar and large molecules cannot readily pass across a biological membrane. The plasma membrane, for instance, transports these molecules into and out of the cell by using membrane proteins. This type of transport is called facilitated diffusion.
Some molecules such as polar and large molecules cannot readily pass across a biological membrane. The plasma membrane, for instance, transports these molecules into and out of the cell by using membrane proteins. This type of transport is called facilitated diffusion.
Note:
The cell regulates the entry and exit of substance through its plasma membrane. Nonpolar molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide easily diffuse across the membrane. This phenomenon applied in pharmaceutical science include : in ultrafiltration, microfiltration, hemodialysis, to estimate the molecular weight of polymers prediction, and elimination of drugs.
Complete answer:
To answer this question you must know about diffusion.
Diffusion is the process resulting from random motion of molecules by which there is net flow of matter from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration under the influence of concentration gradient. For example perfume of a flower that quickly permeates the still air of a room.
In the biological system it is a type of passive transport through a semipermeable membrane. Passive transport refers to the type of cellular transport where in the net movement of substances down their concentration gradient. In contrast, cellular transport where substances have to move to an area that is already saturated or high in concentration is called active transport. Because this movement of substances in passive transport does not go against the concentration gradient, therefore it does not require chemical energy (ATP) to proceed. Rather then it is derived from the kinetic and natural energy. Other examples of passive transport are filtration and osmosis.


Note:
The cell regulates the entry and exit of substance through its plasma membrane. Nonpolar molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide easily diffuse across the membrane. This phenomenon applied in pharmaceutical science include : in ultrafiltration, microfiltration, hemodialysis, to estimate the molecular weight of polymers prediction, and elimination of drugs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




